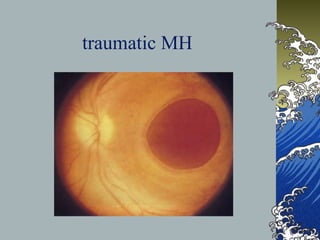
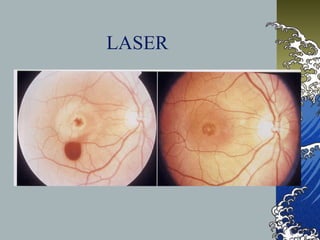
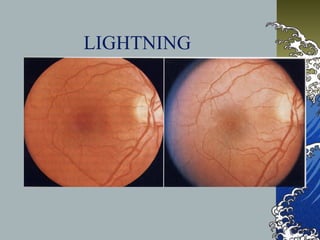
This document provides an overview of macular holes (MH), including their epidemiology, pathogenesis, classification, diagnosis, natural course, treatment, and outcomes. Some key points:
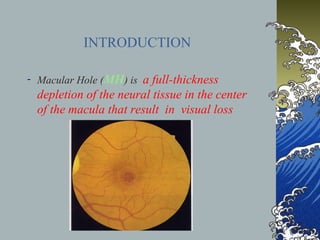
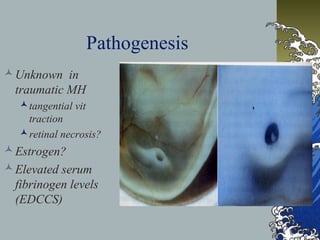
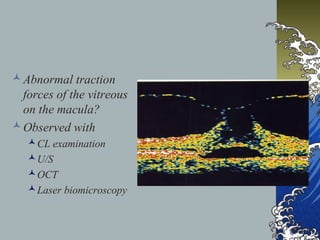
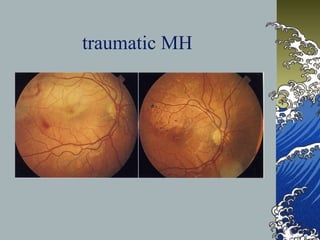
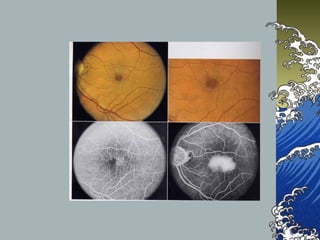
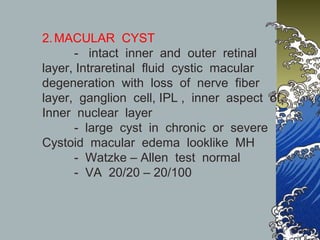
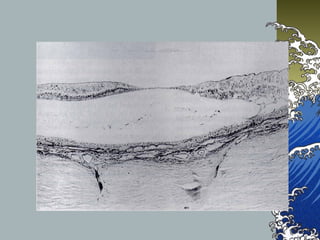
- MHs are full-thickness defects in the macula that result in central vision loss. The most common cause is idiopathic vitreous traction.
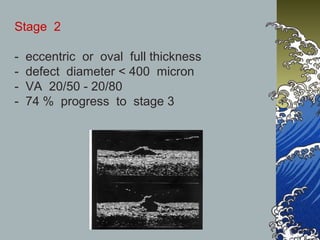
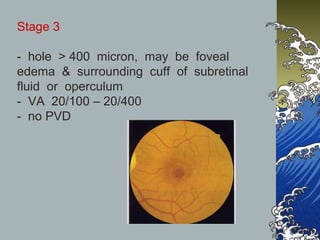
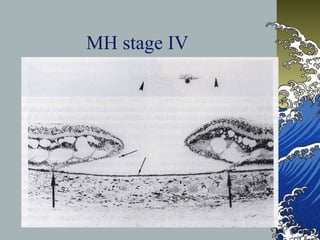
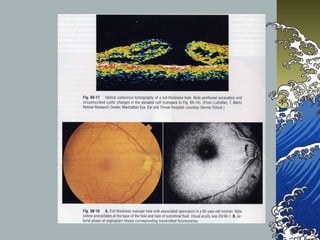
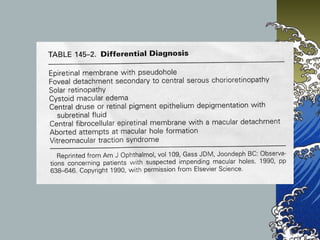
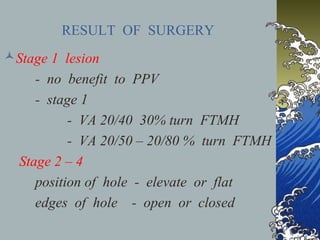
- MHs are classified into 4 stages based on size and the presence of a posterior vitreous detachment. Stage 3 holes over 400 microns rarely close spontaneously.
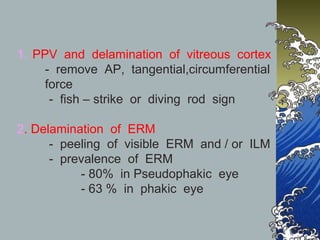
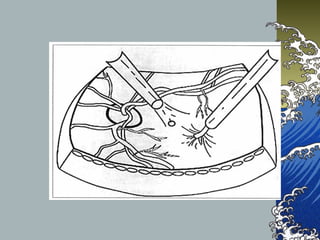
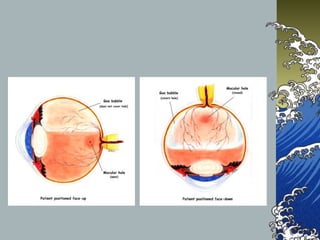
- Treatment involves pars plana vitrectomy to relieve vitreous traction, with or without internal limiting membrane peeling. An air-gas bubble or silicone oil is used to tampon