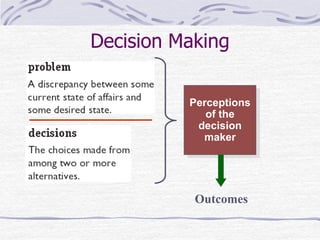
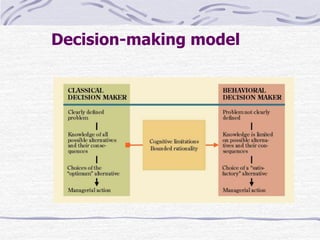
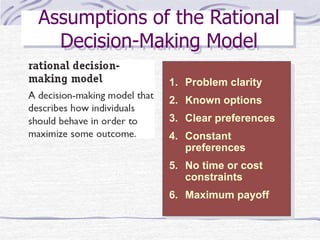
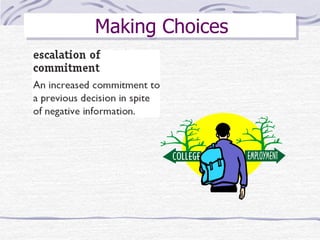
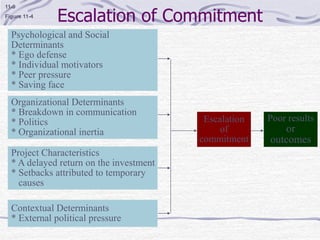
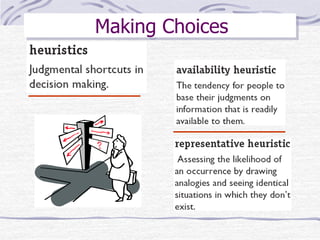
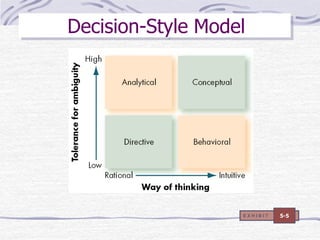
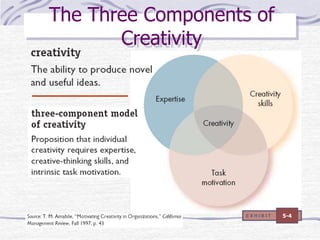
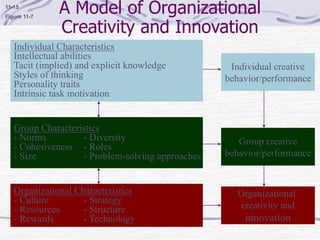
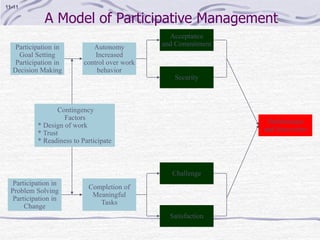
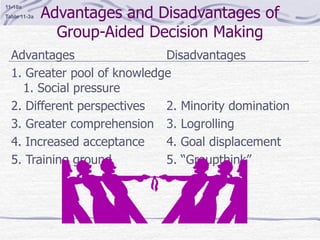
The document discusses decision making processes. It describes steps in systematic decision making as recognizing and defining a problem, identifying alternative actions, choosing a preferred action, and evaluating results. Decision making can occur under conditions of certainty, risk, or uncertainty. Rational and behavioral models of decision making are presented. Group decision making techniques like nominal group technique and Delphi technique are discussed. Organizational constraints on decision makers and reasons for decision making failure are also summarized.