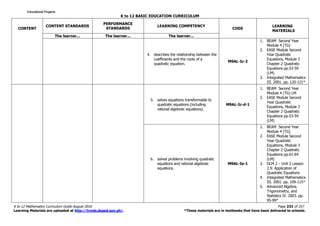
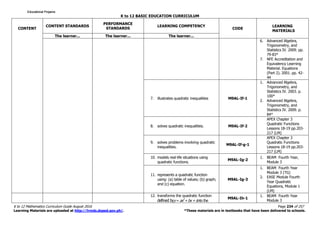
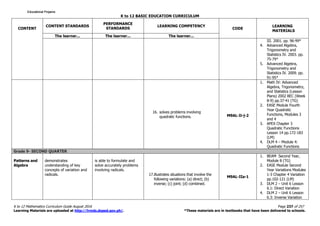
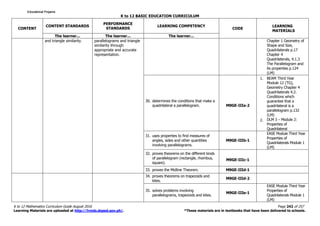
The K to 12 Mathematics Curriculum Guide for Grade 9 emphasizes critical thinking and problem-solving skills through comprehensive study of mathematical concepts. It includes content areas such as numbers, measurement, geometry, algebra, and statistics, and incorporates various learning theories to enhance student engagement and understanding. The curriculum is structured to provide a foundation necessary for students' future academic and real-life applications of mathematics.