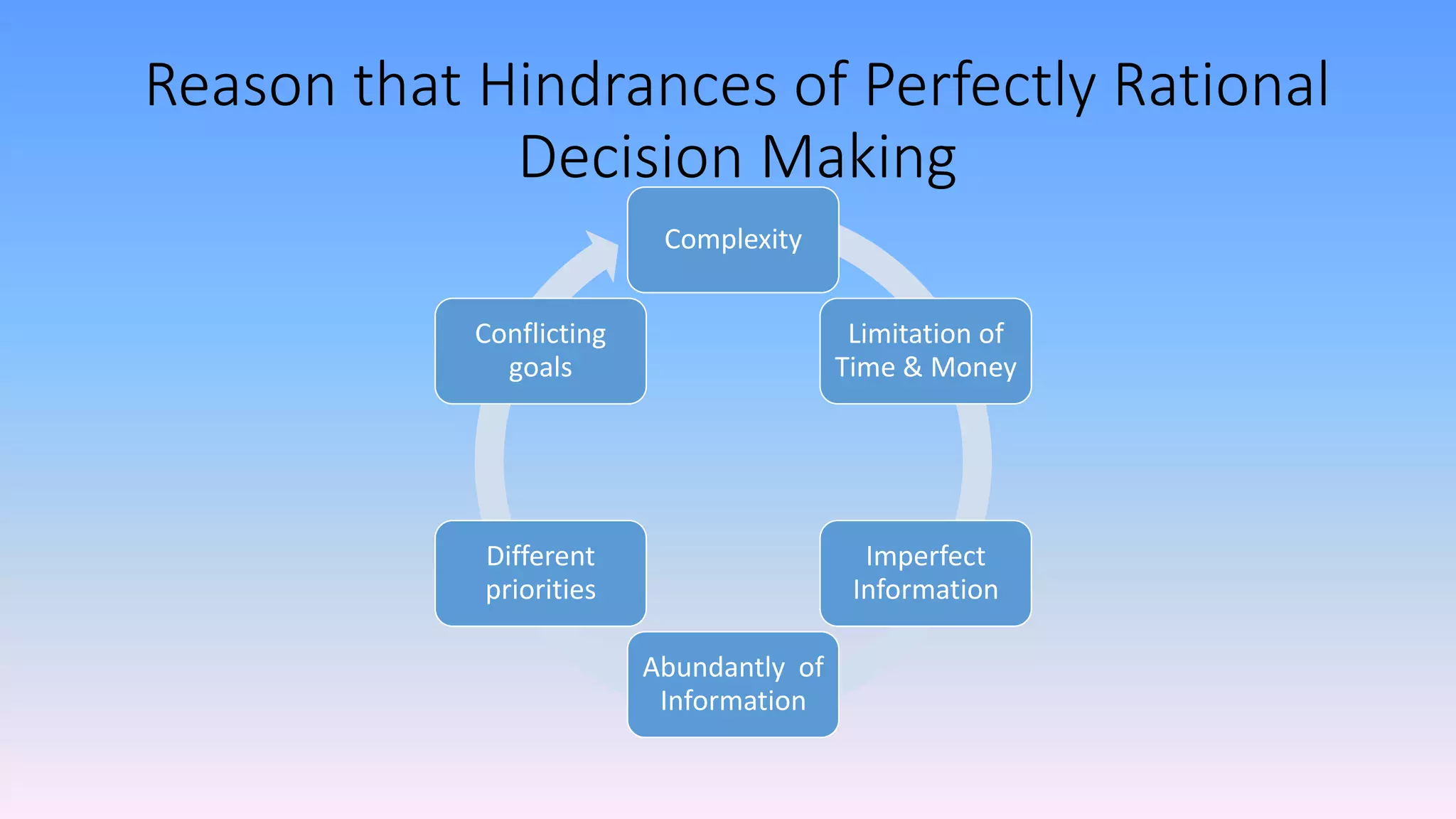
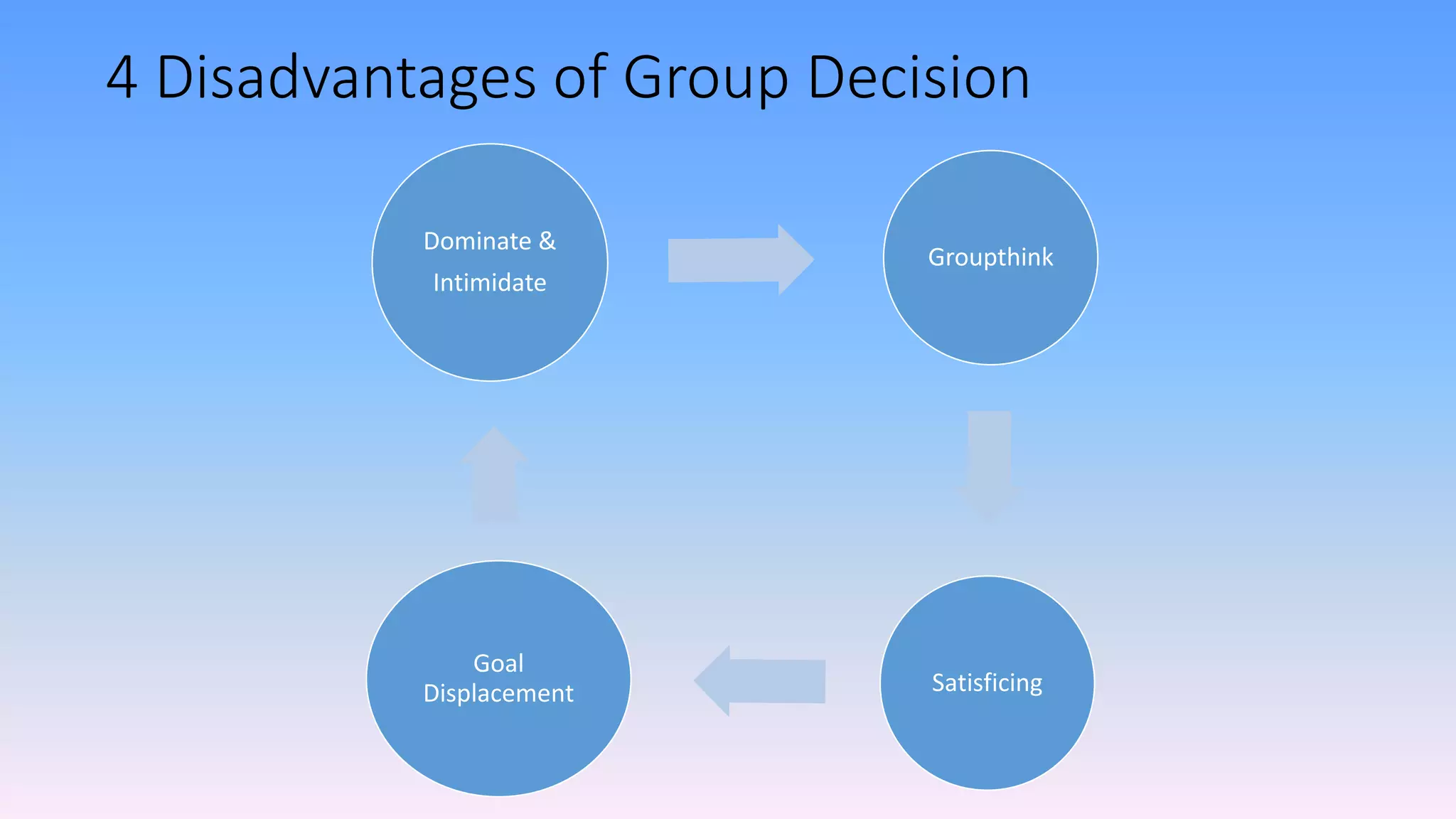
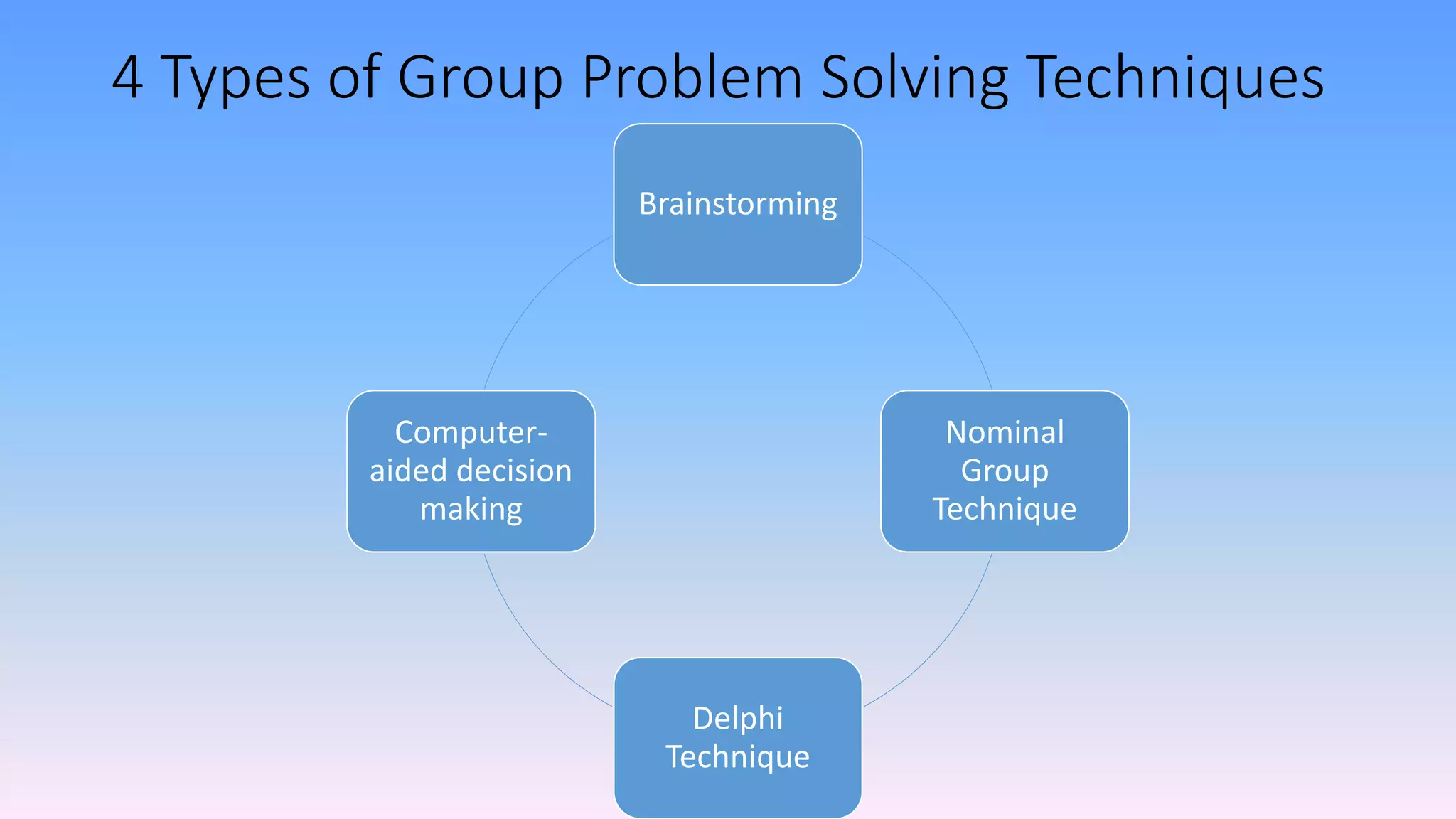
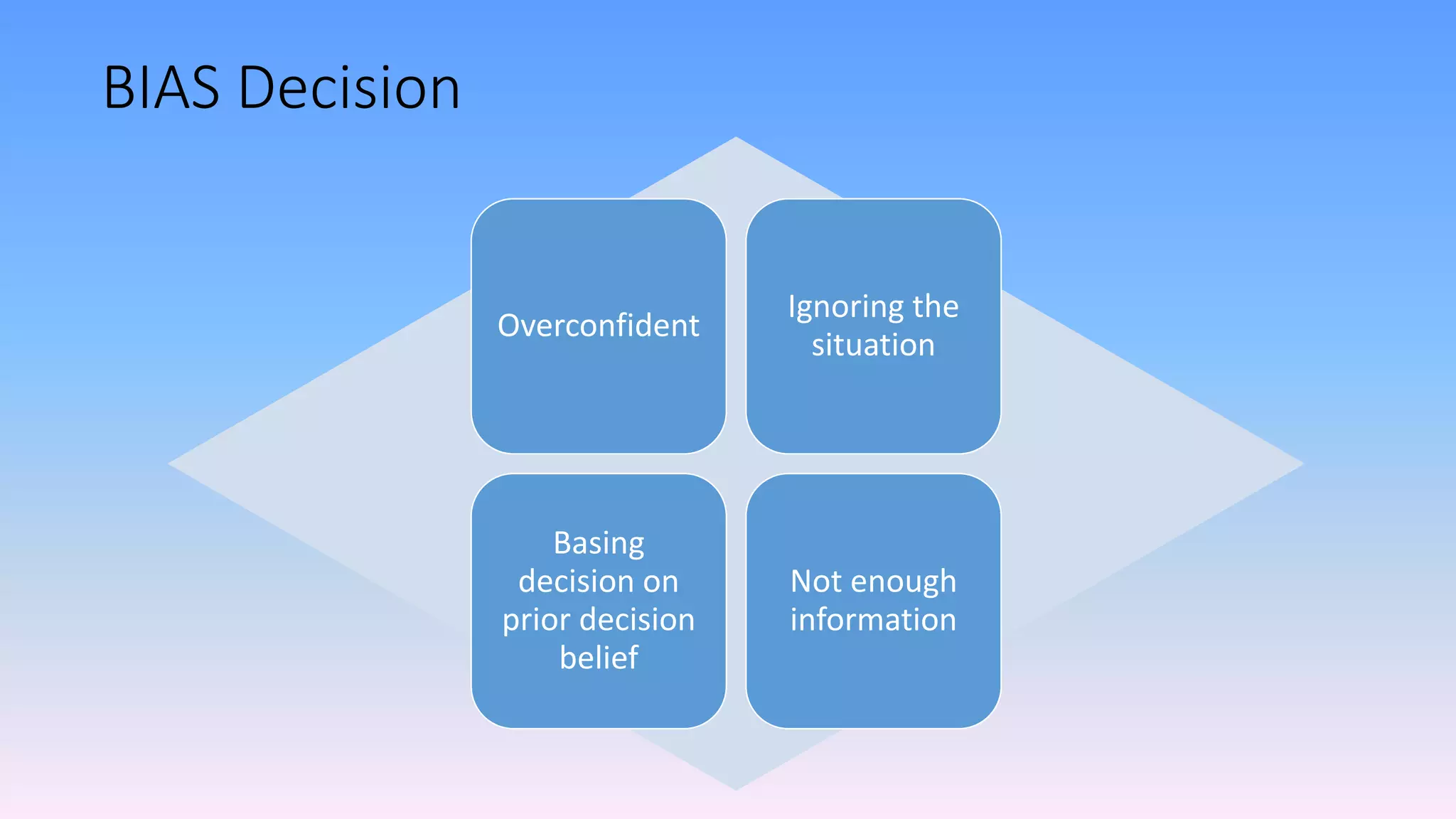
The document discusses individual and group decision-making processes, highlighting the definition of decision making, types of decisions, and various decision-making styles. It outlines the rational decision-making process in four steps, emphasizing the importance of ethical evaluation, implementation, and potential challenges. Additionally, it examines the advantages and disadvantages of group decision making, including techniques for problem-solving.