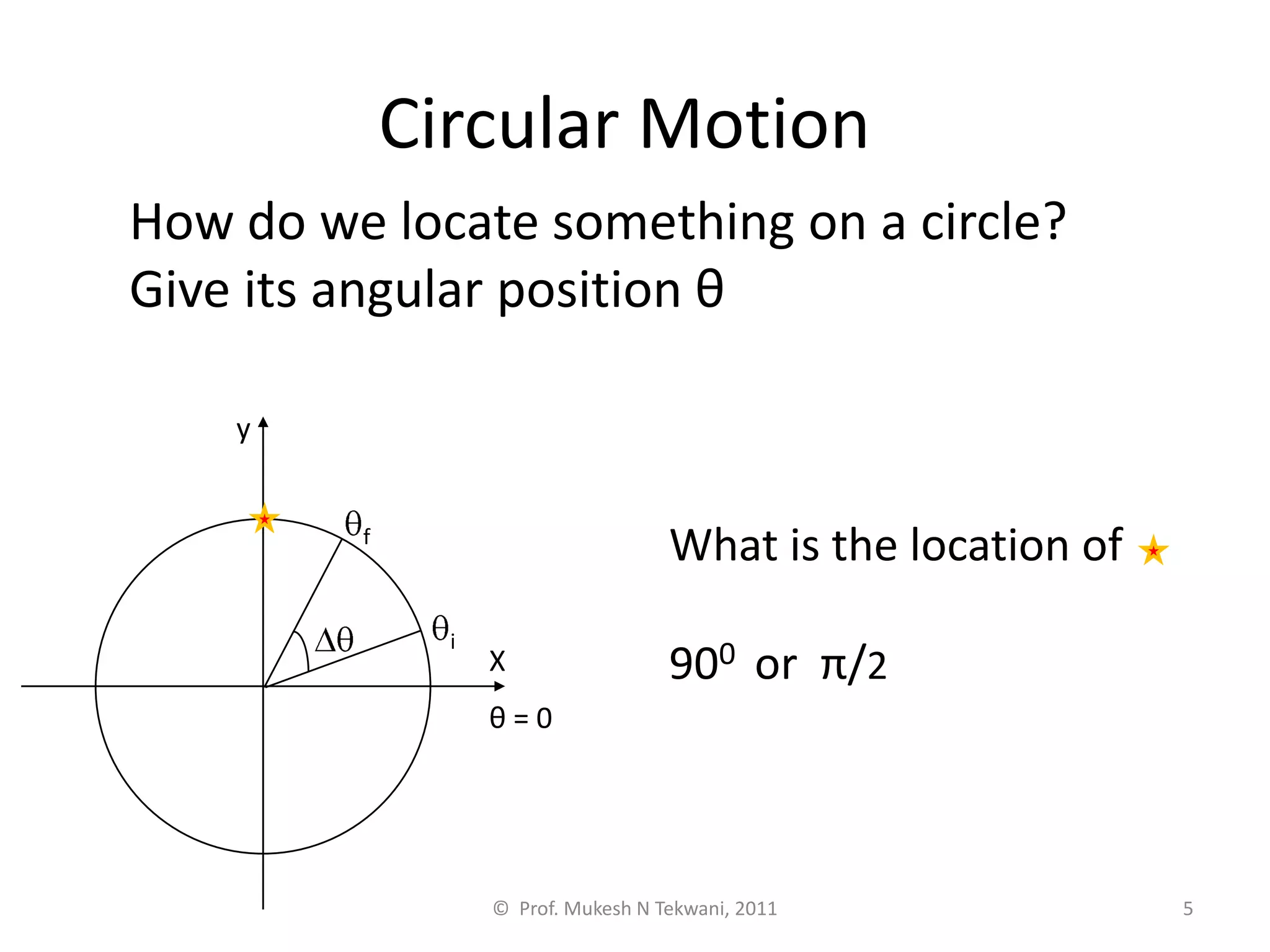
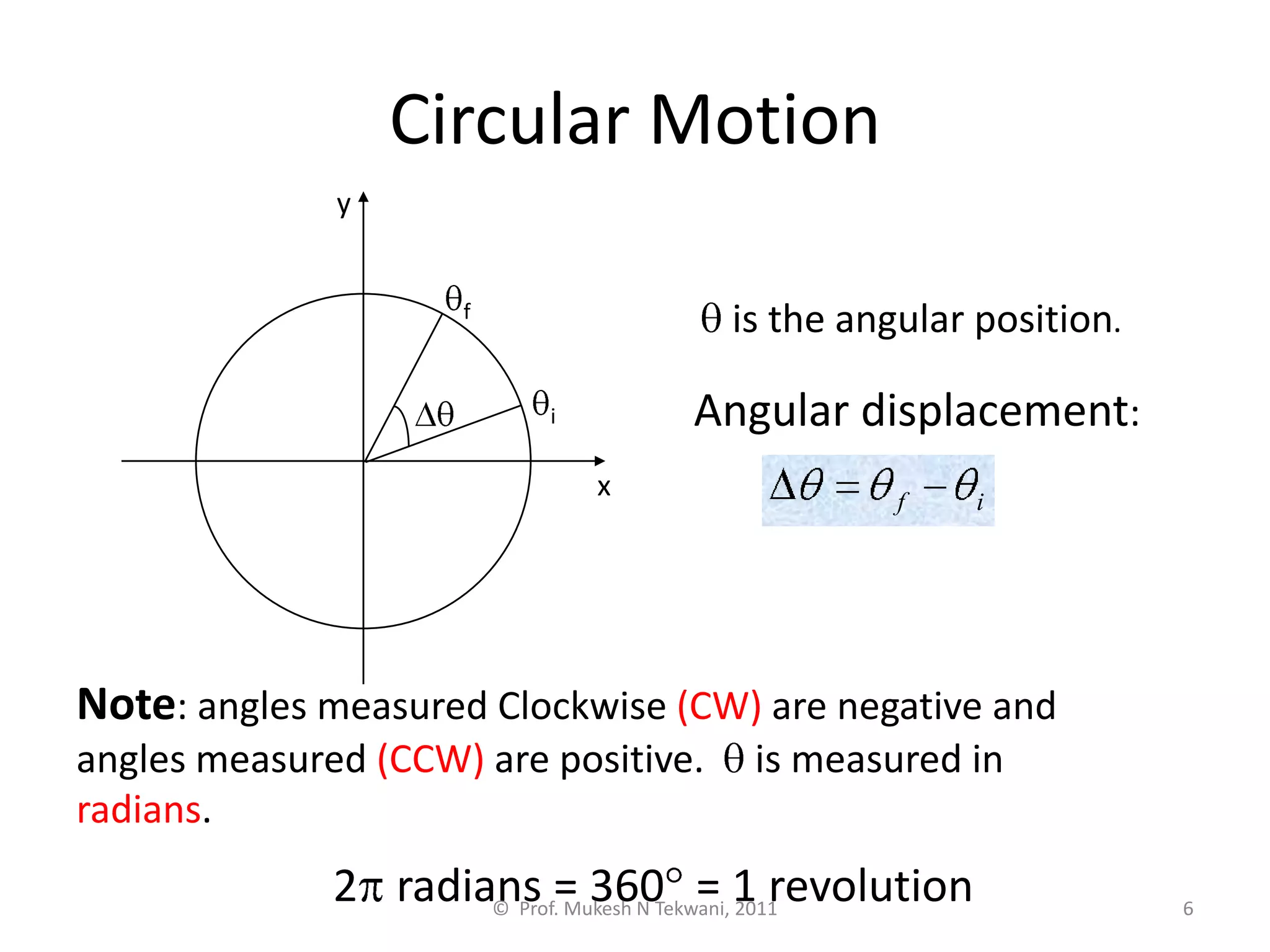
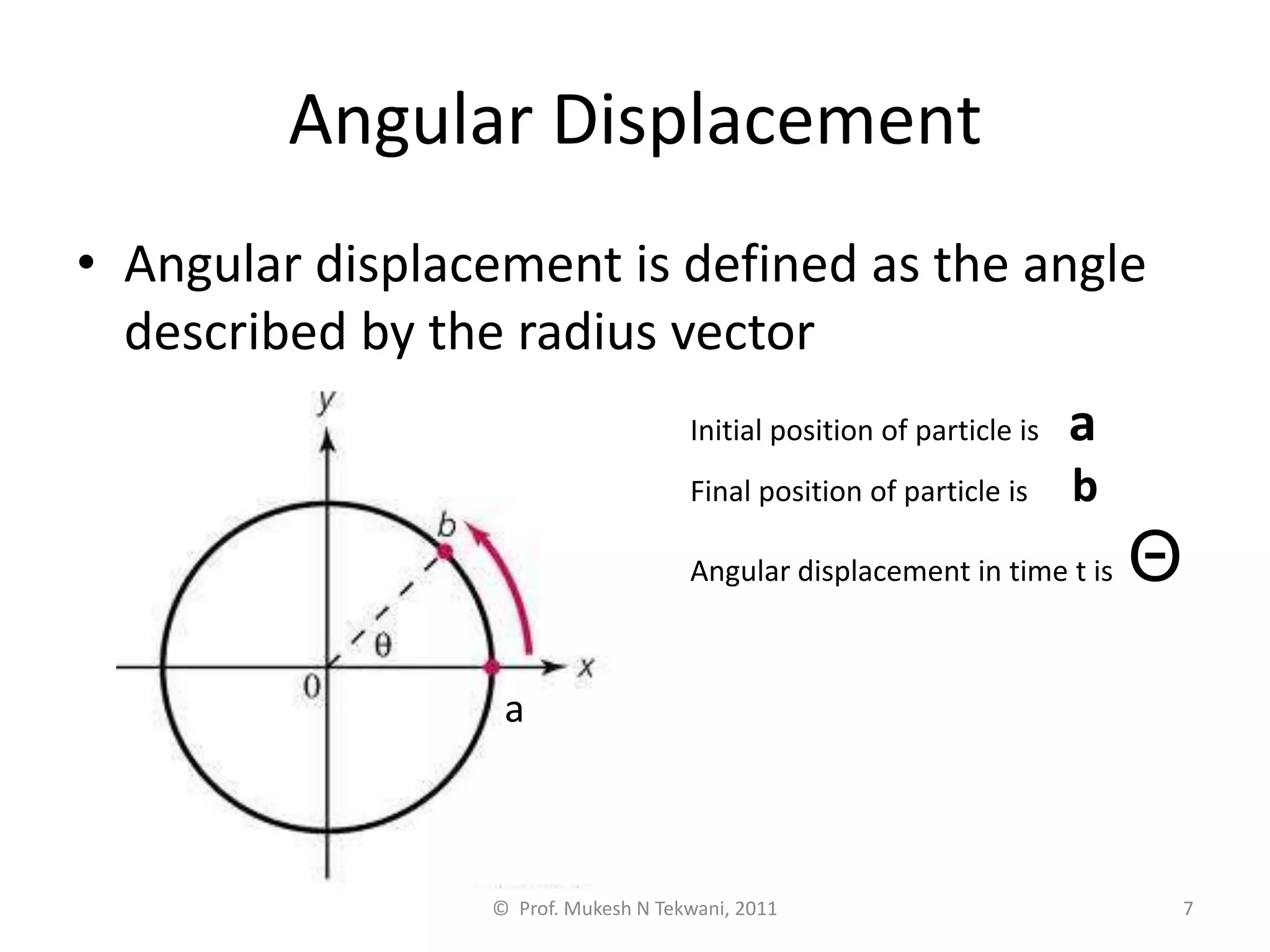
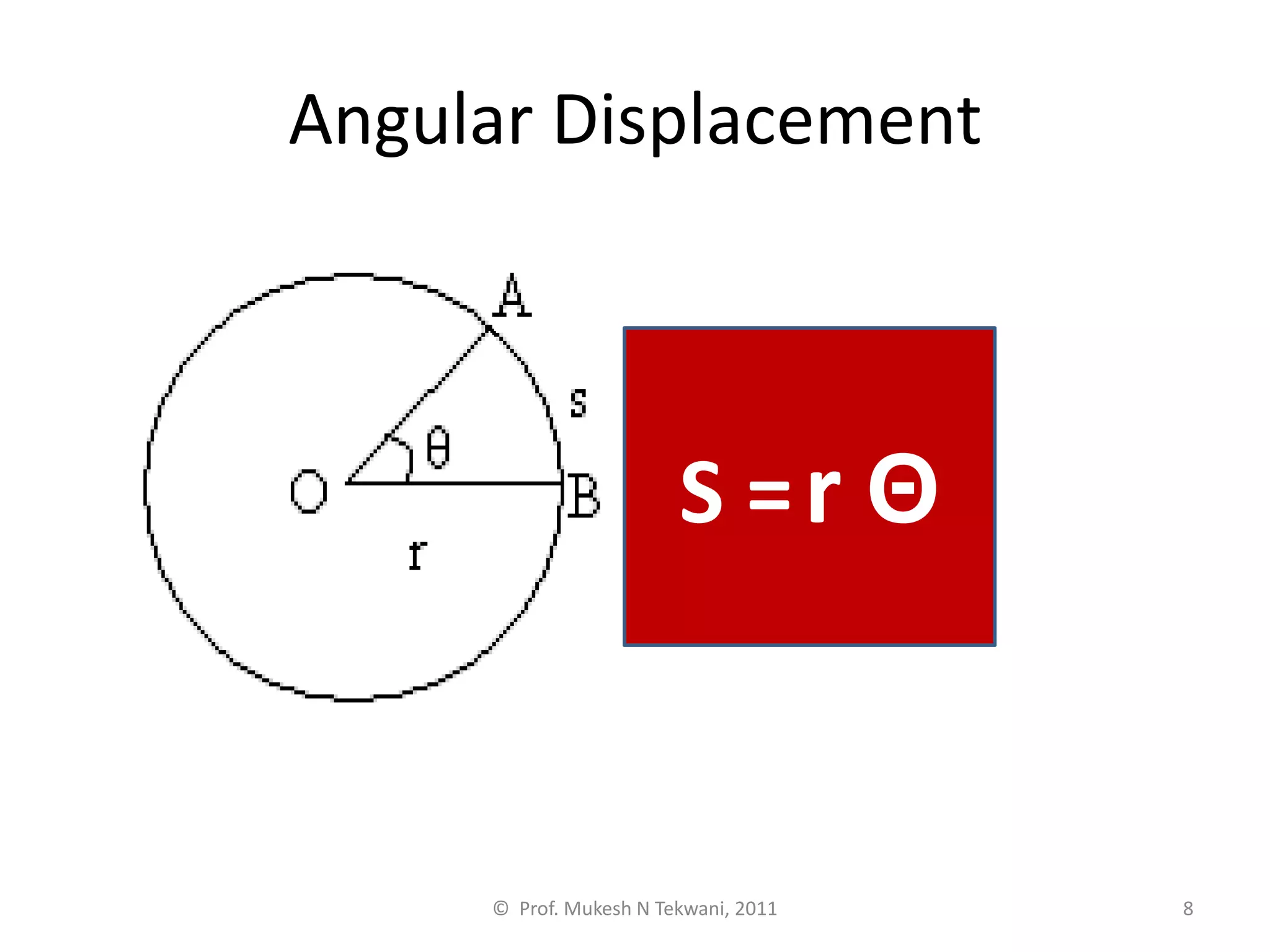
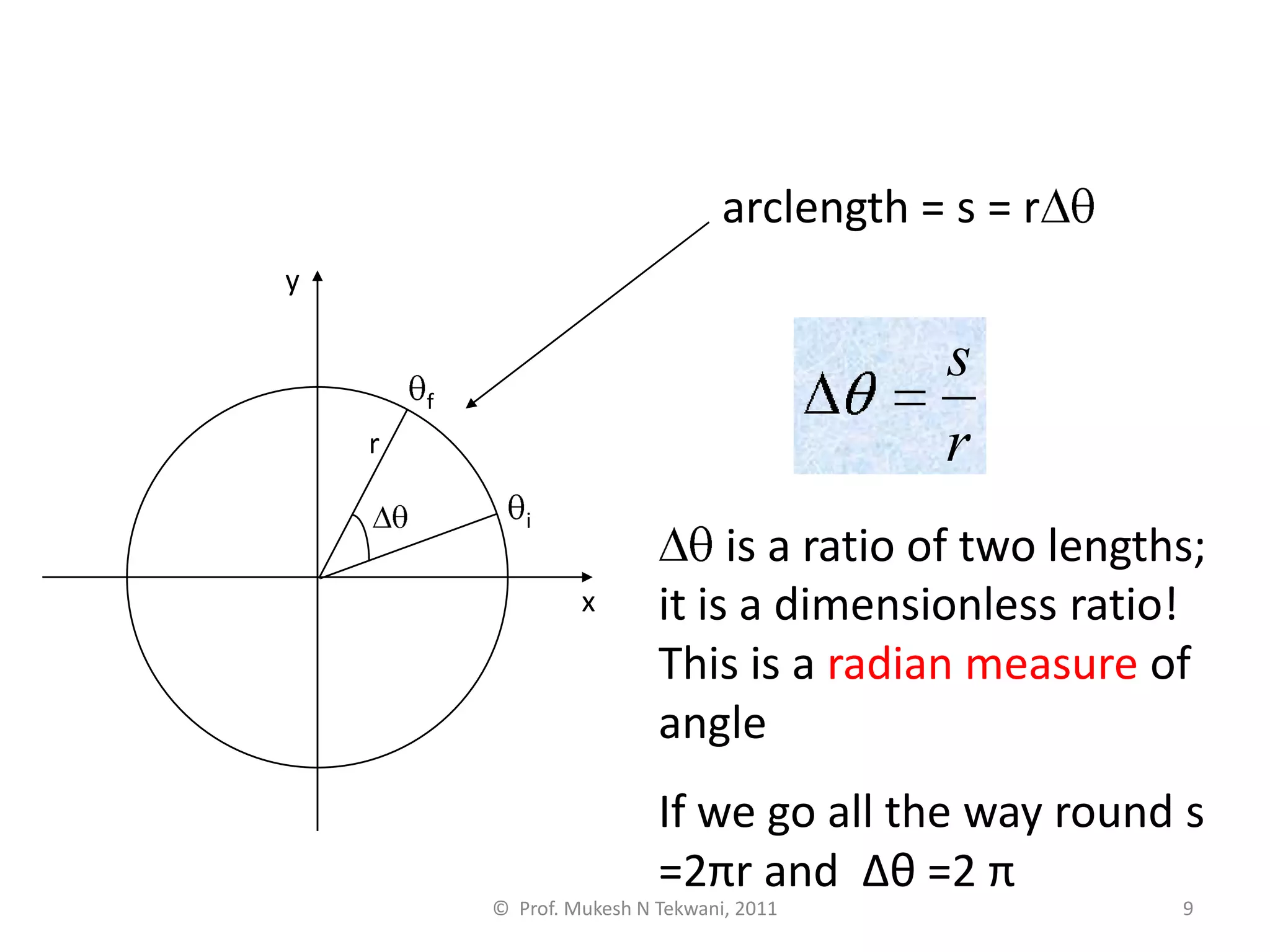
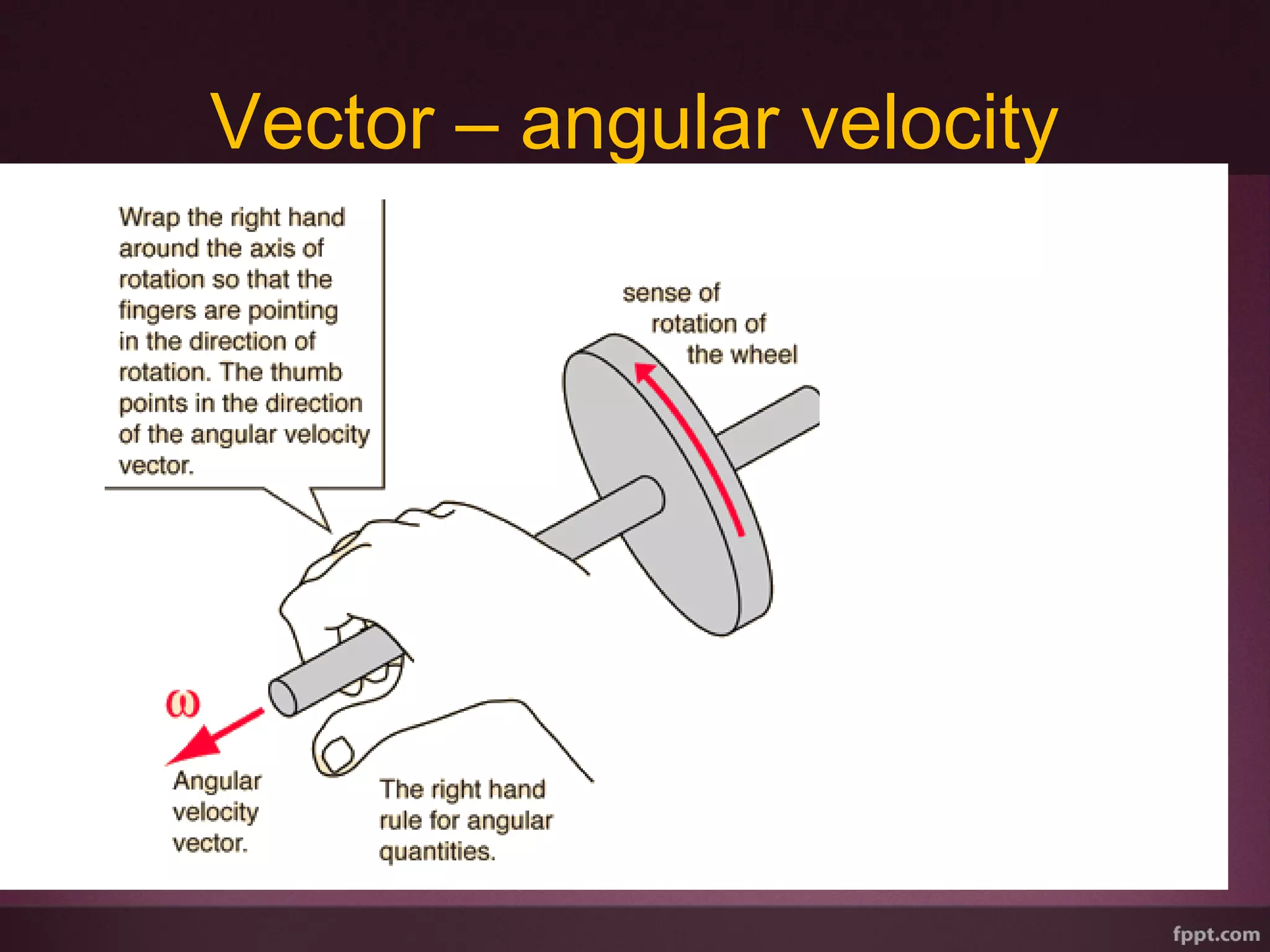
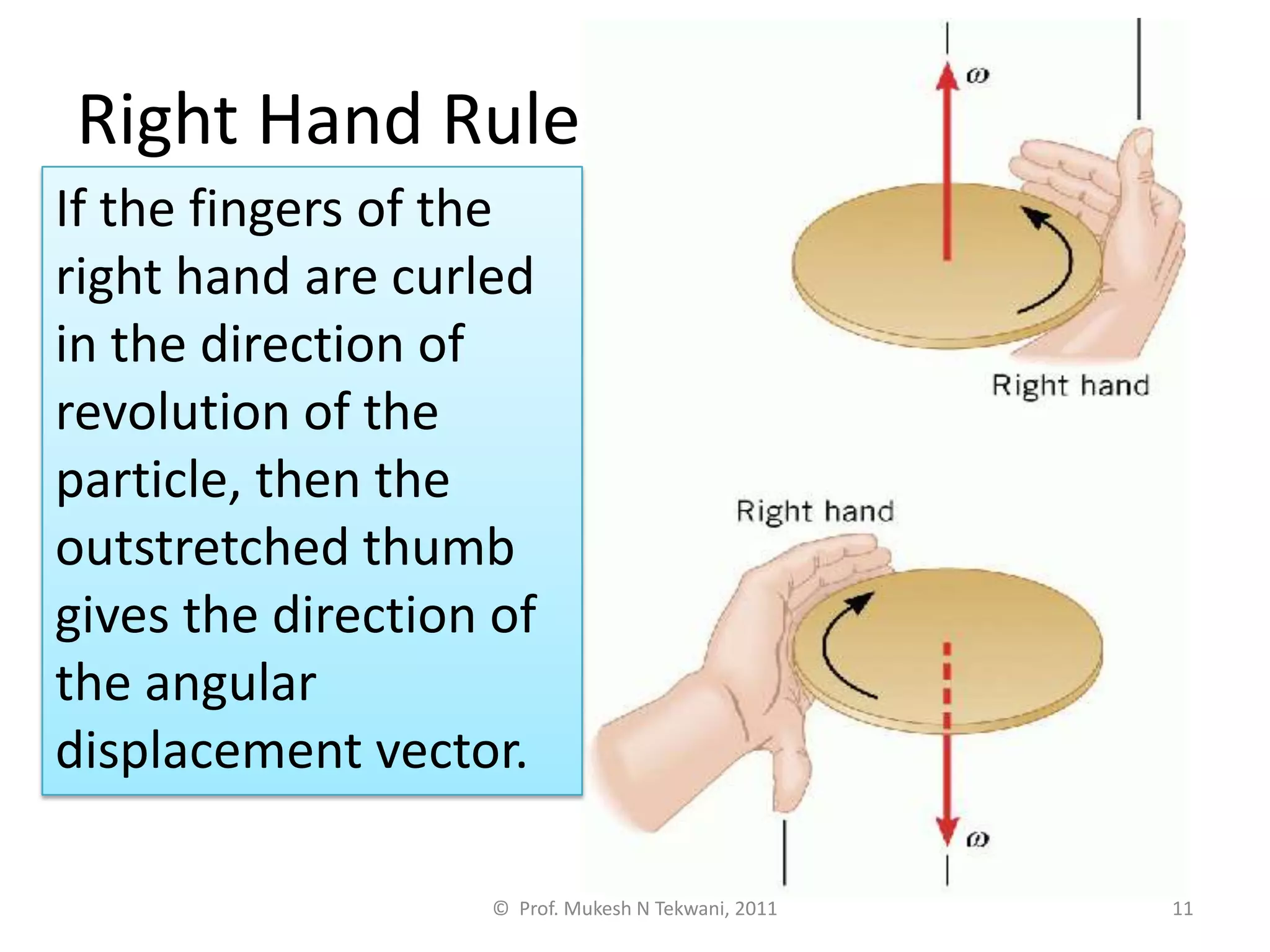
This document discusses circular motion. It defines circular motion as motion along a circular path or arc. Uniform circular motion refers to motion at a constant speed along the path. Angular displacement is defined as the angle described by the radius vector from the initial to final position of an object in circular motion. Angular displacement is measured in radians, with one radian equal to an arc length equal to the radius. Angular velocity refers to the rate of change of the angular displacement and indicates both the magnitude and direction of rotational motion. Centripetal forces are also discussed as providing the inward acceleration needed for circular motion.