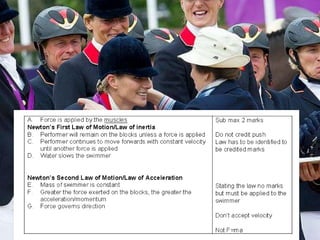
All students will be able to explain the factors that affect projectile motion and angular motion, including conservation of angular momentum and the relationship between moment of inertia and angular velocity. Some students will also be able to apply this knowledge to exam questions. The key learning outcomes are factors relating to projectile motion, angular motion, and definitions and equations for angular velocity, momentum, moment of inertia, and their relationships.