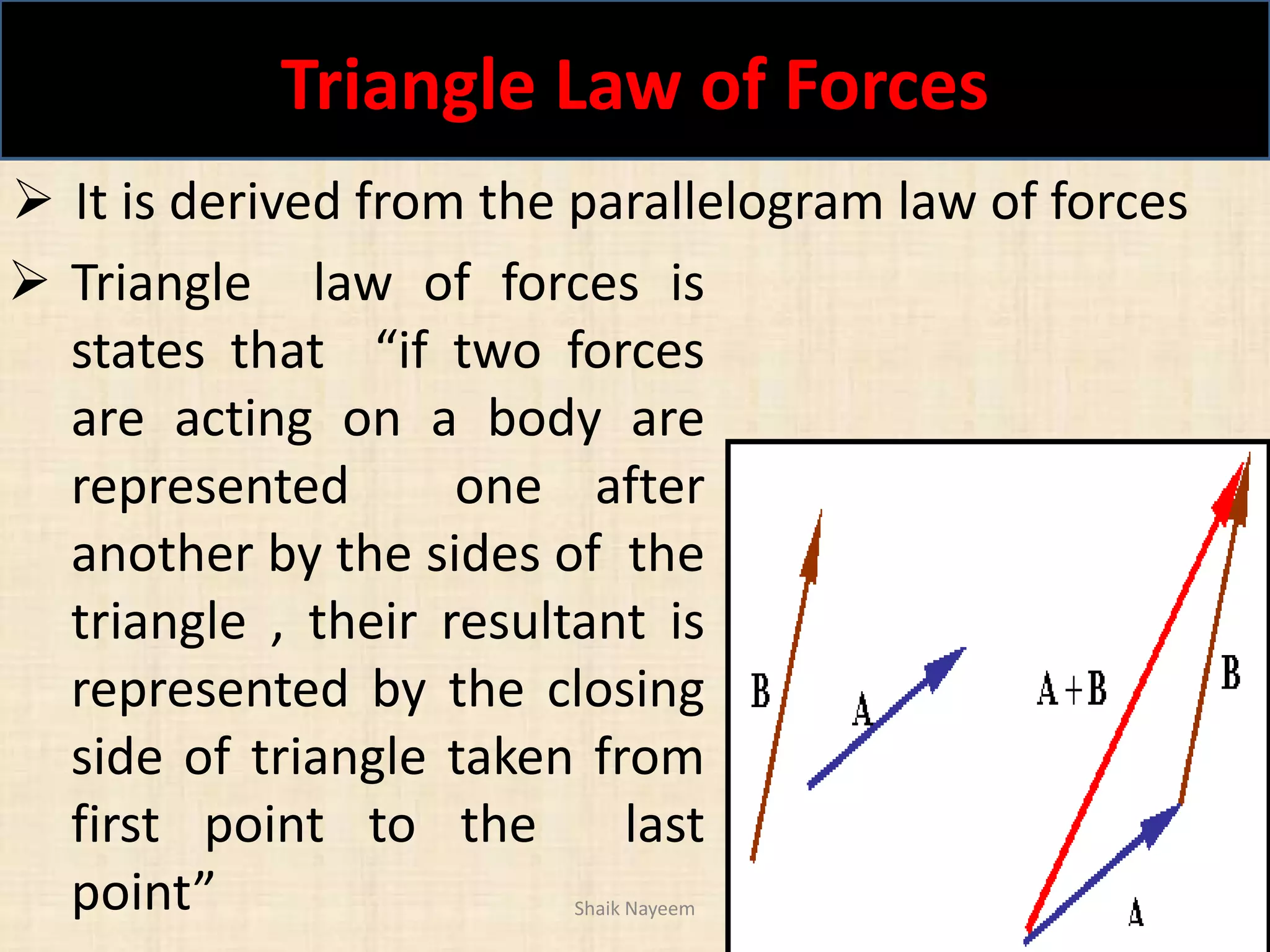
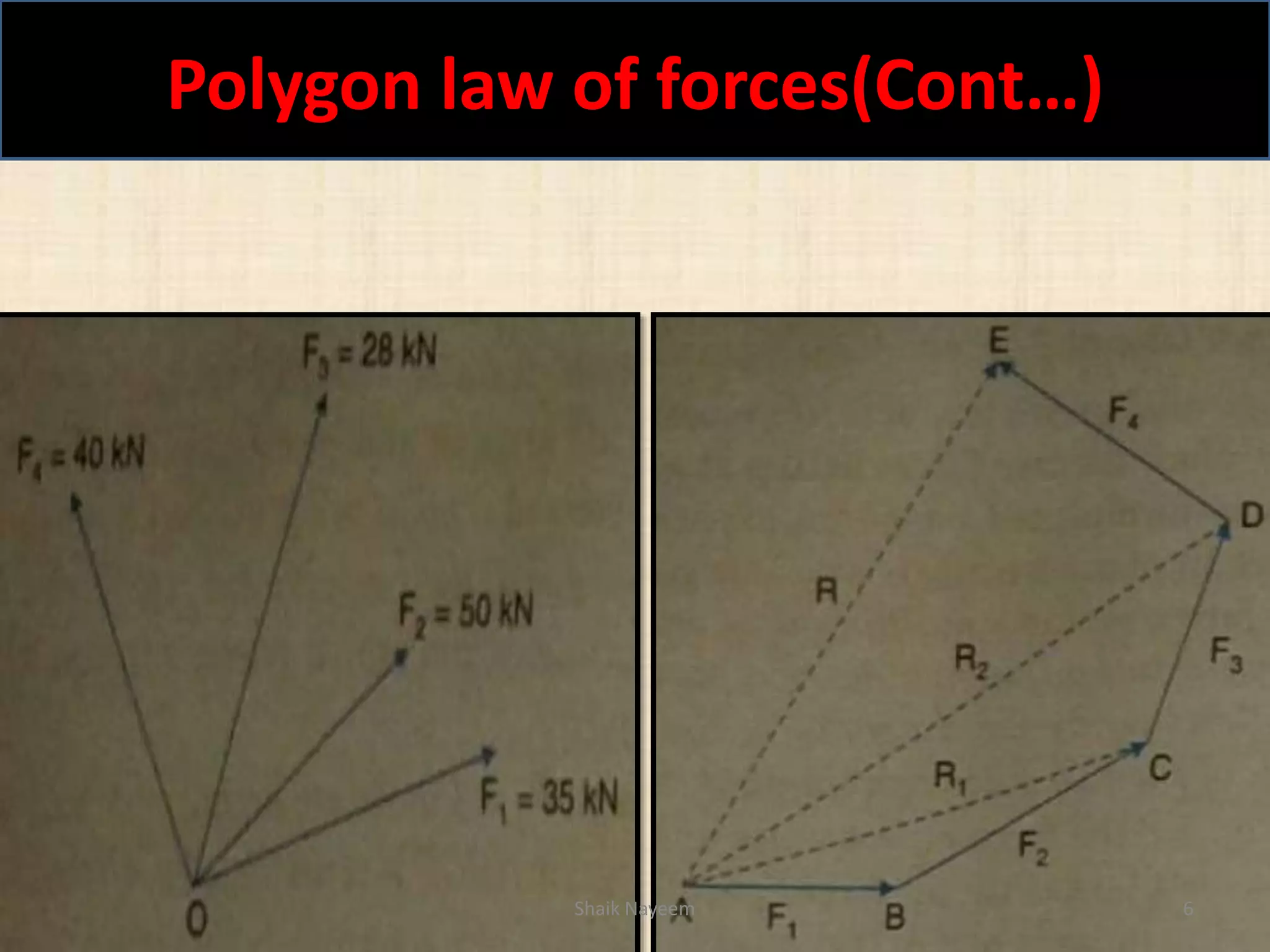
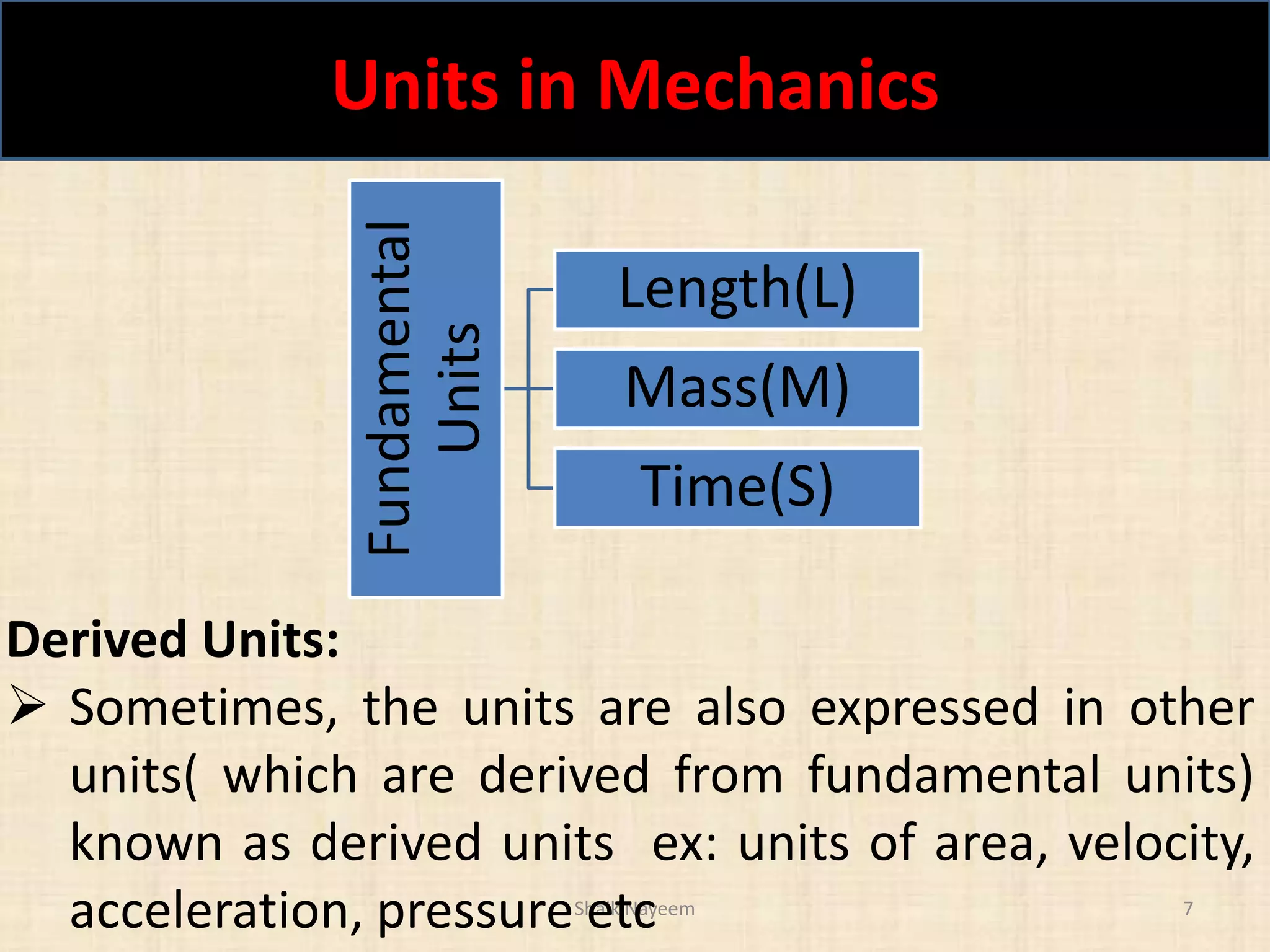
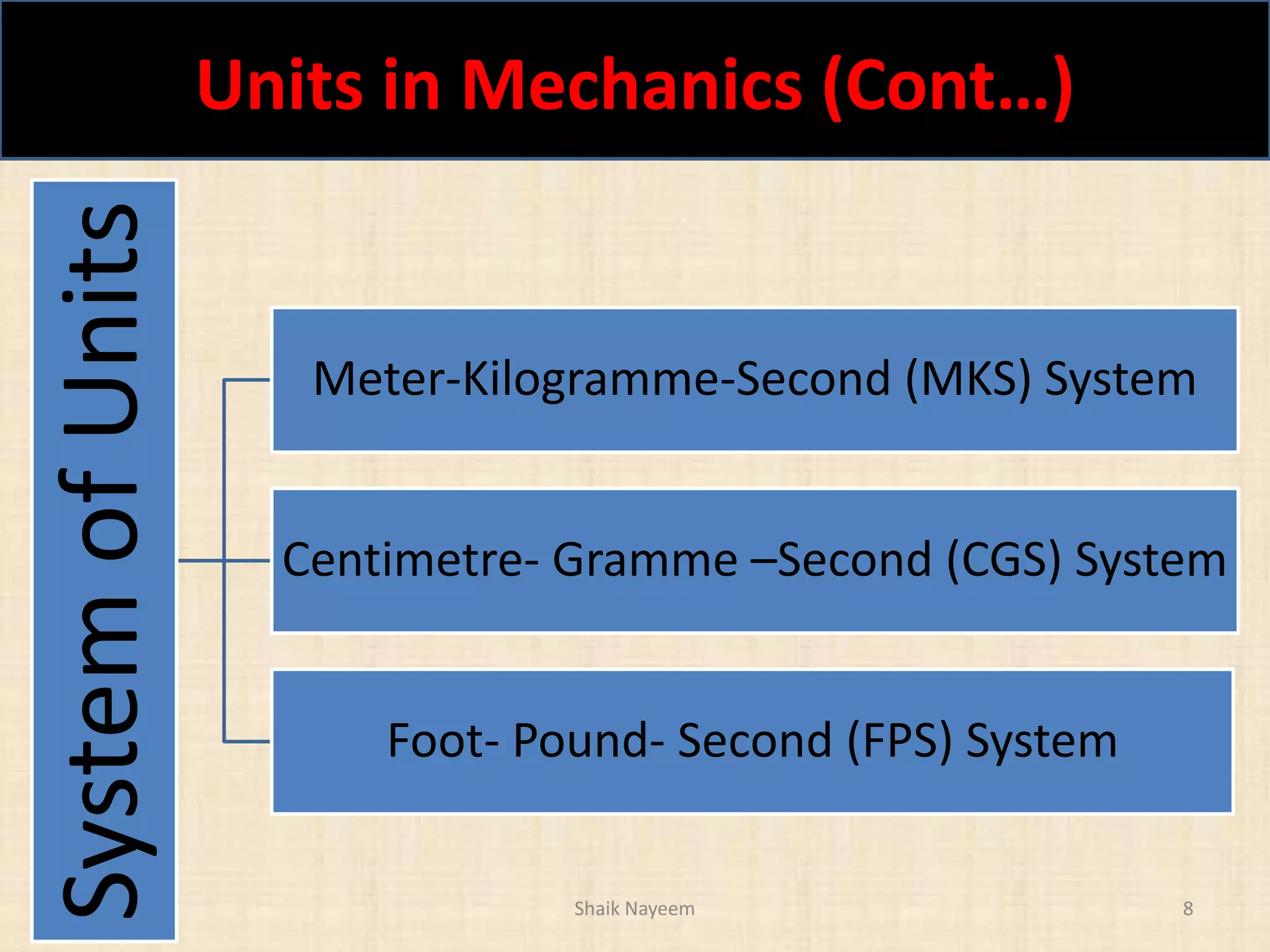
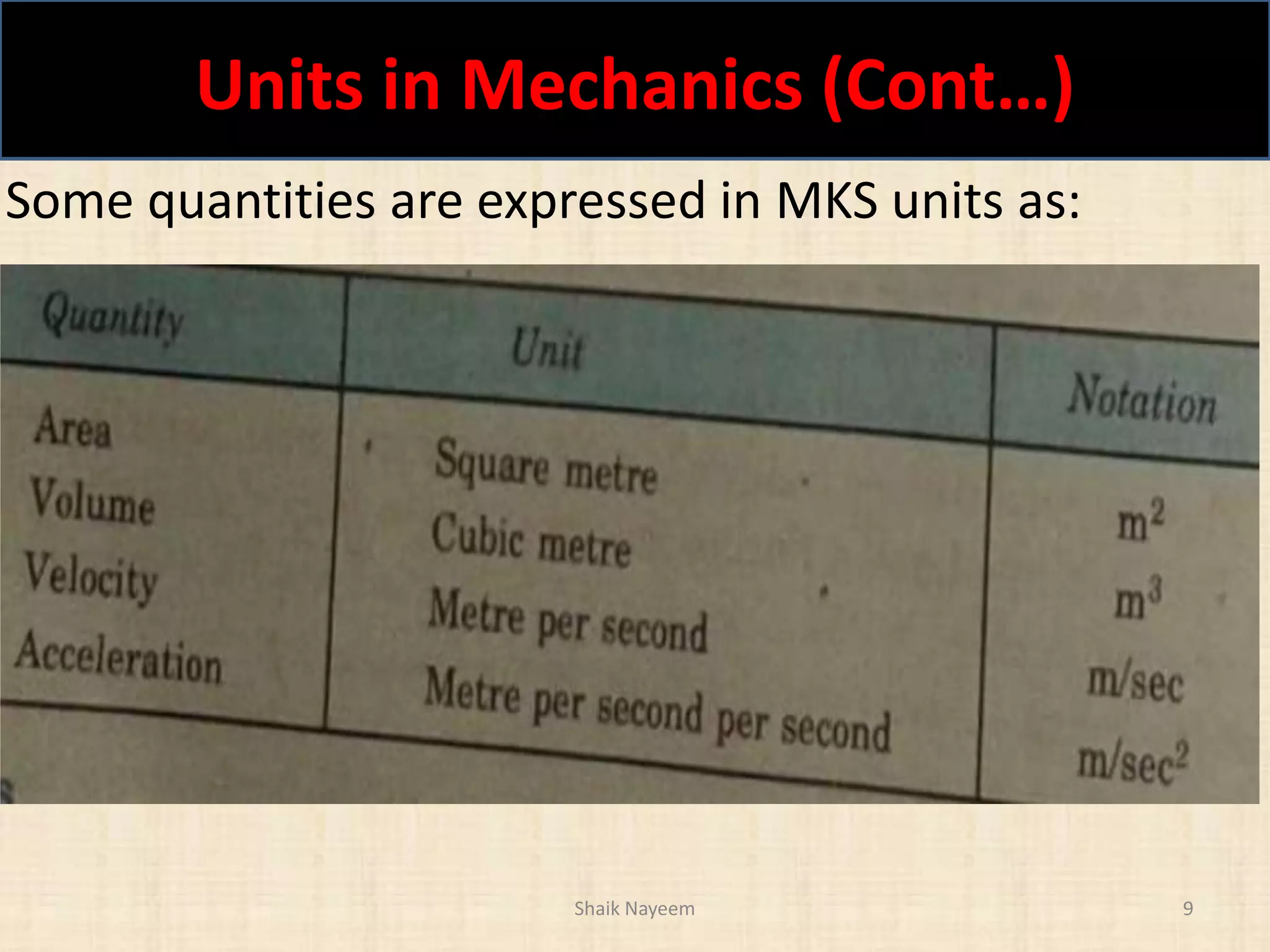
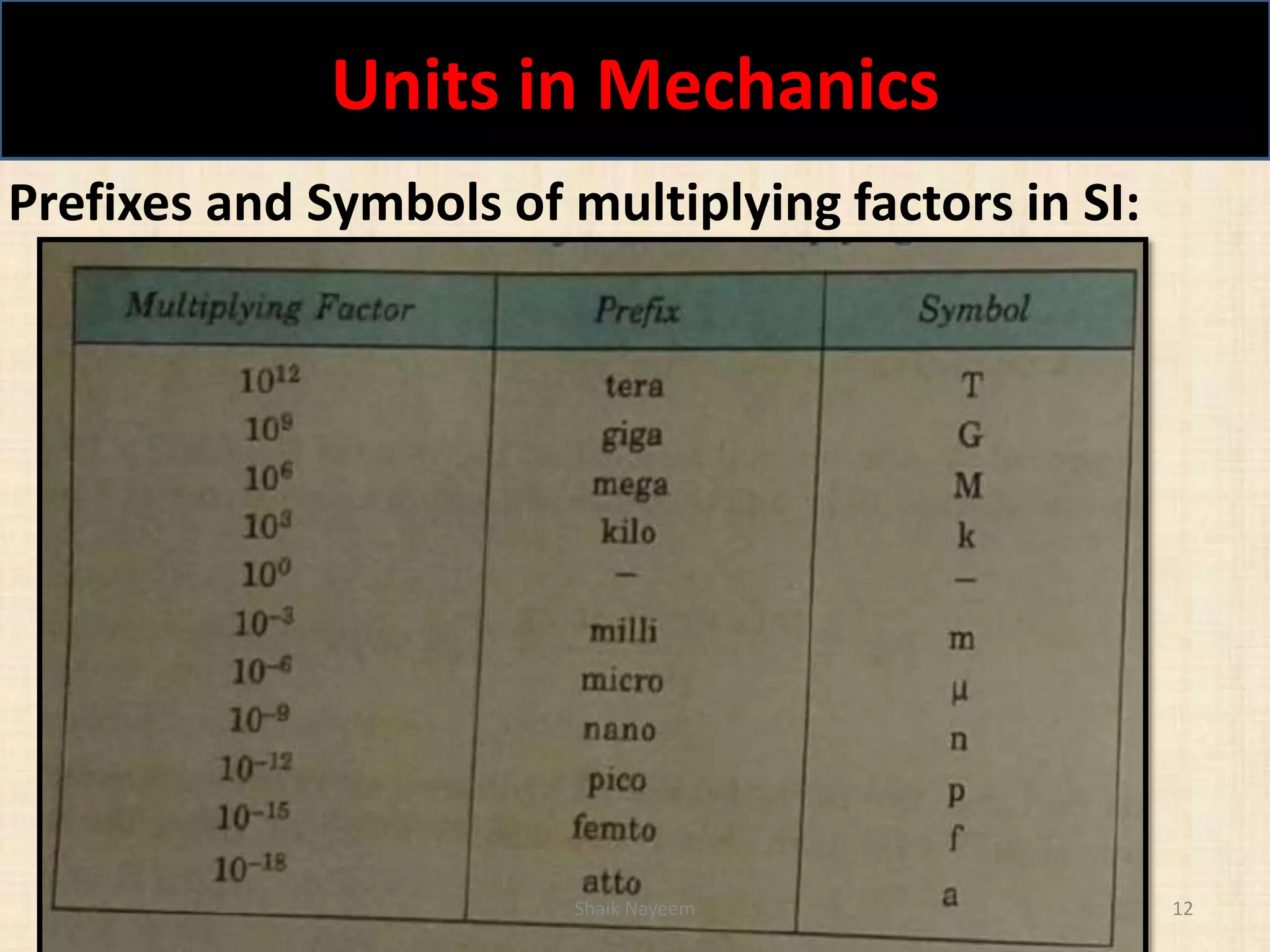
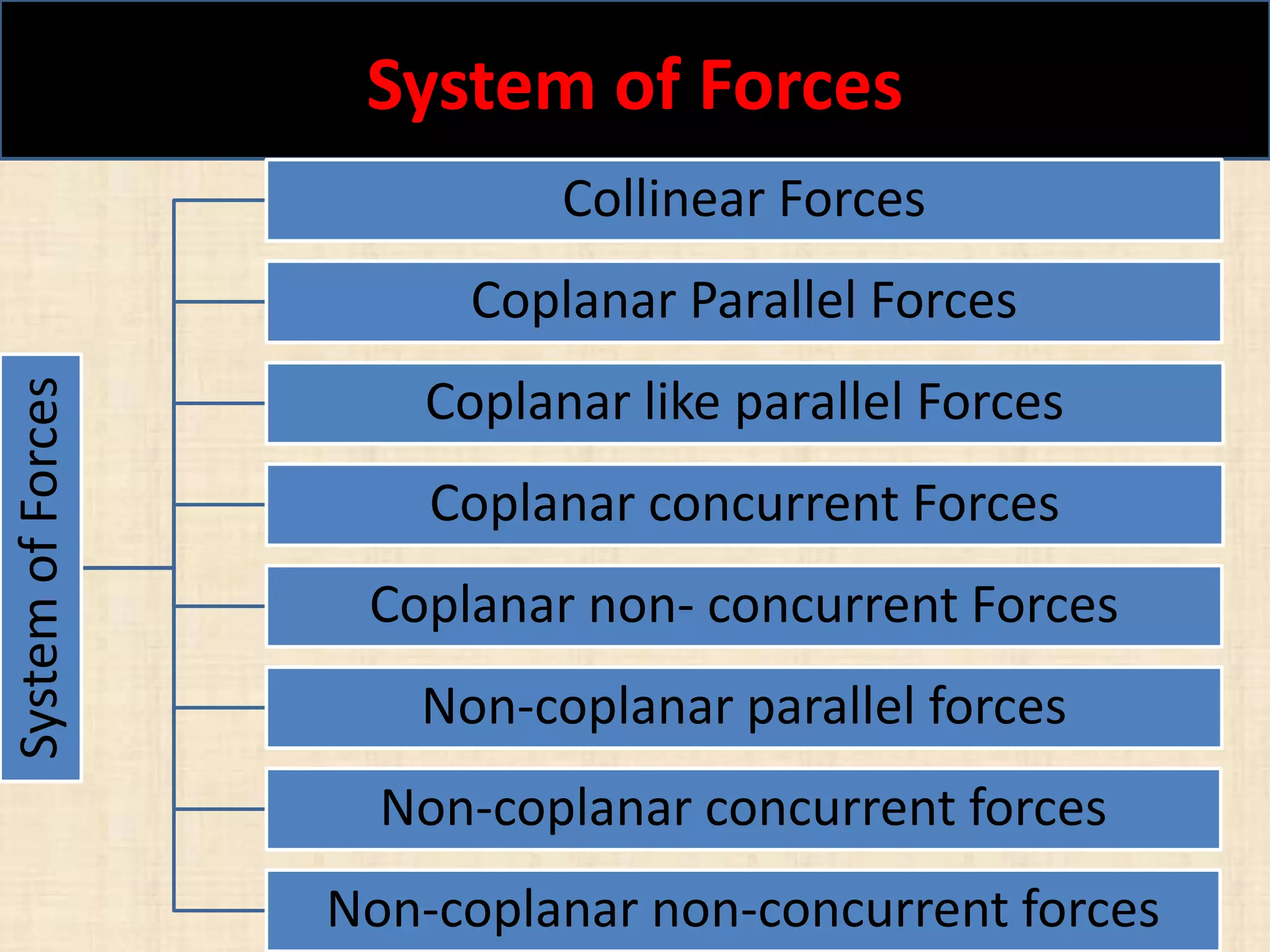
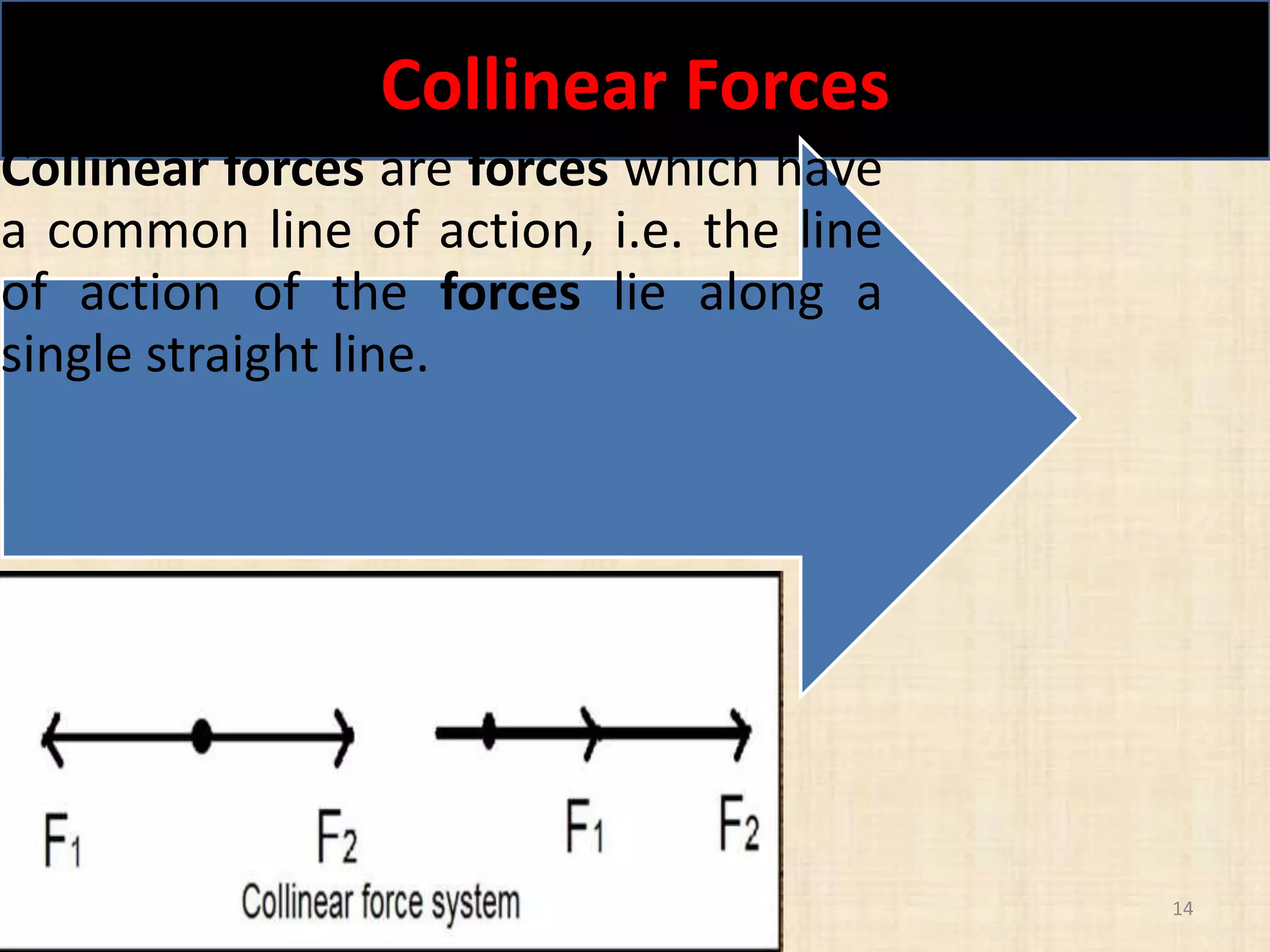
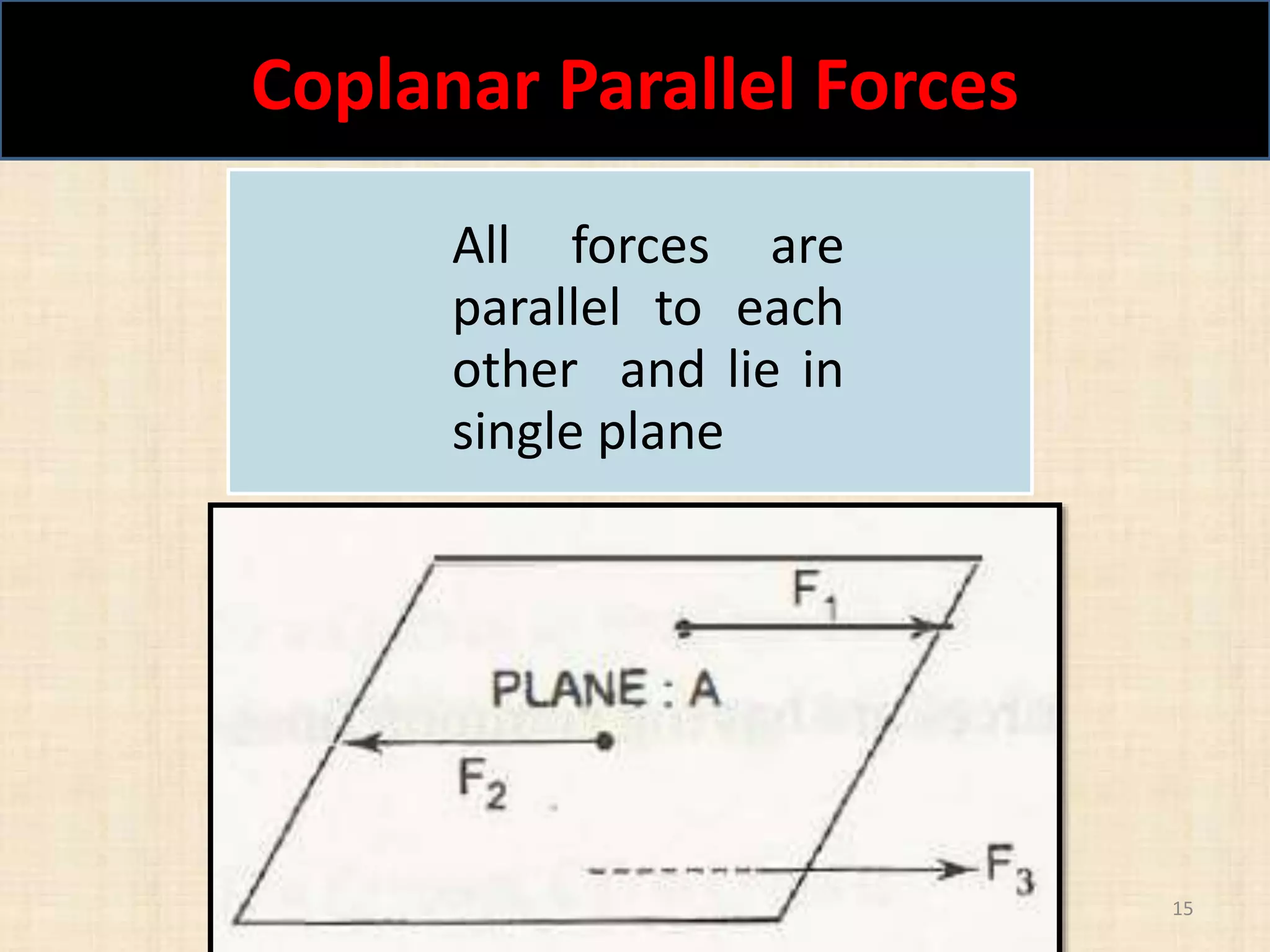
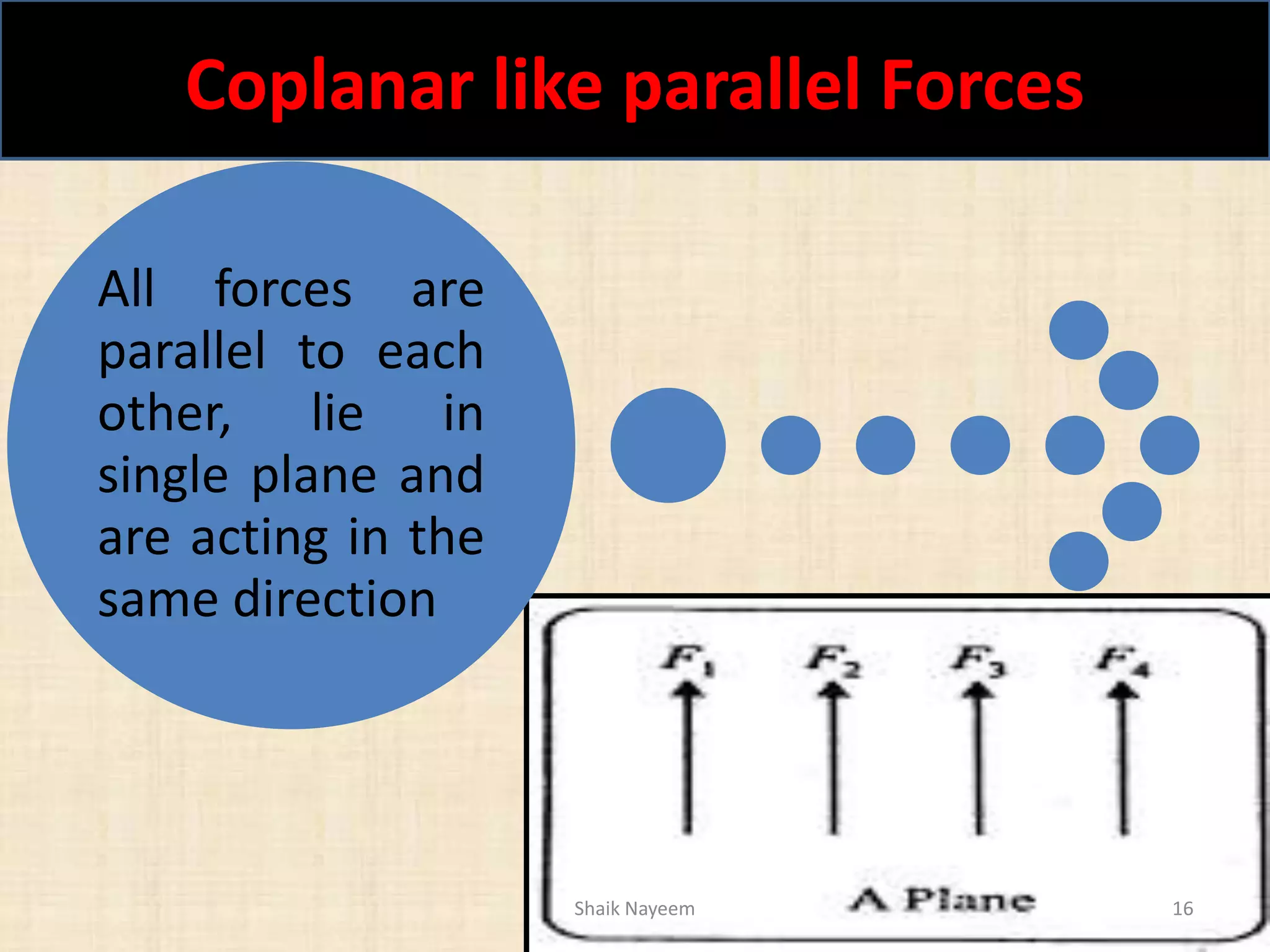
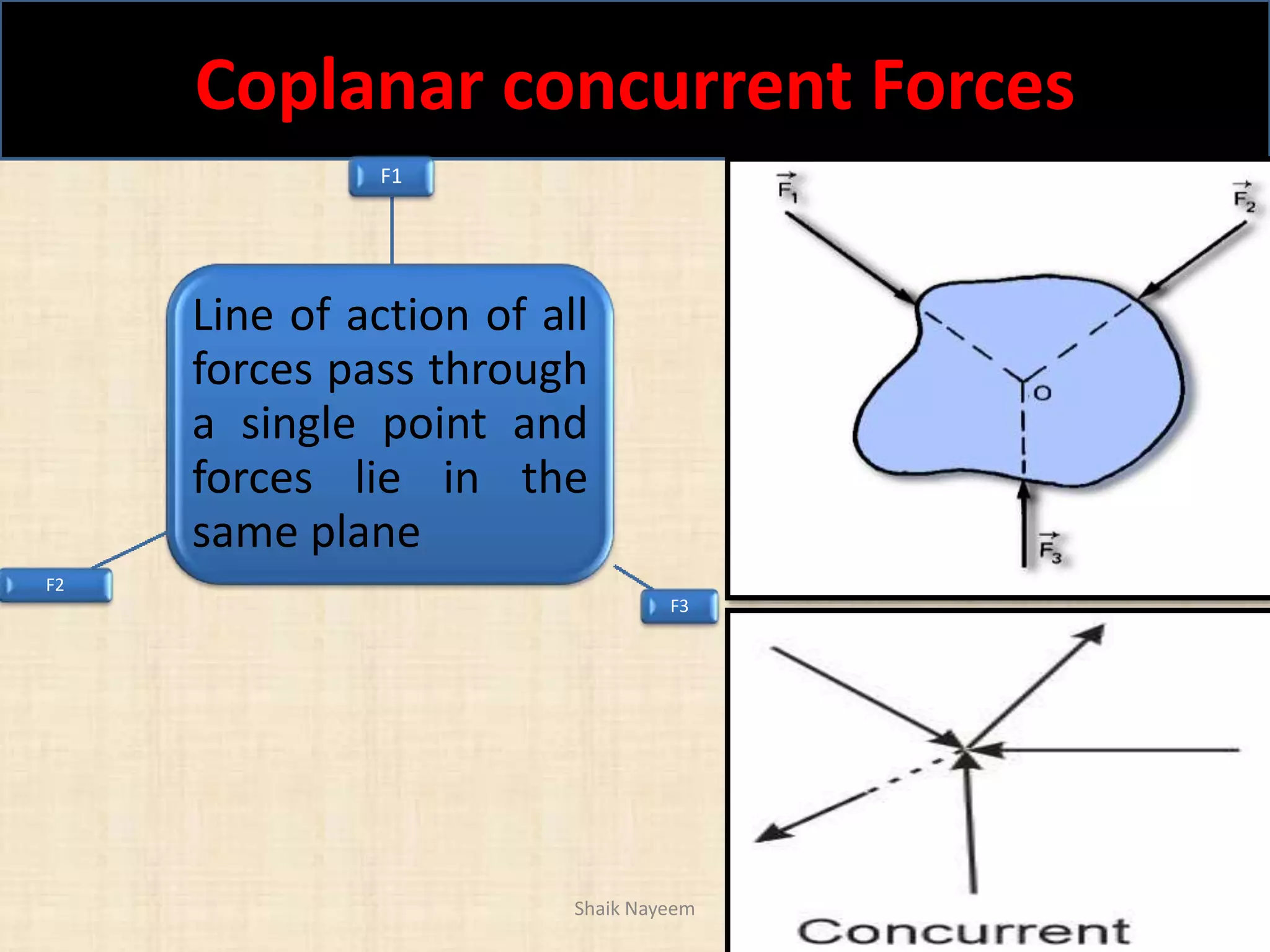
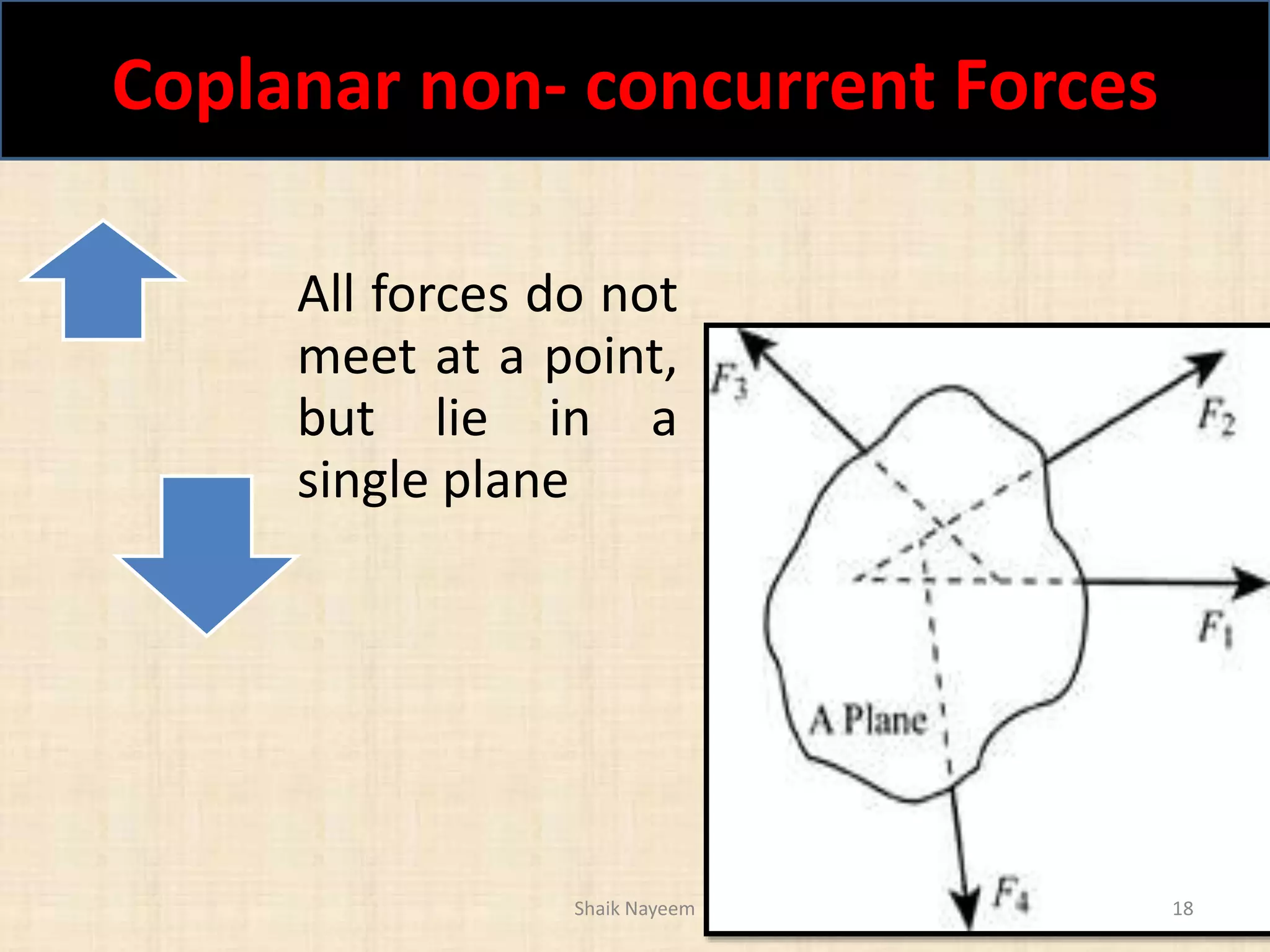
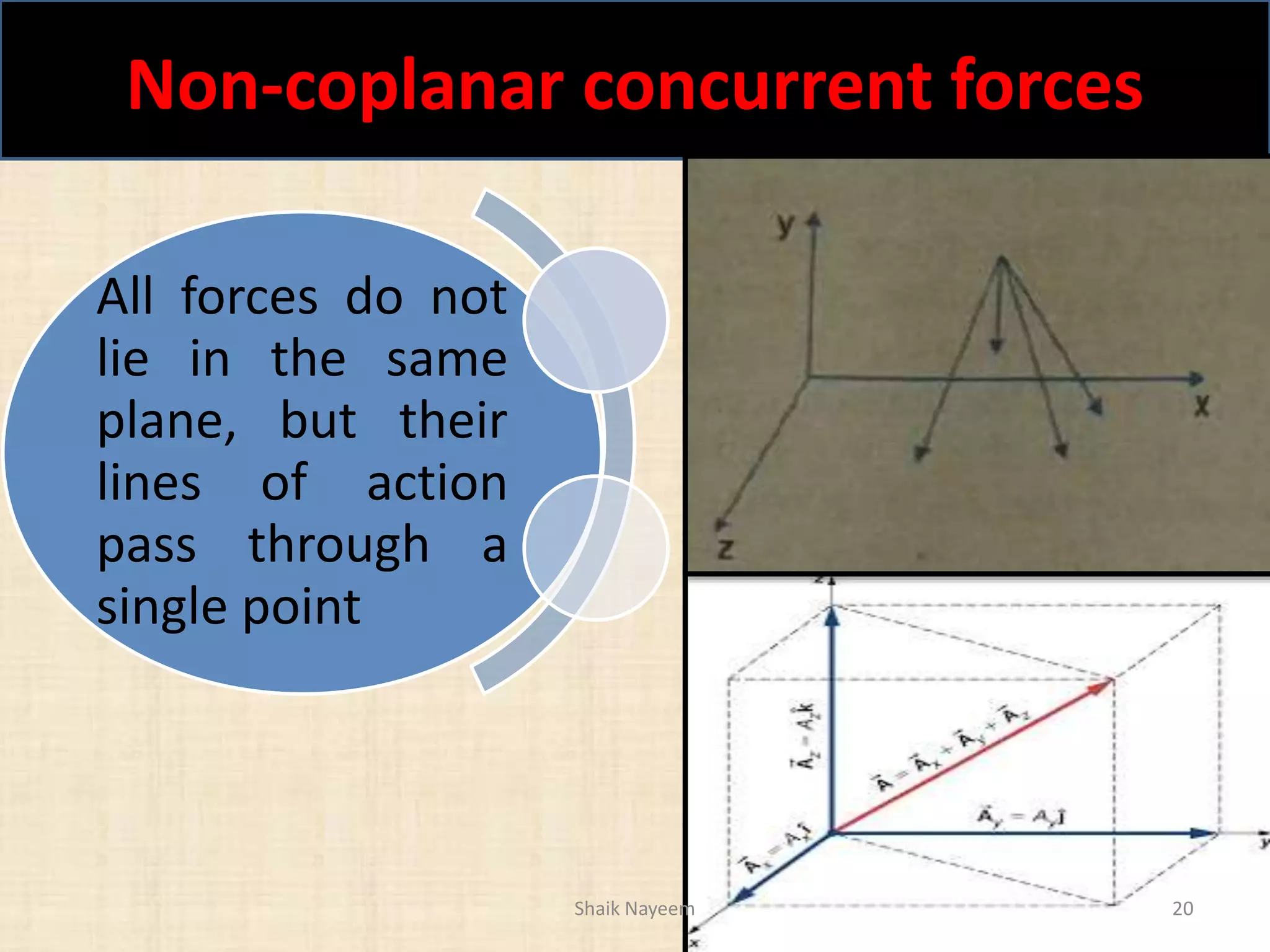
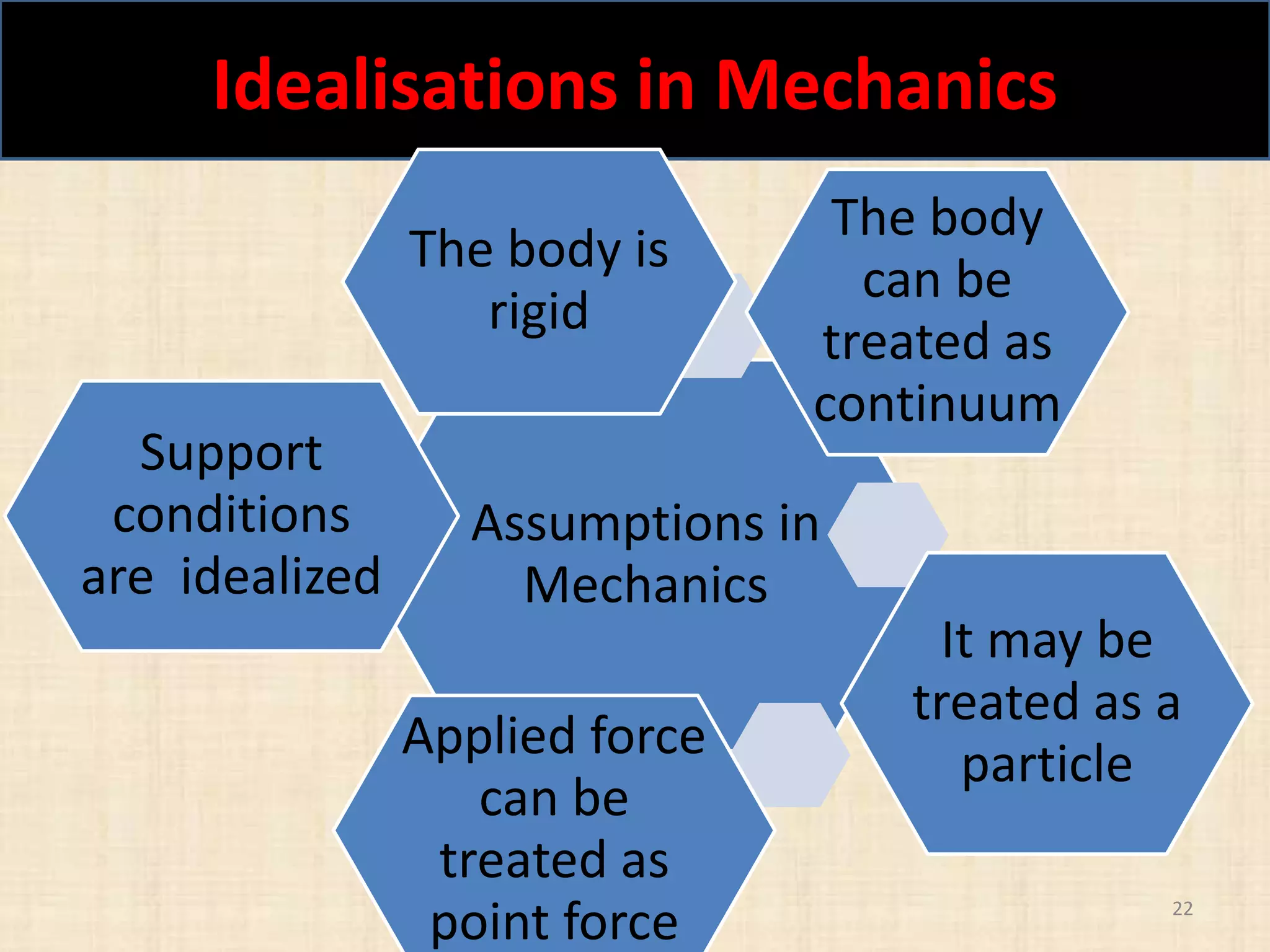
This document discusses concepts in engineering mechanics including derived laws of forces, units of measurement, and systems of forces. It defines the triangle law and polygon law of forces, which describe the resultant force of multiple concurrent forces. Fundamental and derived units used in mechanics like the MKS and SI systems are also outlined. Finally, different types of force systems are defined, such as collinear, coplanar, and non-coplanar forces that can be concurrent, parallel or non-parallel. Idealizations commonly made in mechanics like treating bodies as rigid or applying point forces are also mentioned.