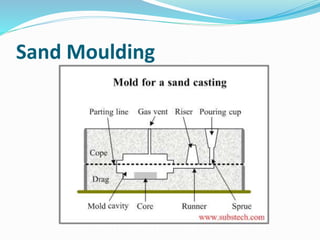
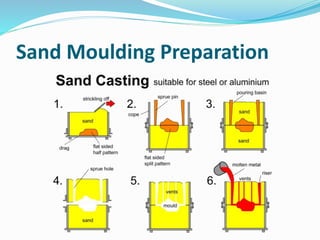
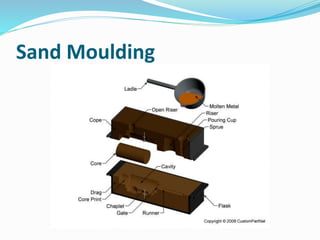
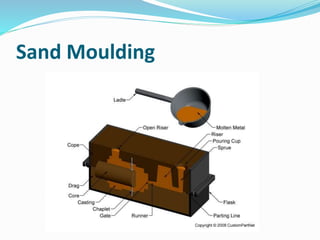
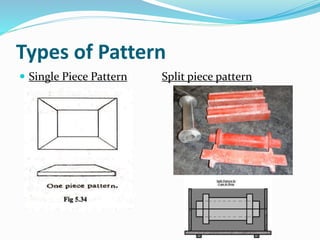
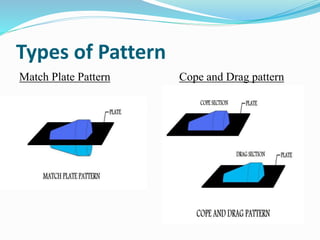
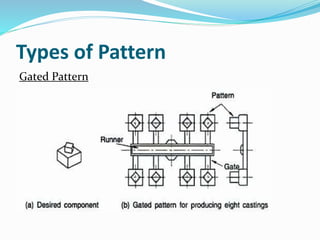
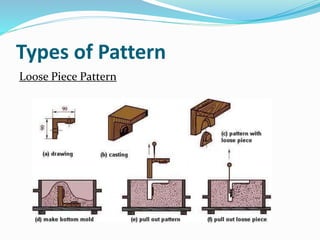
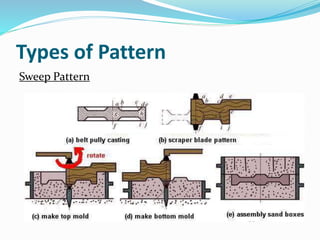
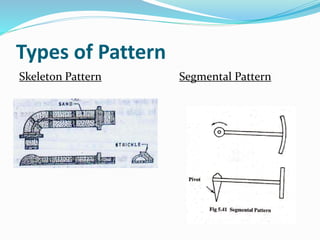
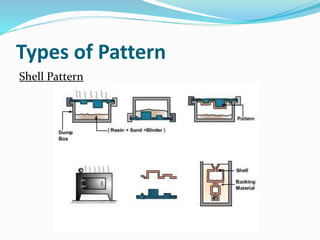
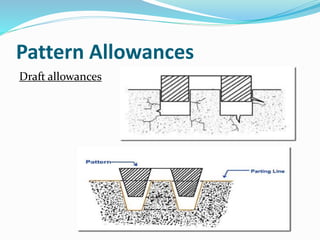
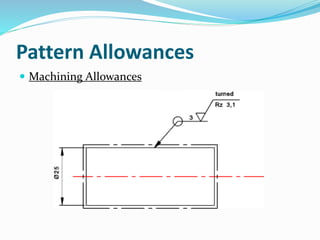
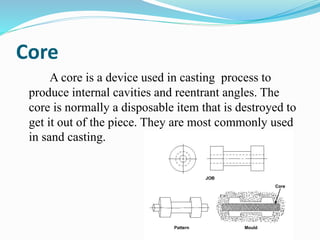
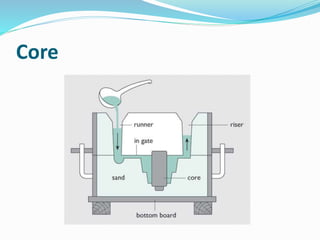
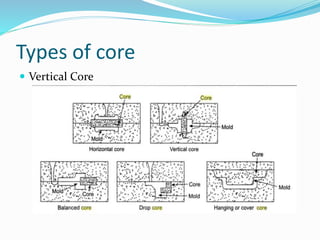
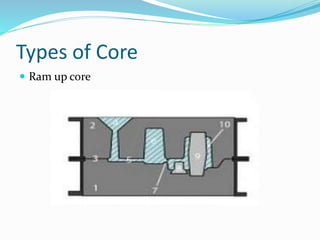
This document discusses various metal casting processes and techniques. It covers topics like sand casting, pattern making, molding sand properties, core making, and casting defects. Sand casting involves pouring molten metal into an expandable sand mold and allowing it to solidify. Different types of sand and patterns are used depending on the application. Properties of molding sand like permeability and strength are important. Cores are used to create internal cavities and angles in castings.