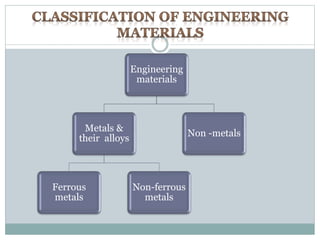
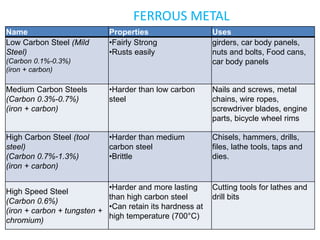
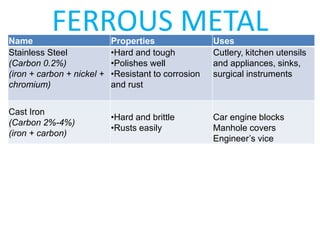
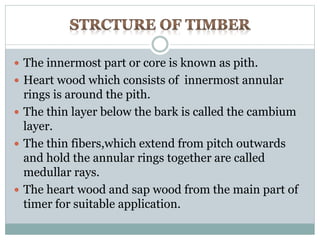
This document provides information on important engineering materials. It discusses metals including ferrous metals like steel and cast iron, and non-ferrous metals like aluminum, copper, lead, tin, and nickel. It also covers non-metallic materials like wood, ceramics, and abrasives. For each material, the document outlines key properties and applications in engineering.