Embed presentation
Downloaded 74 times

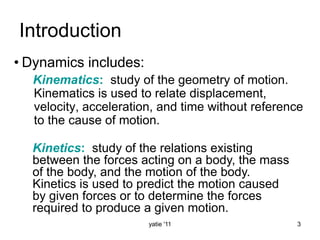
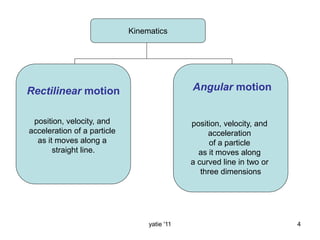
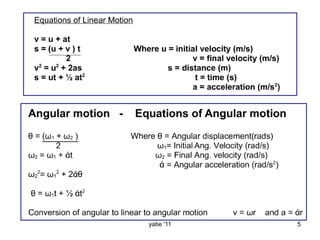
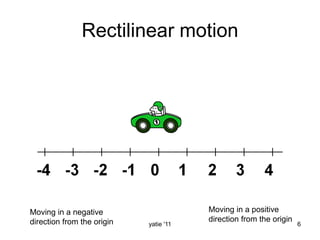
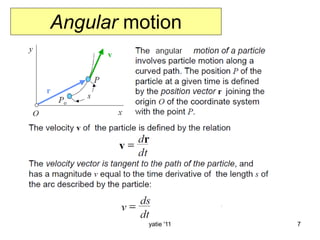
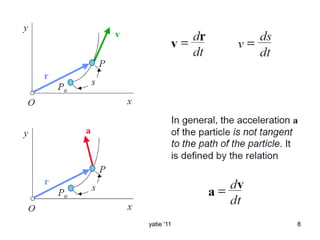
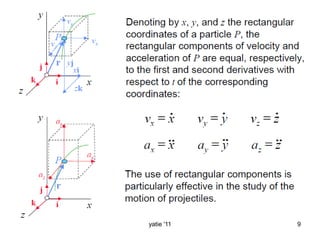
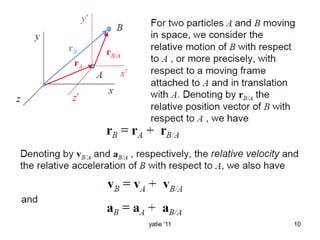
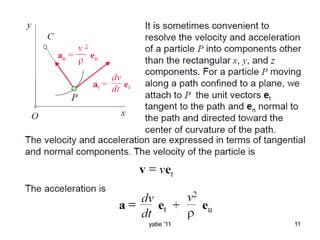
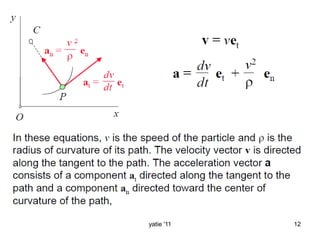
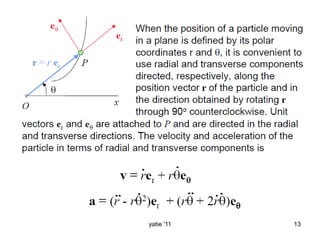
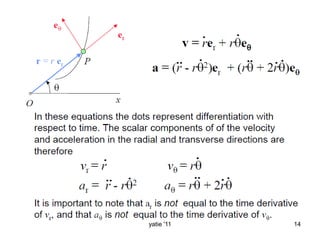
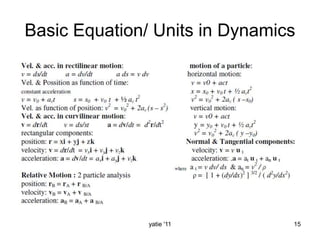


This document discusses basic concepts in dynamics, including kinematics and kinetics. Kinematics is defined as the study of motion geometry, relating displacement, velocity, and acceleration without considering forces. Kinetics is defined as studying the relationships between forces, mass, and motion, and using forces to predict or determine motion. The document explains that kinematics includes rectilinear motion along a straight line and angular motion along a curved line, and provides examples of rectilinear and angular motion. It concludes by stating that basic equations and units in dynamics will be covered.















