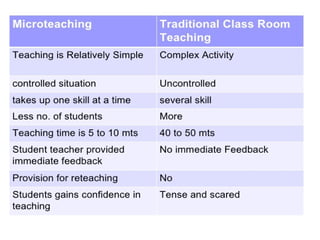
This document provides an overview of microteaching, including its origins at Stanford University in the 1960s. Microteaching involves teaching a short lesson (5-20 minutes) to a small group of students (5-10) and receiving feedback to improve specific teaching skills. It occurs in cycles of plan, teach, receive feedback, re-plan, re-teach, and receive additional feedback. Some core teaching skills practiced include questioning techniques, explaining concepts, using examples, maintaining student engagement, classroom management, and blackboard usage. Microteaching aims to break down the complex act of teaching into individual skills that can each be practiced and mastered.