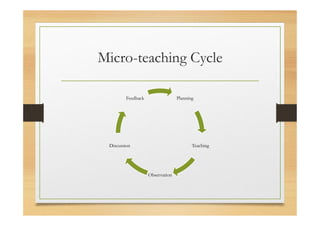
This document discusses micro-teaching, a teacher training technique where teachers practice specific teaching skills in short lessons recorded for feedback. It was developed in the 1960s at Stanford University. The key aspects covered are: micro-teaching focuses on developing one skill at a time through short 5-10 minute lessons with 5-10 students; it involves planning, teaching, observation, feedback, re-planning, and re-teaching lessons until skills are mastered; and it aims to help teachers improve their techniques in a low-stakes environment before student teaching.