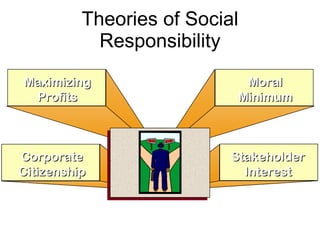
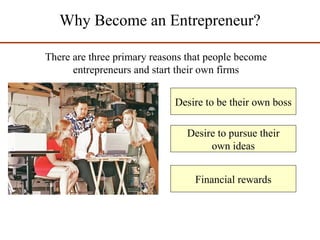
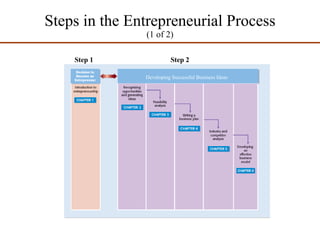
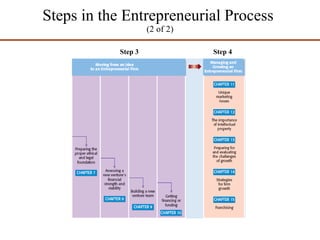
Operations management (OM) is essential for planning and controlling resources needed to produce goods and services, transforming inputs into outputs while adding value and ensuring efficiency. The document discusses various operations examples, types of transformation processes, and new trends in OM such as mass customization and supply chain management. It also covers the importance of social responsibility and entrepreneurship, defining key concepts and theories associated with these areas.





























![Thank You! Stay in touch: Facebook: ProfManish Parihar Blog: www.pariharmanish.blogspot.com E-mail: [email_address] Cell: 9274807737](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontooperationsmanagement-111013195816-phpapp01/85/Introduction-to-operations-management-46-320.jpg)