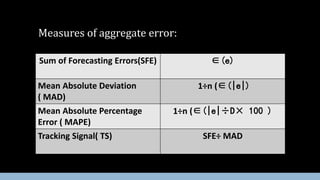
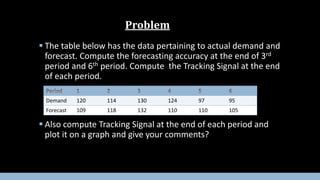
Forecasting involves making predictions about future events based on historical data. Forecasting errors are measured as the difference between actual and predicted values. This document discusses various methods of measuring forecasting errors over time (calendar errors) and across different products (cross-sectional errors). It defines important error metrics like mean absolute deviation and mean absolute percentage error, and the tracking signal ratio, which are used to evaluate forecast accuracy and consistency over multiple periods. The document also includes an example calculating these metrics based on actual and forecast demand values.