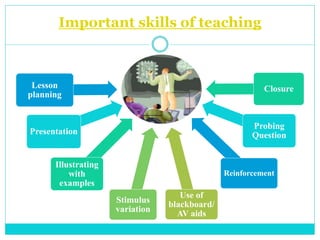
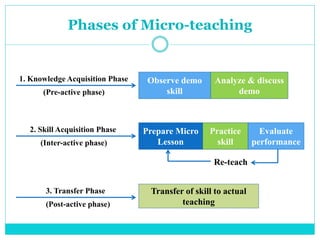
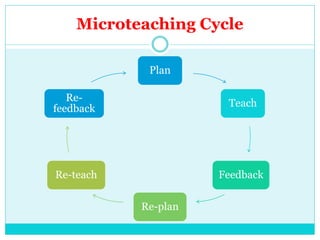
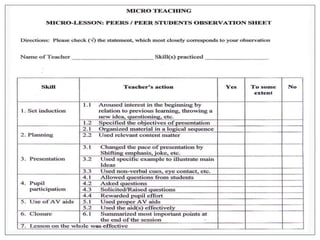
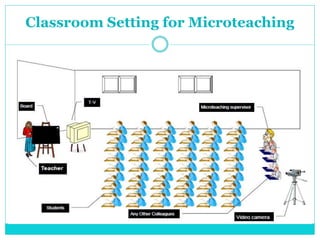
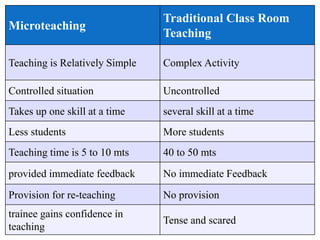
Microteaching is a technique developed by D.W. Allen to improve teaching skills. It involves teaching a short "micro" lesson to a small group while focusing on one skill. The lesson is observed, feedback is provided, and the lesson is revised and retaught to further develop the skill. This process allows teachers to systematically practice and master teaching skills one by one with feedback in a low-pressure environment.