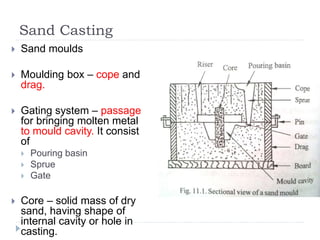
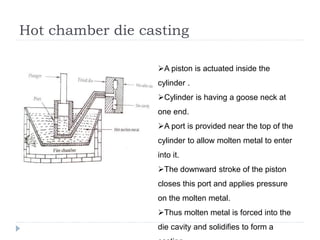
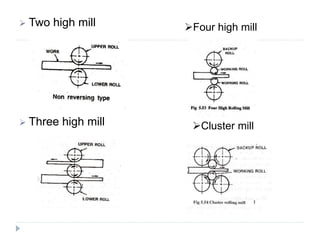
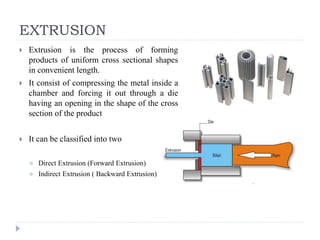
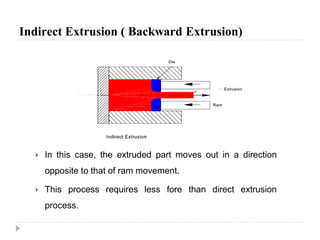
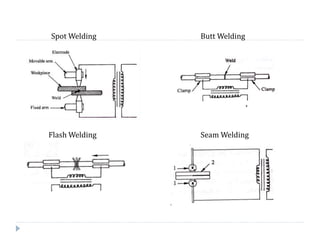
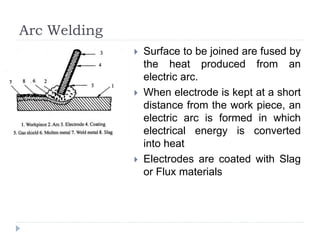
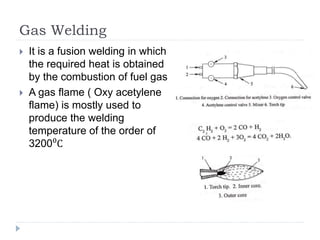
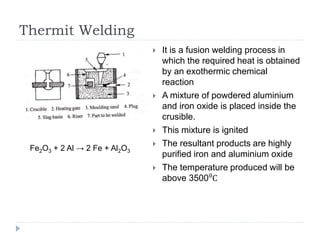
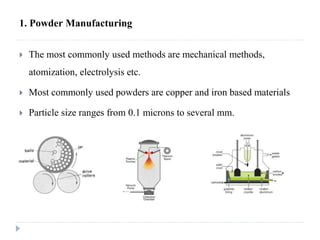
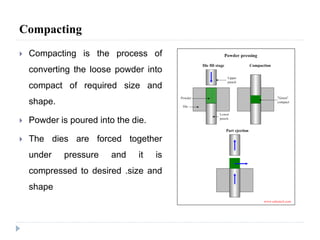
This document describes various manufacturing processes used to produce finished products from raw materials. It discusses 5 main categories of processes: 1) shaping processes like casting and forging that change the shape and size of materials, 2) machining processes like turning and milling that remove material, 3) joining processes like welding and soldering that join parts, 4) finishing processes that improve surface quality, and 5) property changing processes that modify material properties. Specific shaping processes covered include casting, forging, rolling, and extrusion. Joining processes discussed are welding, brazing, and soldering.