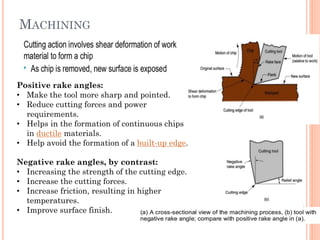
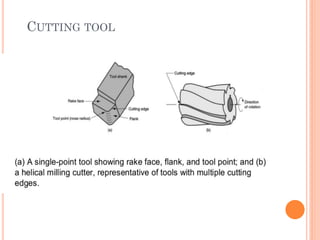
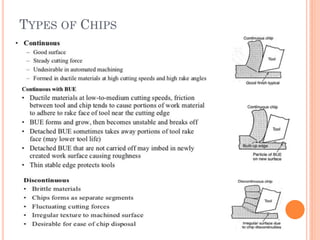
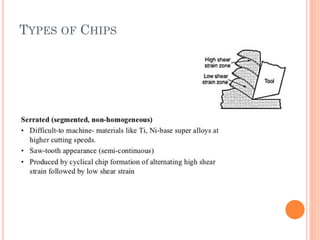
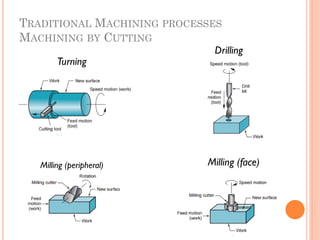
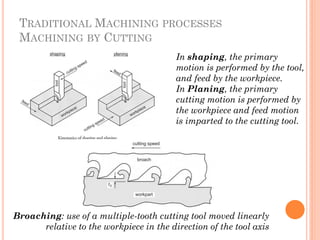
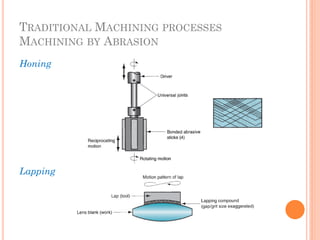
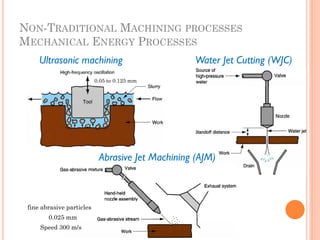
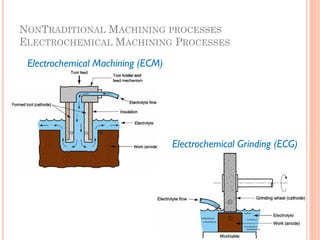
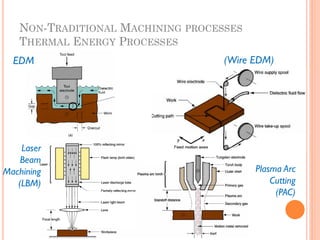
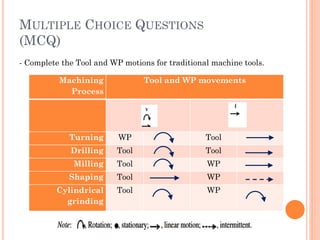
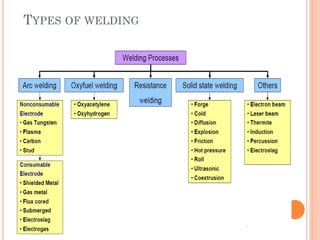
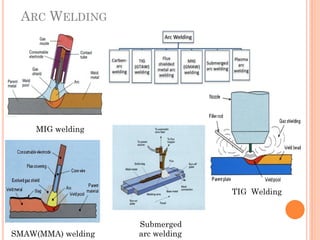
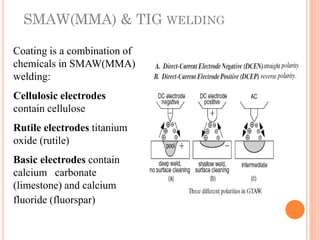
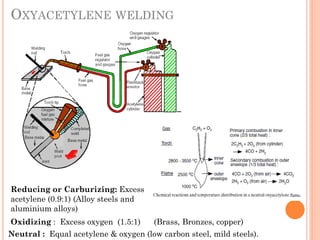
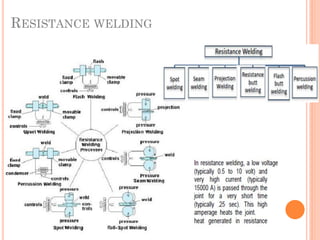
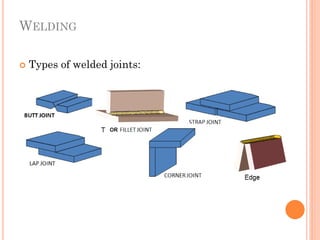
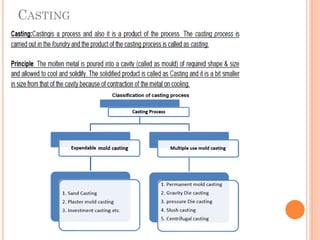
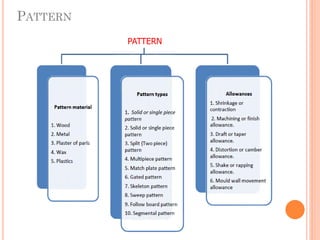
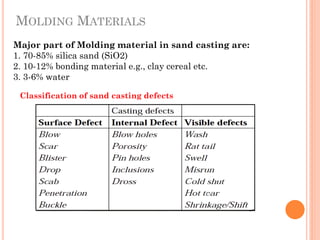
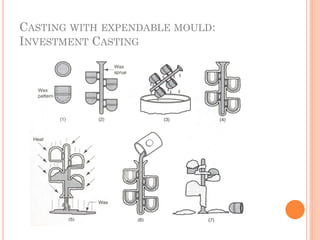
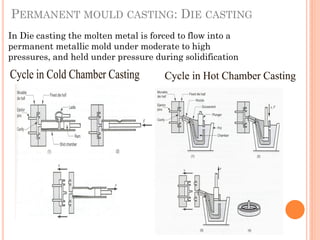
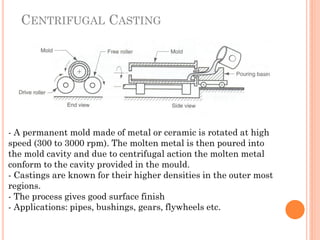
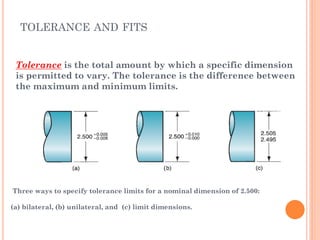
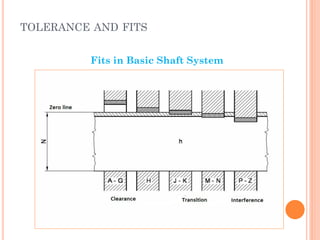
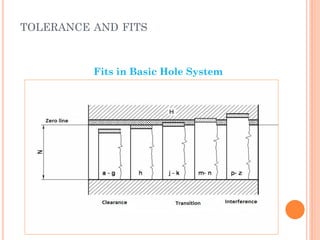
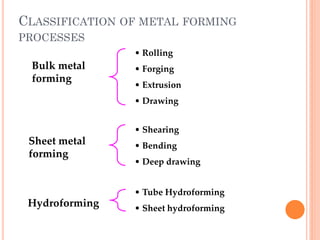
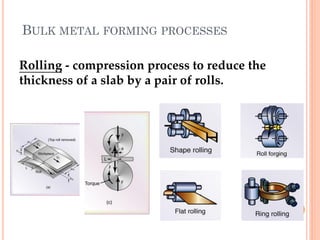
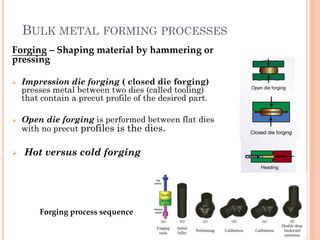
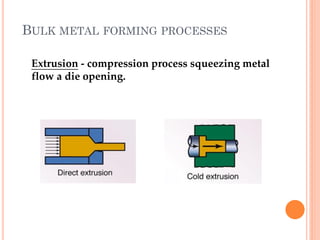
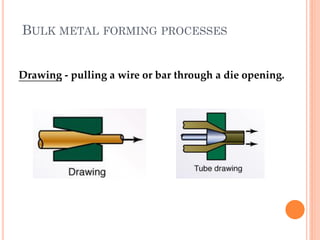
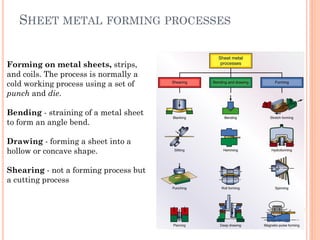
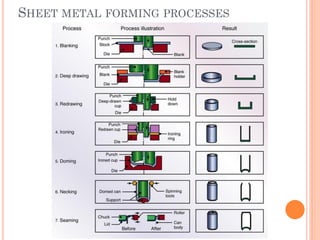
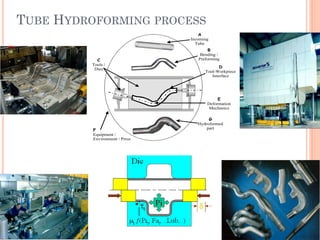
This document discusses various manufacturing processes and techniques. It begins by outlining metal cutting theory and traditional machining processes like turning, drilling, and milling. It then covers non-traditional processes such as ultrasonic machining and electrochemical machining. Further sections discuss welding and casting techniques, tolerances and fits, and metal forming processes like rolling, forging, drawing, and hydroforming. The document provides examples, equations, and multiple choice questions related to these manufacturing topics.