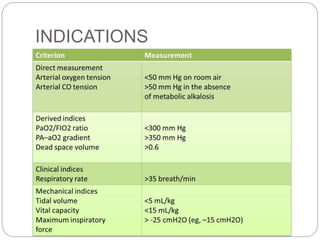
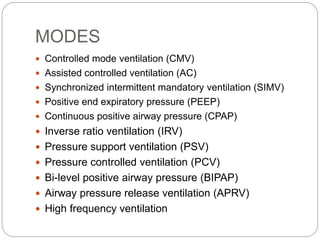
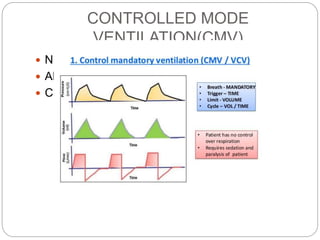
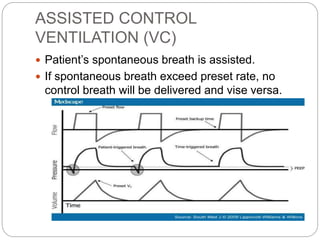
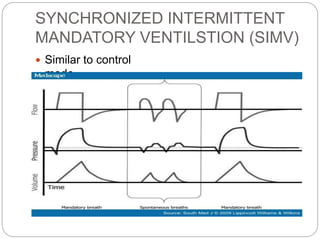
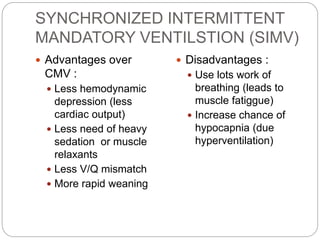
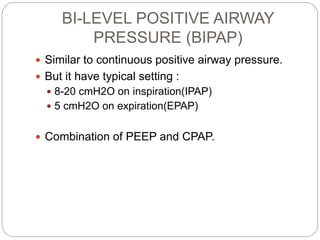
Mechanical ventilation provides positive pressure to move gas into the lungs. There are two main types: volume-controlled ventilation which preselects tidal volume and pressure-controlled ventilation which preselects pressure. Modes include controlled mandatory ventilation (CMV), assisted control ventilation (AC), and synchronized intermittent mandatory ventilation (SIMV). Positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) is used to prevent alveolar collapse. Weaning involves gradually reducing ventilator support by shifting modes and rates until the patient can breathe independently. Complications include barotrauma, infection, and weakness.