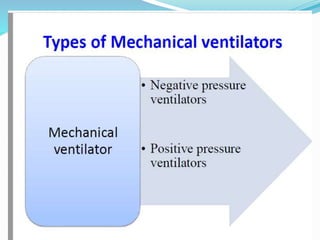
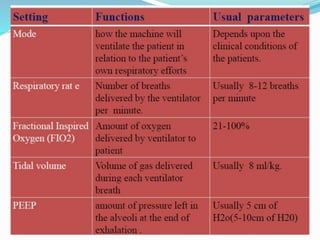
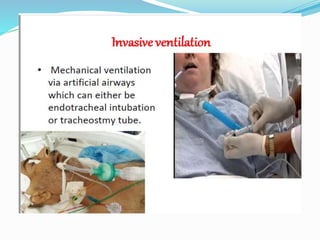
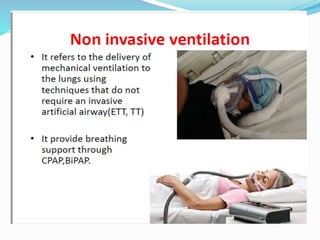
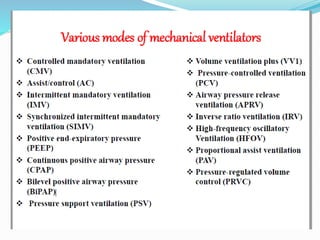
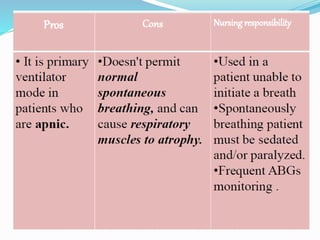
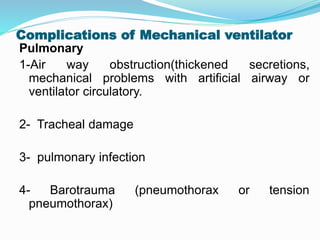
The document provides an overview of mechanical ventilation including its basic principles, types, indications, purposes, modes, settings, advantages, complications, weaning process, and nursing care of patients on ventilators. Mechanical ventilation delivers mechanically generated breaths to oxygenate the blood and remove carbon dioxide. It can be invasive or non-invasive. Modes include controlled mandatory ventilation, synchronized intermittent mandatory ventilation, pressure support ventilation, continuous positive airway pressure, and bi-level positive airway pressure. Nurses monitor patients closely, assess readiness for weaning, and provide comfort during the process.