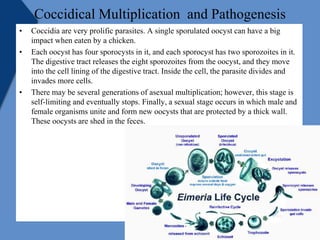
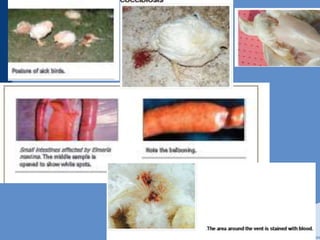
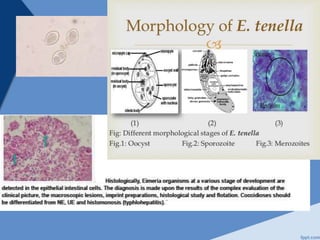
Coccidiosis is caused by parasitic protozoa of the genus Eimeria that infect the intestinal tract of poultry. There are seven species that commonly infect chickens. The parasite undergoes asexual reproduction within intestinal cells causing damage before being shed in feces. Clinical signs include diarrhea, poor growth, and decreased egg production. Post-mortem examination reveals damage to the intestinal lining. Diagnosis involves finding oocysts in feces. Control is through vaccination, anticoccidial drugs, and biosecurity measures to prevent transmission between flocks.




![Transmission
• Ingestion of the infective form of oocytes (sporulated oocytes) is the only
natural method of spread.
• Oocytes can be spread mechanically by animals, insects,contaminated
equipments ,wild birds and dust.
• Movement of people and equipments between farms.
• The spread of coccidiosis is less during hot dry wheather (summer) and
greater in cooler wetter weather (Rainy and Winter season).
• Coccidia are almost universally present in poultry-raising operations, but
clinical disease occurs only after ingestion of relatively large numbers of
sporulated oocysts by susceptible birds.
• Both clinically infected and recovered birds shed oocysts in their
droppings, which contaminate feed, dust, water, litter, and soil.
• Fresh oocysts are not infective until they sporulate; under optimal
conditions (70°–90°F [21°–32°C] with adequate moisture and oxygen), this
requires 1–2 days. Coccidia are host-specific, and there is no cross-
immunity between species of coccidia.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/coccidioispoultry-200415195437/85/Coccidiois-poultry-5-320.jpg)