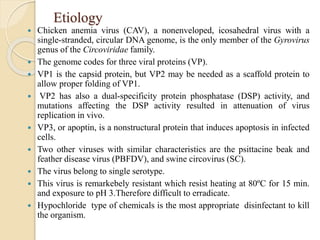
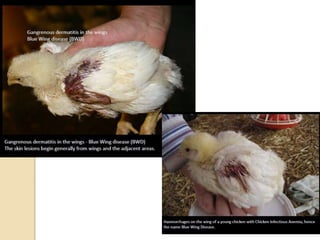
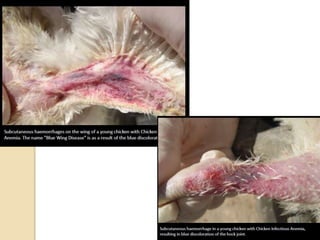
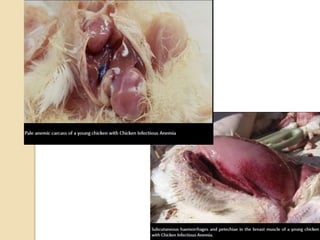
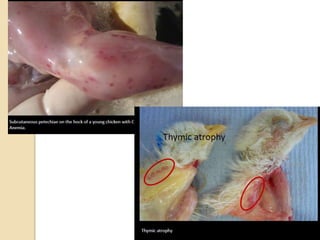
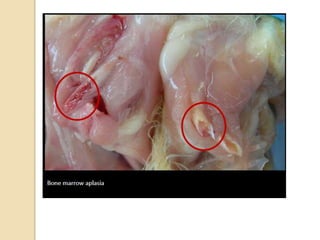
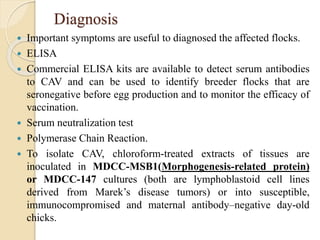
Chicken Infectious Anaemia, also known as Chicken anaemia virus syndrome, is caused by the Chicken anaemia virus (CAV). It affects young chickens less than 3 weeks old. CAV is transmitted both vertically from hen to egg and horizontally between chickens. Affected chickens appear depressed, pale and have reduced weight gain. Post mortem findings include reduced thymus and bone marrow sizes, fatty liver and haemorrhages. Diagnosis is through ELISA, PCR and virus isolation from tissues. Treatment focuses on supportive care and secondary infections. Control relies on vaccination of breeders and monitoring flocks for antibodies.