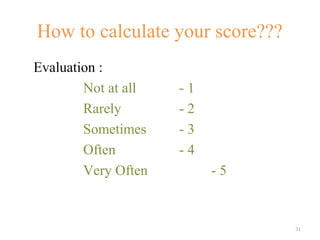
The document discusses various aspects of management decision-making including what management is, the importance of decision-making in management, characteristics of decision-making, approaches to decision-making including normative and descriptive analyses, models of decision-making including classical, administrative and political models, techniques for improving decision-making, and guidelines for making decisions more effective. It also provides a practical test on decision-making skills.