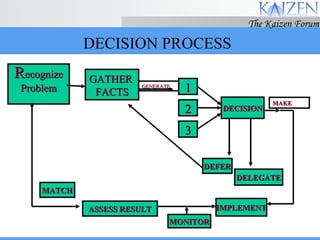
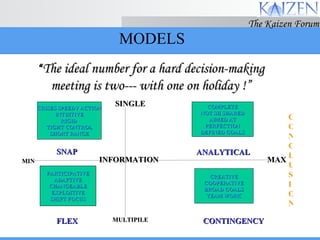
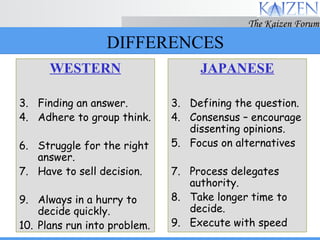
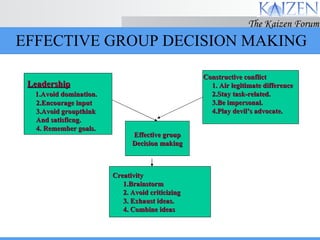
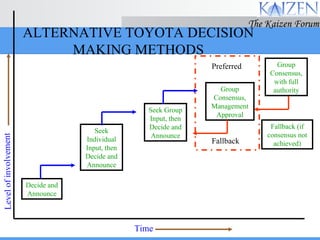
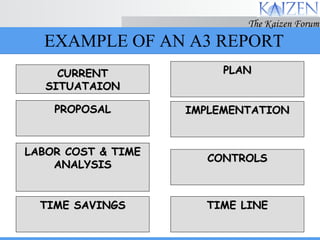
The document discusses various concepts and models related to decision making. It covers rational and intuitive decision making styles, individual versus group decision making, and reasons why decisions may fail. It also provides guidelines for effective decision making, such as gathering facts, considering alternatives, flexibility, and follow through. Decision making involves judgment calls between alternatives that are rarely clear-cut and require balancing incomplete information.