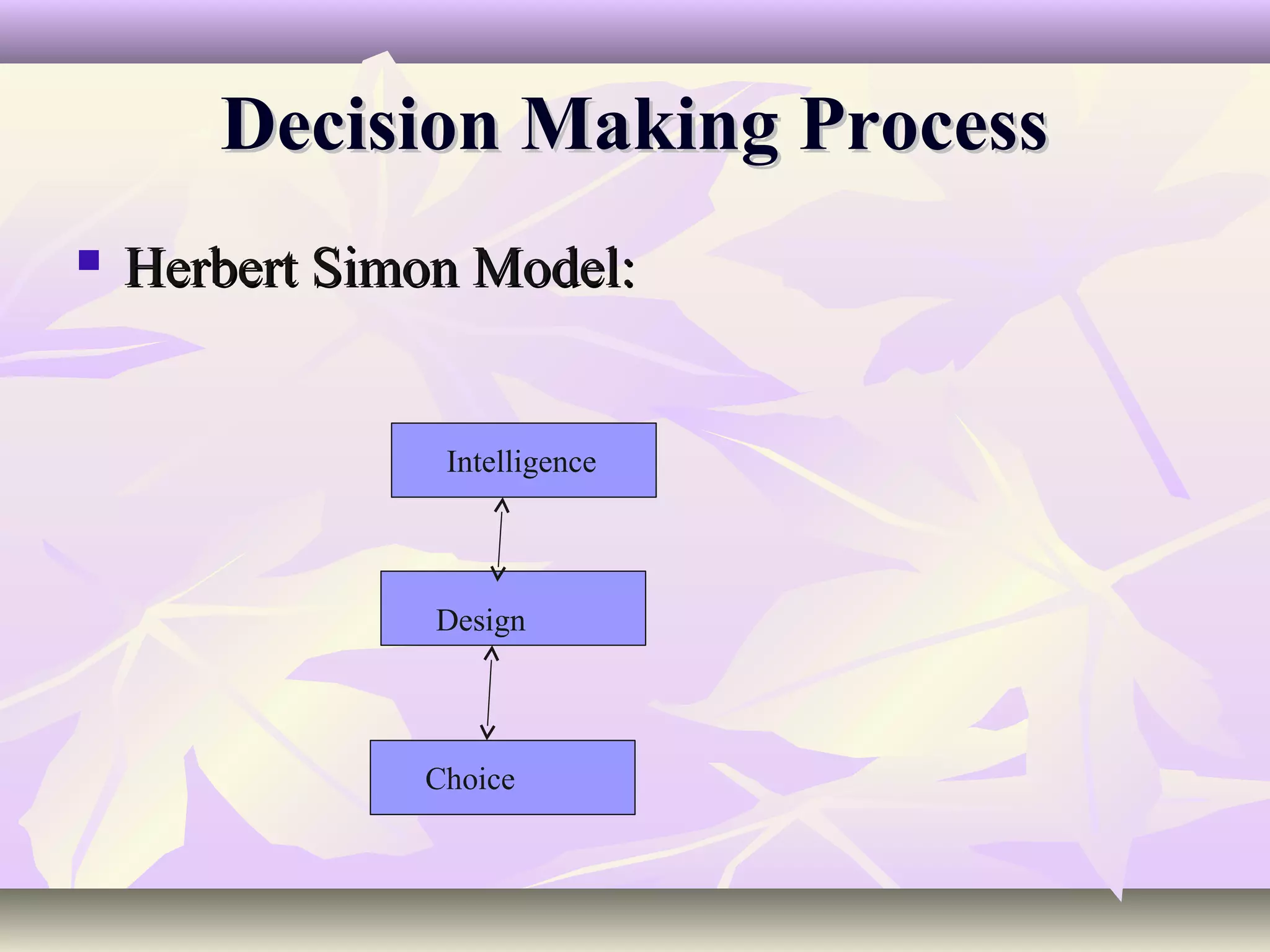
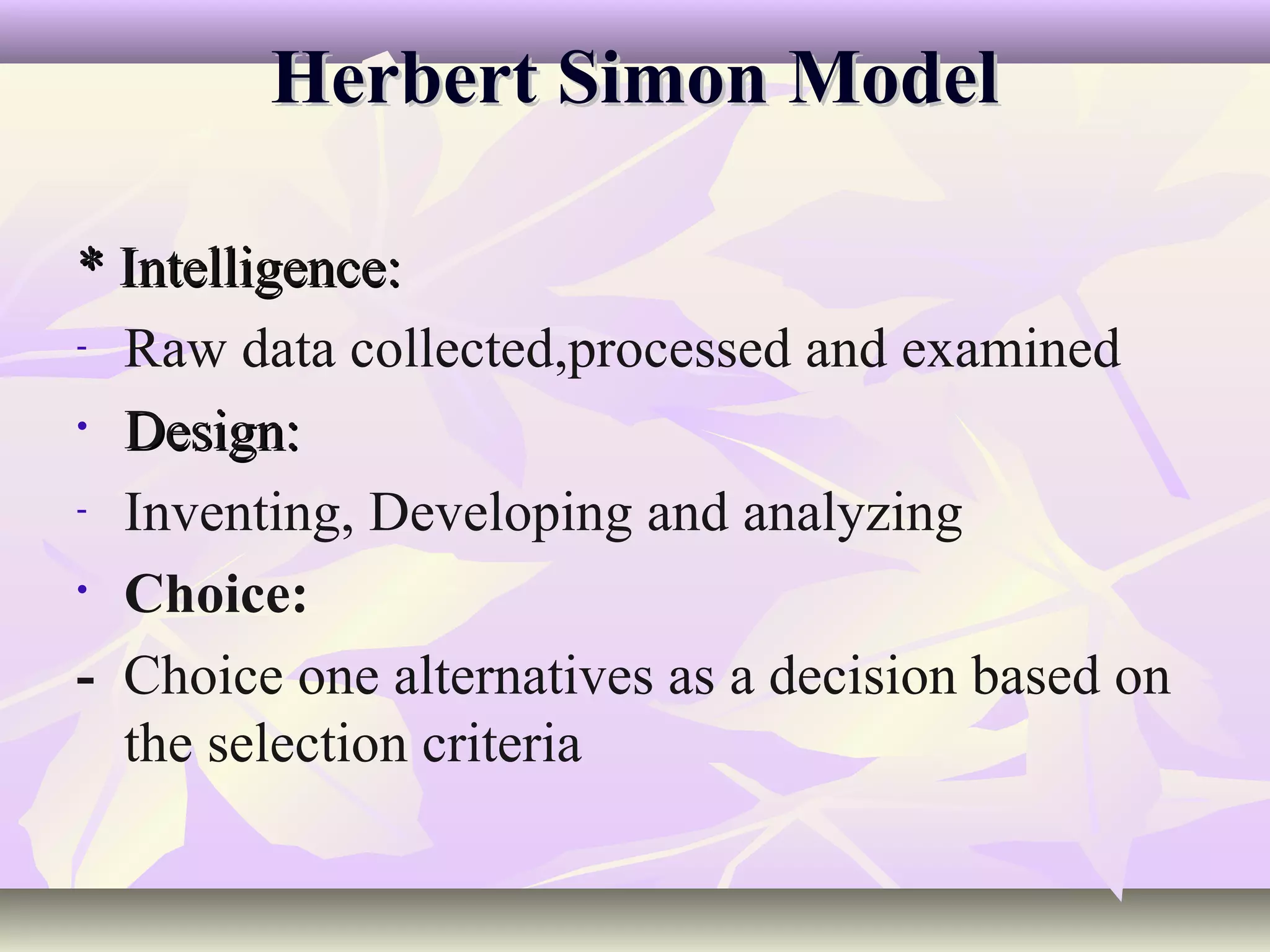
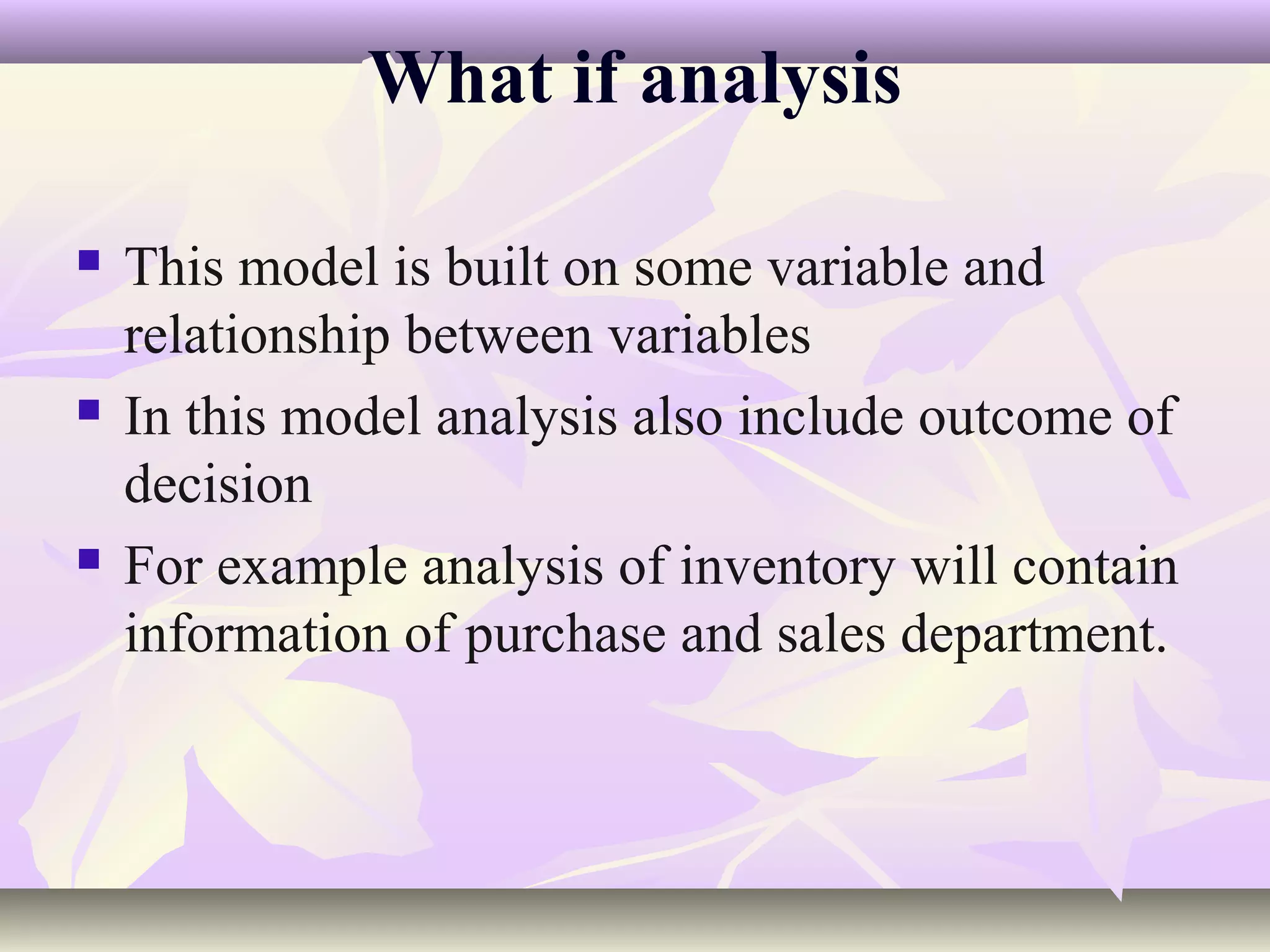
This document discusses concepts related to business decision making. It defines business decisions and their characteristics. Rational decision making and Herbert Simon's model of intelligence, design and choice are explained. The document also covers types of decisions, decision alternatives, decision analysis techniques, behavioral concepts, and how organizations can deal with uncertainty and learn from past decisions. MIS can support decision making by providing flexible decision support systems and incorporating organizational and cultural factors.