The document discusses various aspects of decision making including:
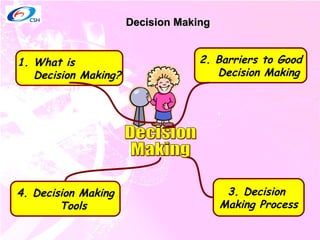
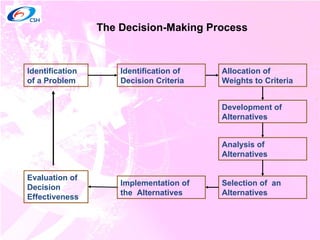
1) The decision making process which involves identifying problems, criteria, alternatives, analyzing options, selecting an alternative, implementing, and evaluating.
2) Barriers to good decision making such as being hasty, narrow, scattered, or fuzzy.
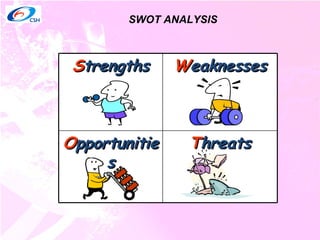
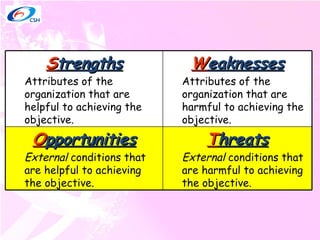
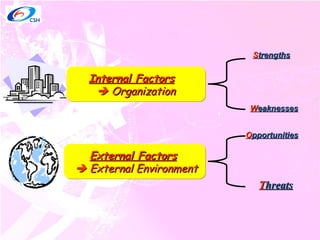
3) Tools that can help facilitate decision making including the SWOT analysis technique of identifying strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
4) Different decision making styles like directive, analytical, conceptual, and behavioral.