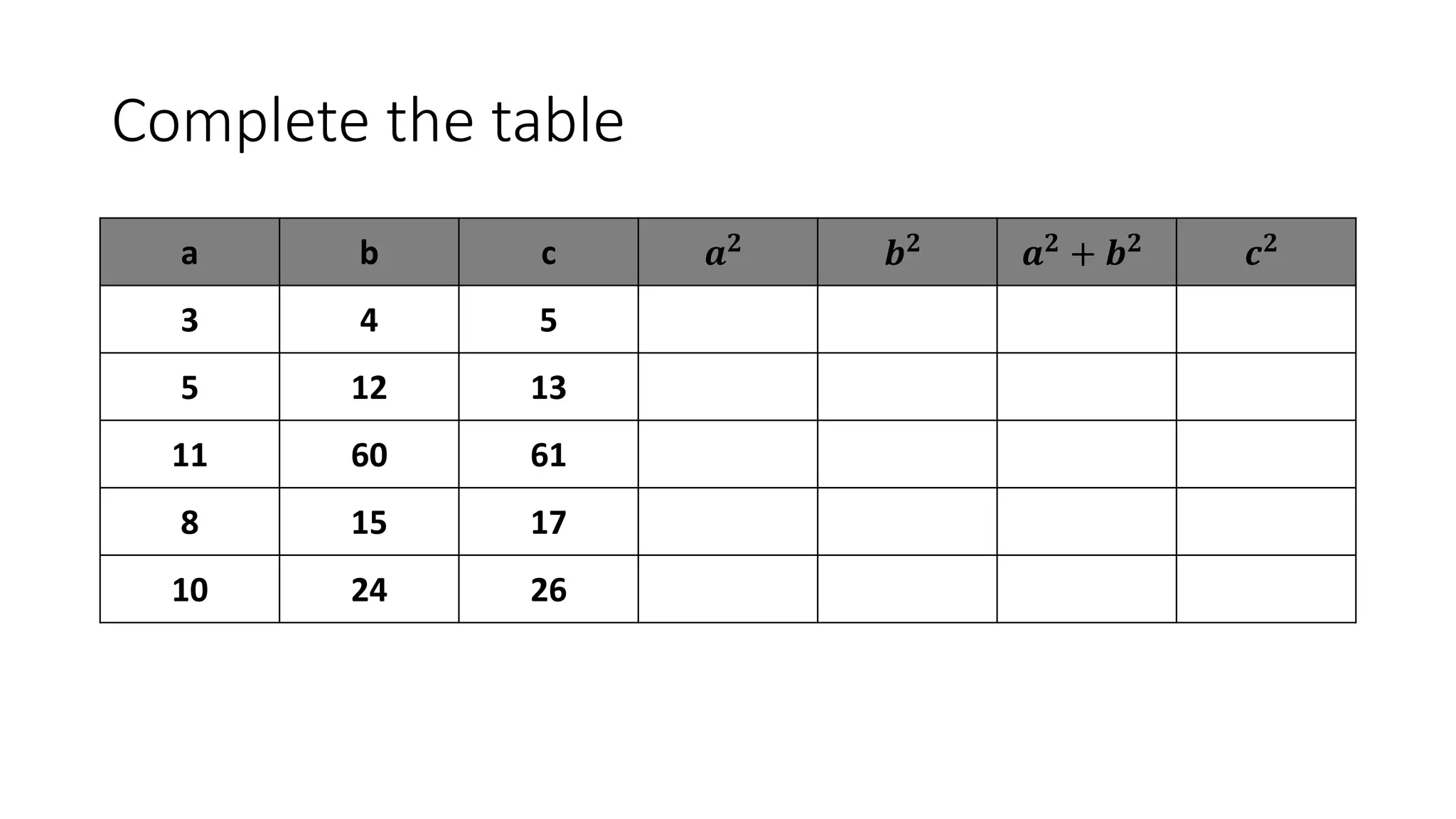
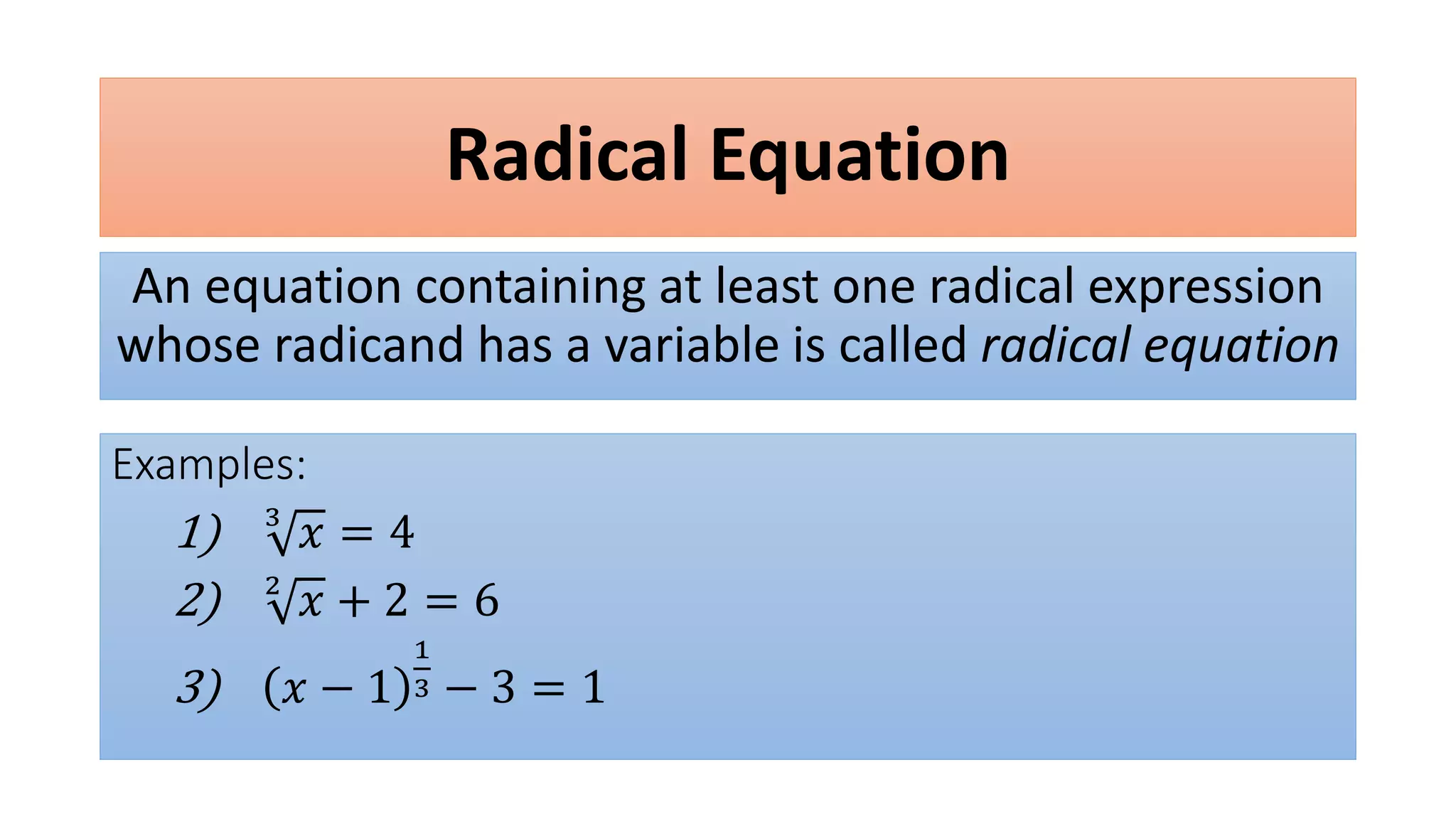
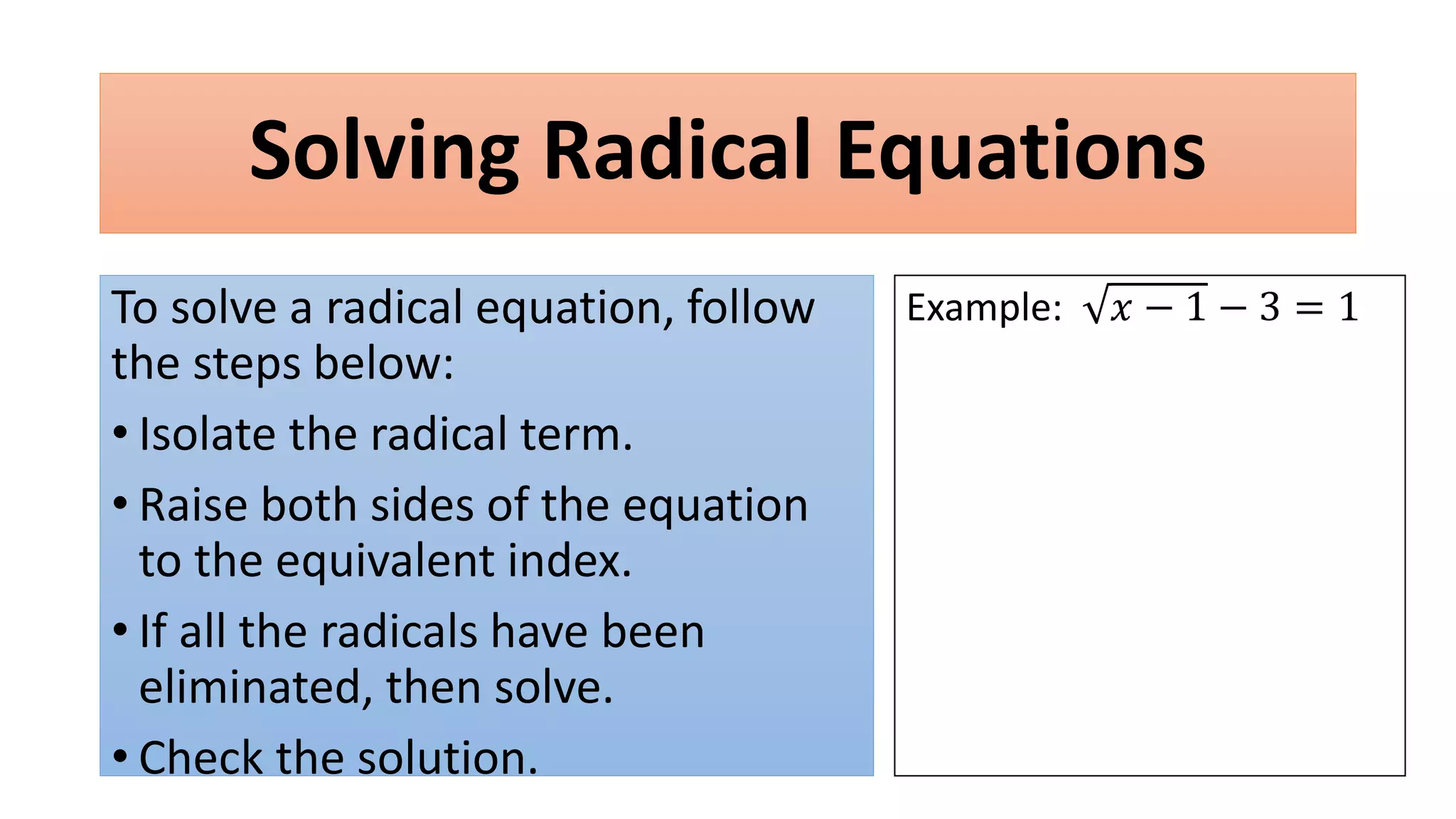
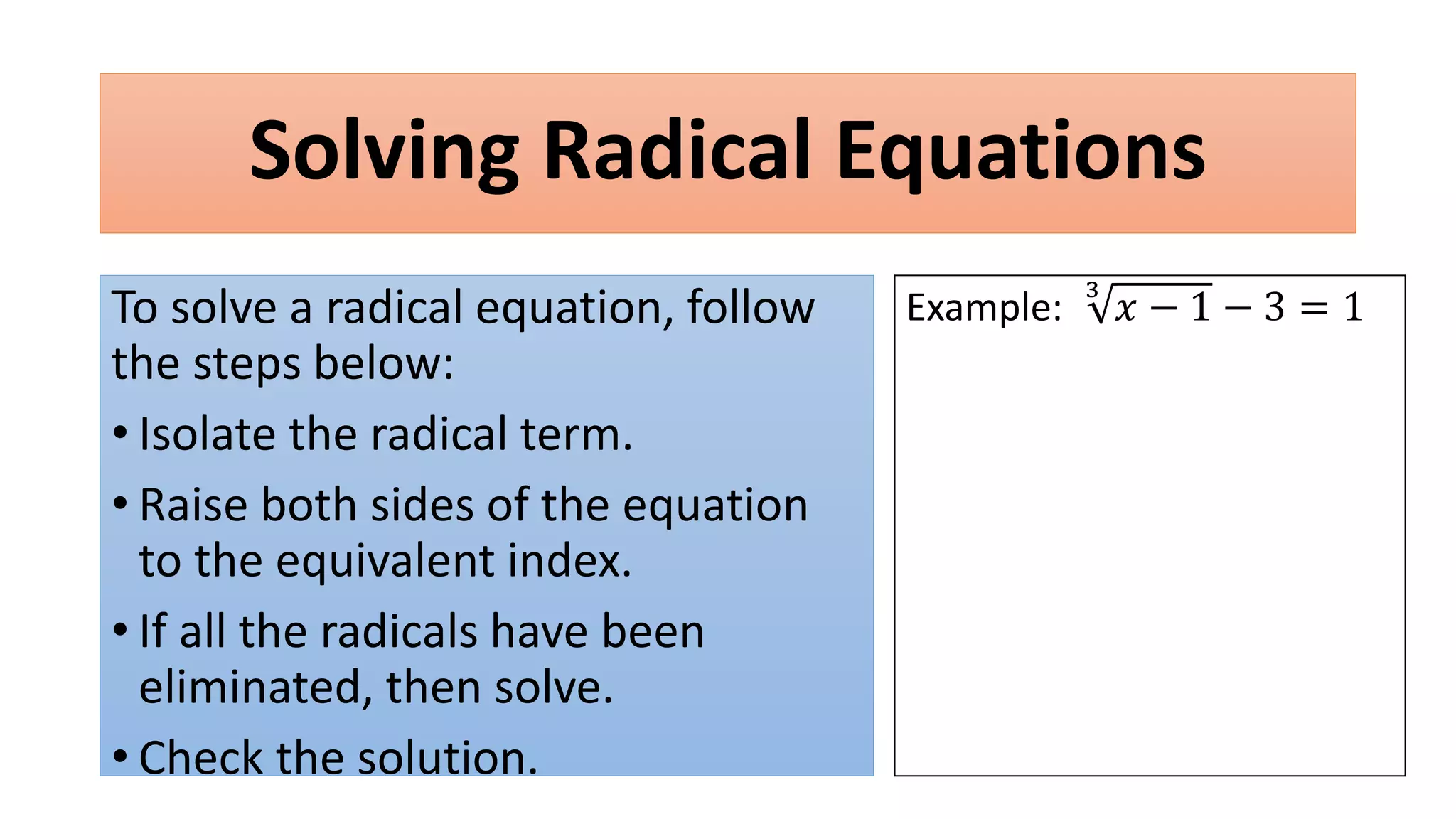
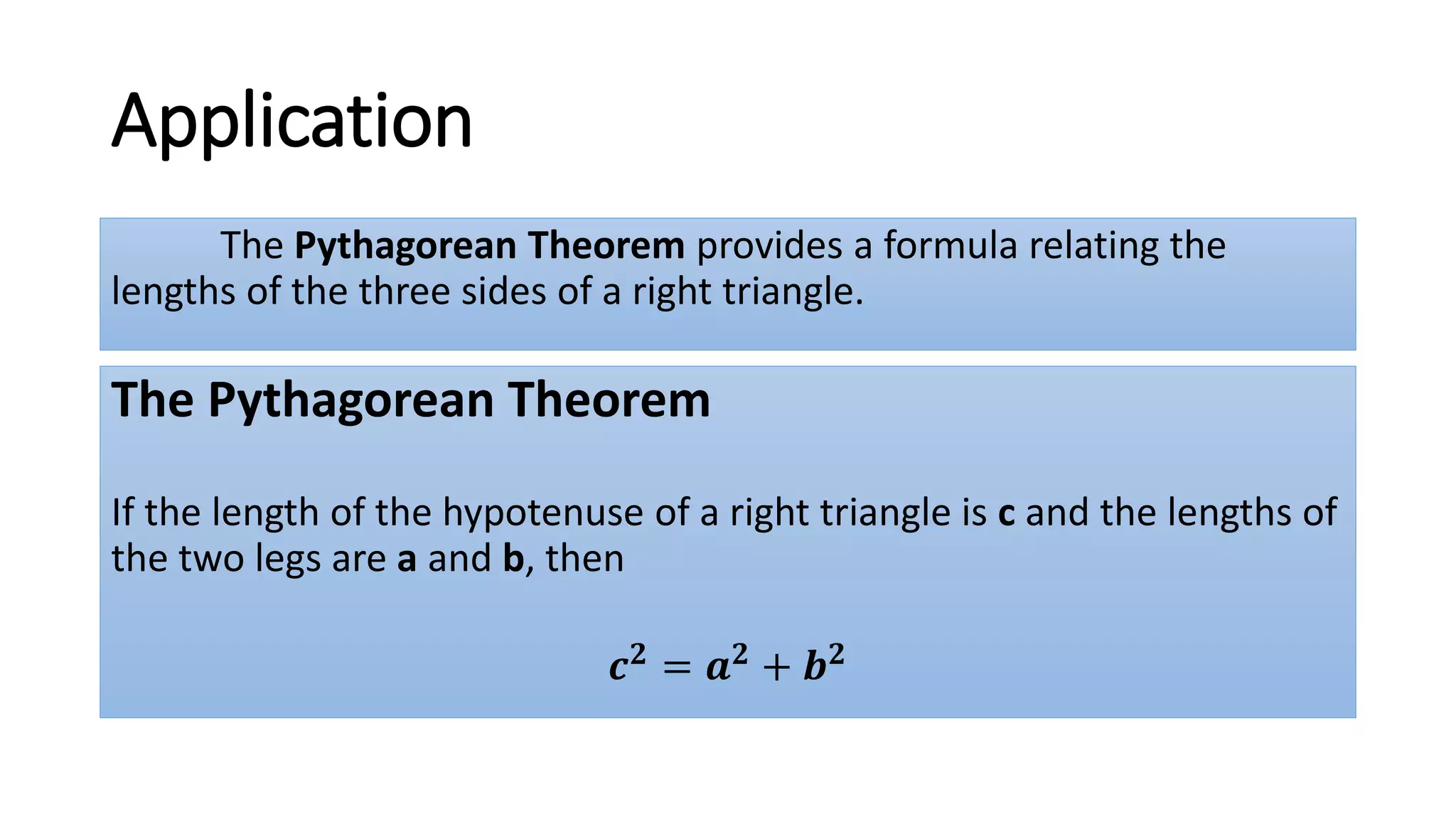
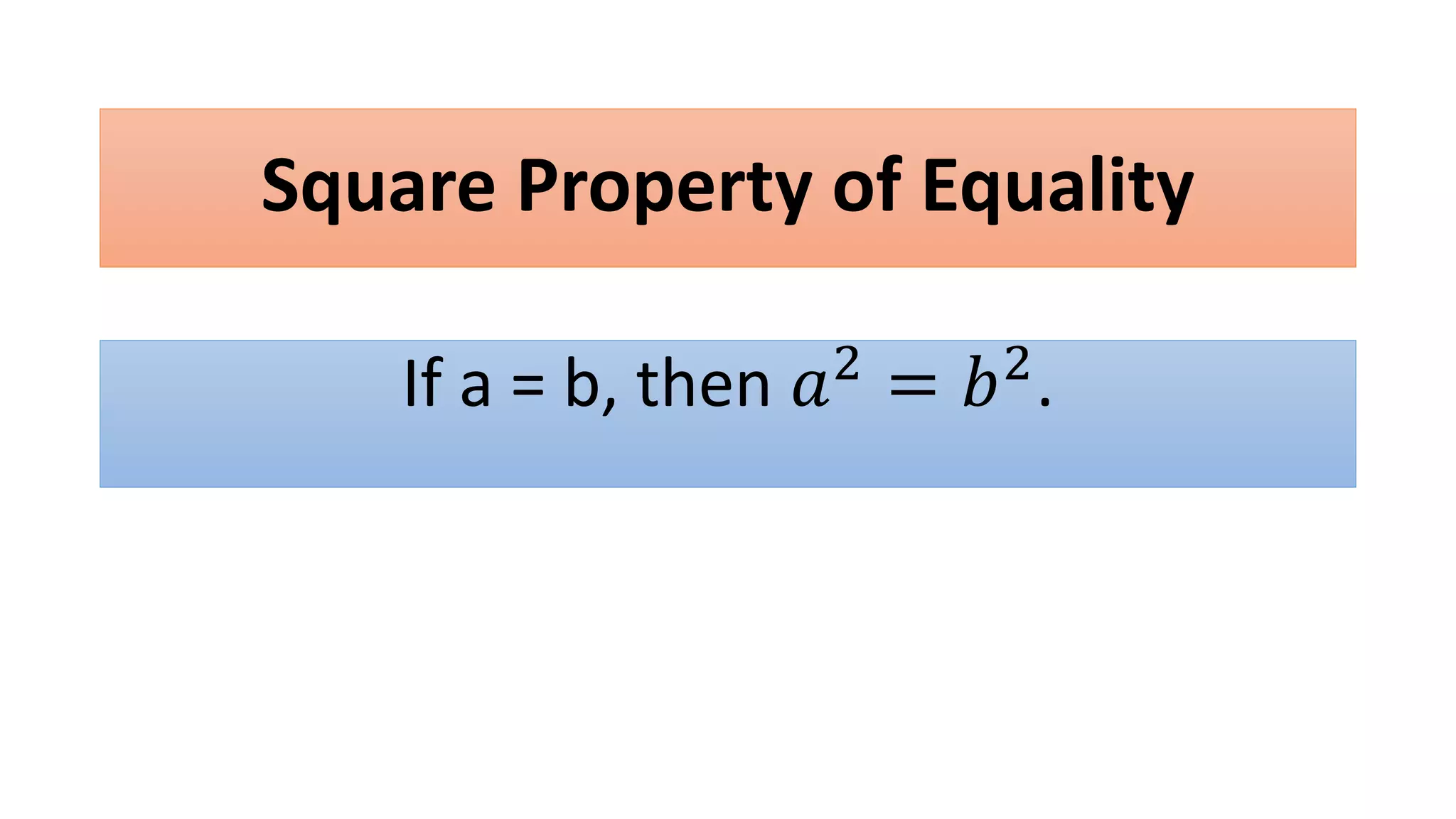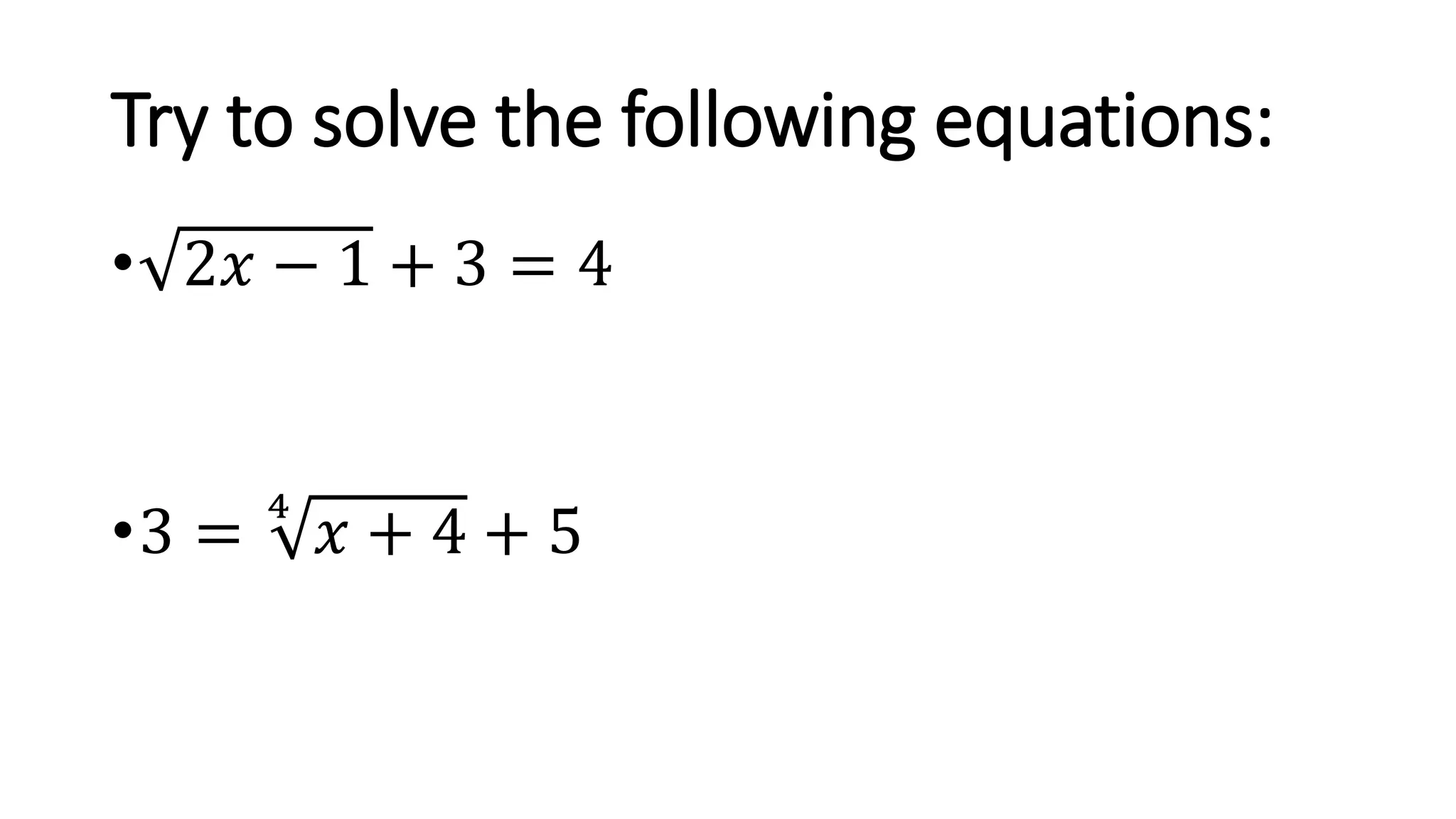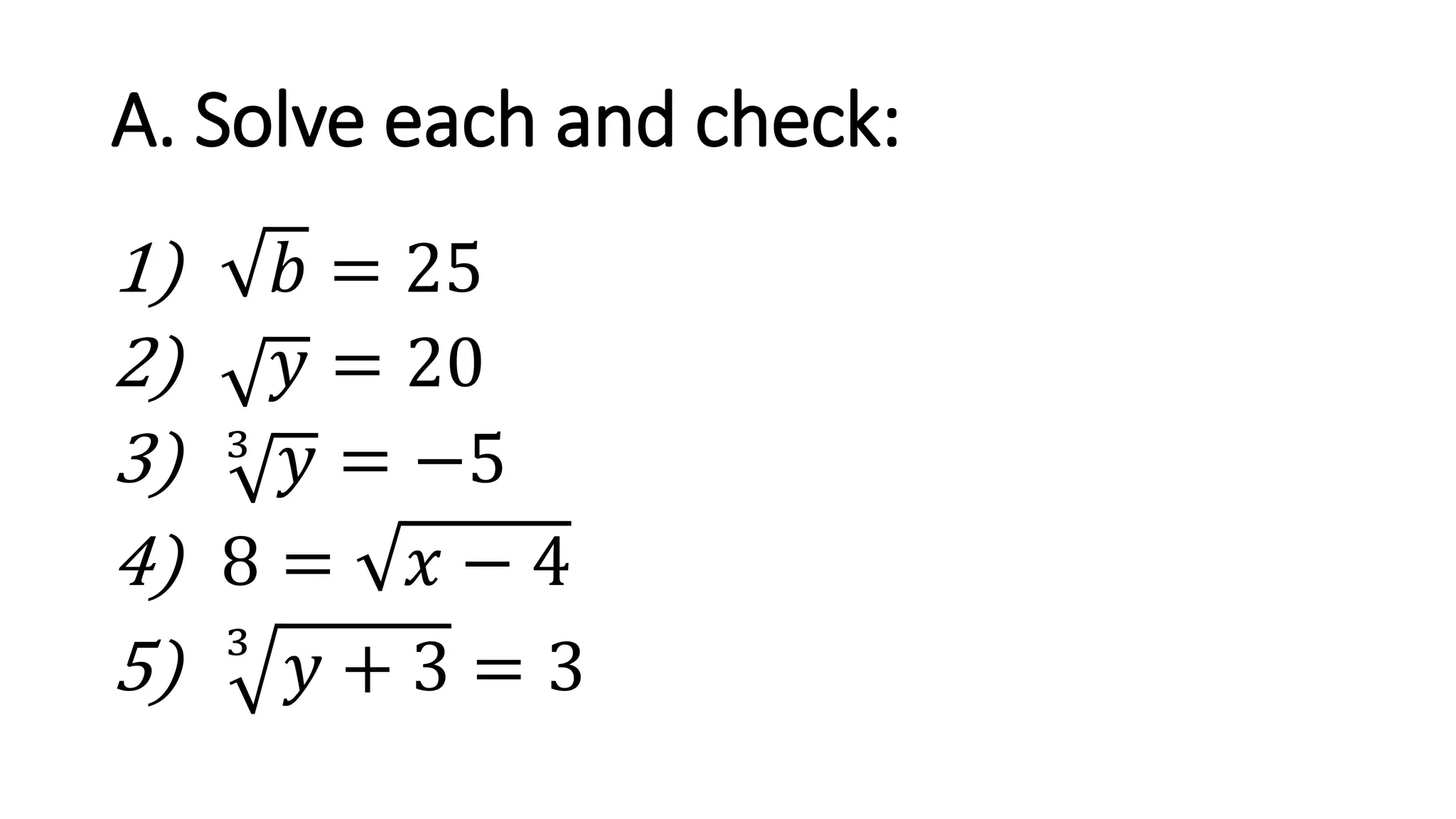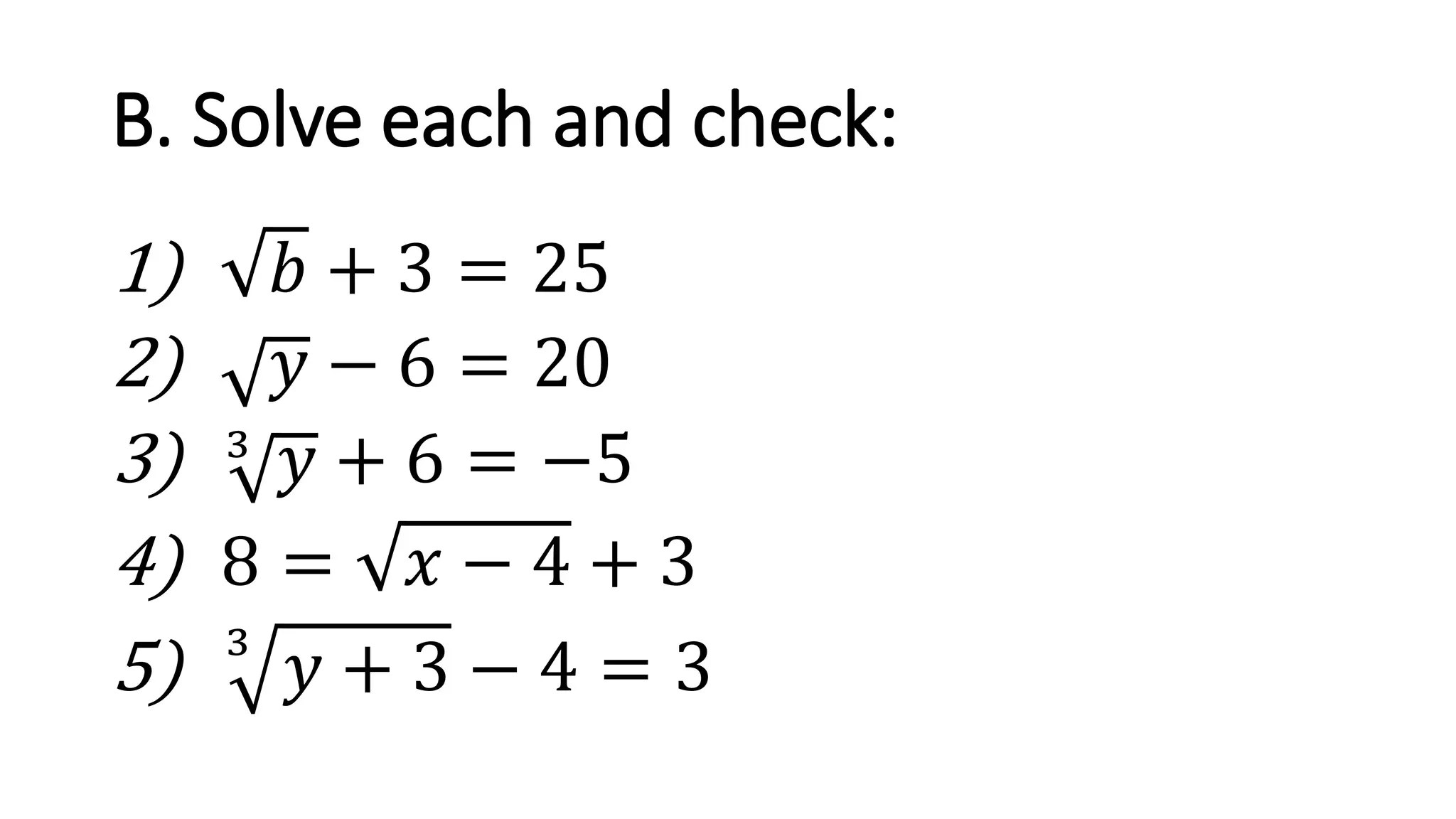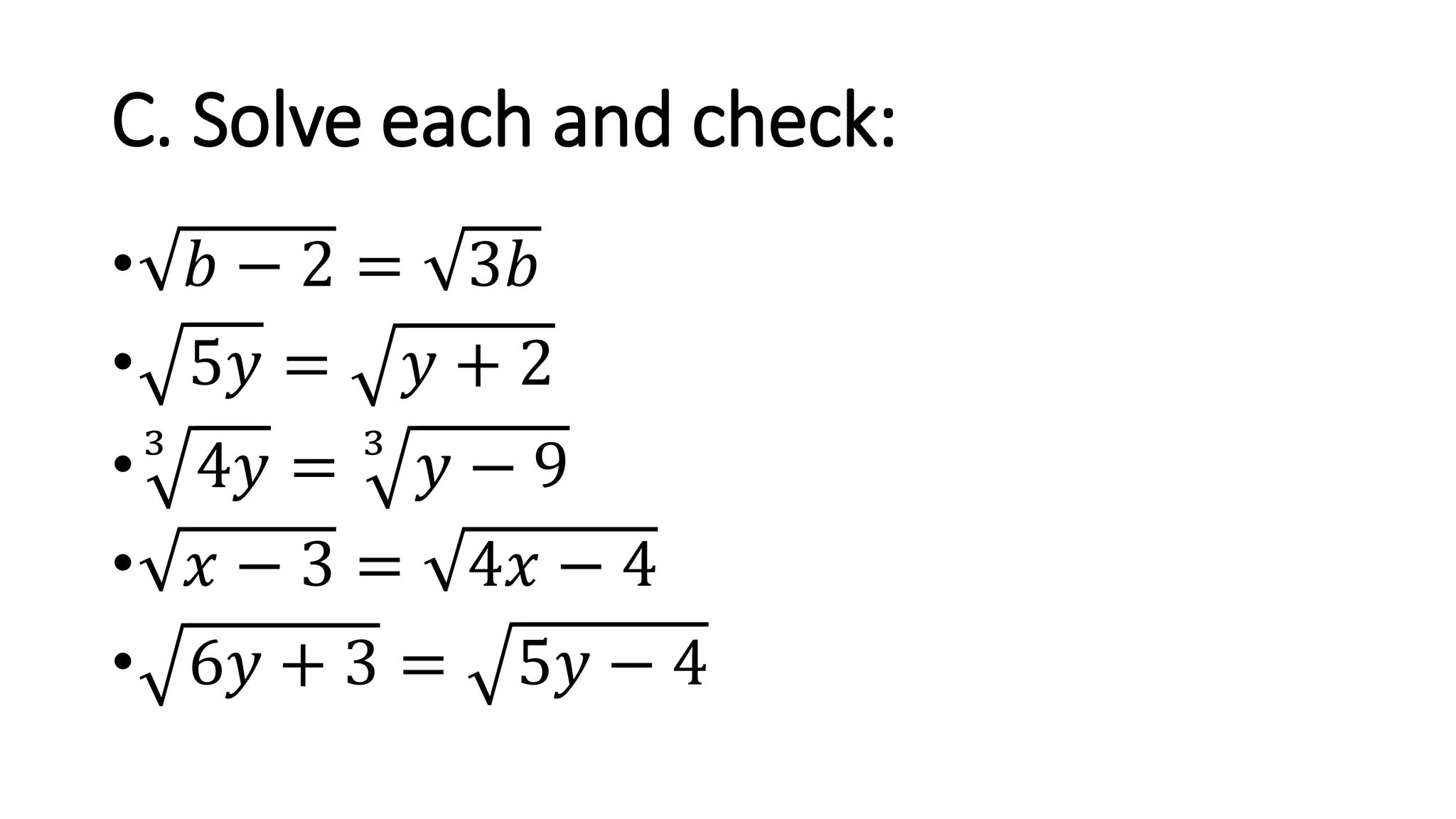The document discusses solving radical equations. It introduces radical equations and explains that to solve them, one isolates the radical term, raises both sides of the equation to the equivalent index to eliminate the radical, solves the resulting equation, and checks the solution. It provides examples of solving various radical equations and checking the solutions. It also discusses using the Pythagorean theorem and solving problems involving areas of squares and lengths of sides and diagonals.