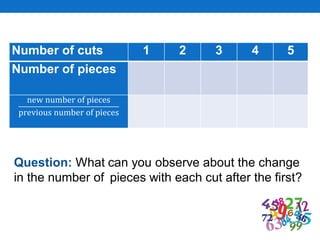
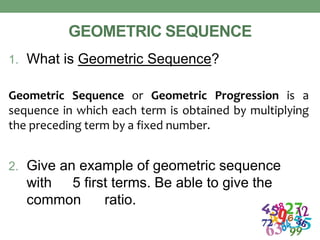
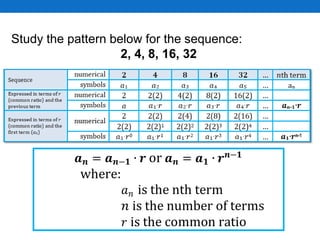
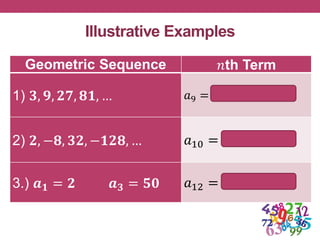
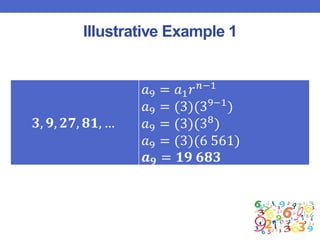
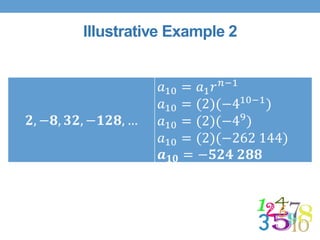
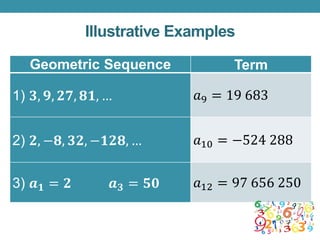
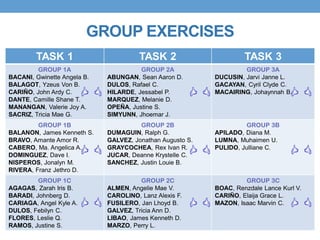
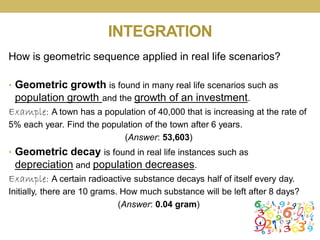
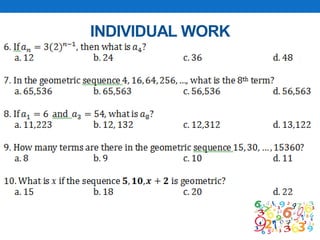
This document outlines a lesson plan focused on geometric sequences, detailing learning objectives and activities such as defining geometric sequences, determining their nth terms, and their real-life applications. It includes drills, exercises, group tasks, and real-world examples like population growth and depreciation. The lesson encourages interactive learning through paper cutting activities, problem-solving assignments, and group exercises.