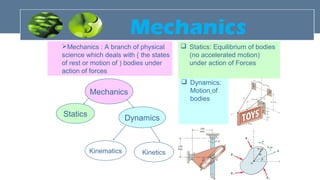
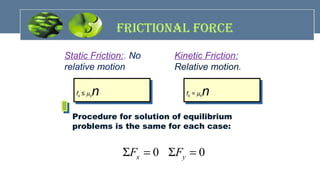
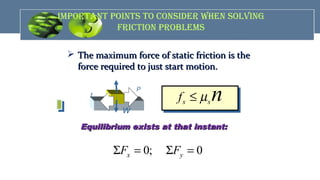
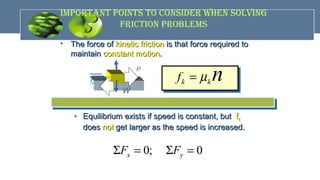
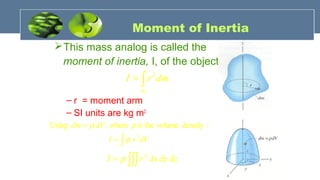
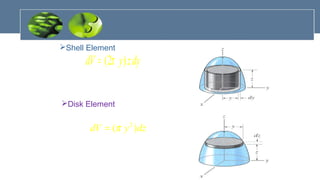
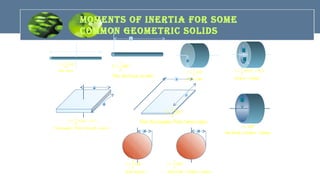
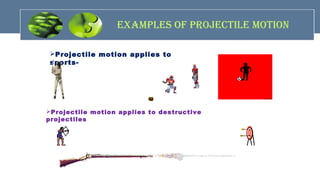
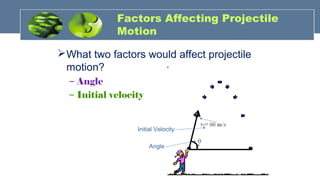
The document provides an overview of mechanics, including key concepts such as statics, dynamics, kinematics, and kinetics, as well as Newton's laws of motion that govern the behavior of objects. It discusses frictional forces, moment of inertia, radius of gyration, and projectile motion, detailing both their definitions and applications. The content is structured around group members' contributions, emphasizing fundamental principles and equations relevant to physics and engineering.