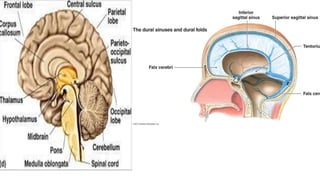
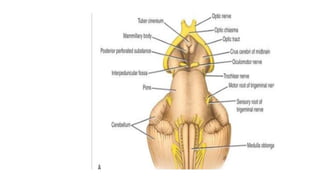
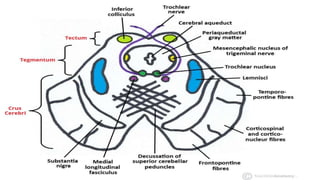
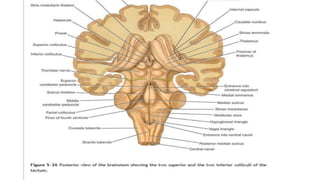
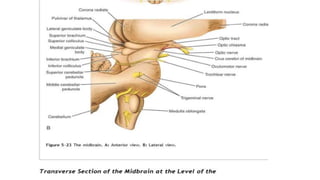
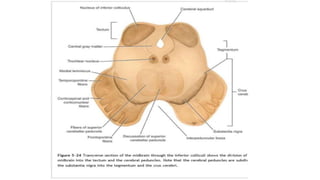
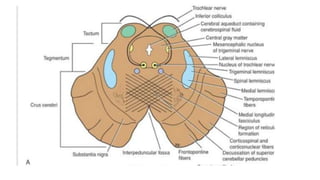
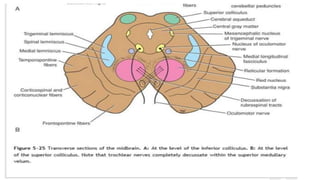
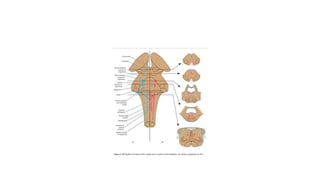
The midbrain connects the pons and cerebellum to the forebrain. It contains several important structures including the cerebral aqueduct, superior and inferior colliculi, trochlear nerve nuclei, and substantia nigra. The midbrain also contains ascending and descending tracts that connect different parts of the brain and spinal cord. On transverse sections, the midbrain shows gray matter structures like the red nucleus and various cranial nerve nuclei, as well as white matter tracts that transmit signals up and down the central nervous system.