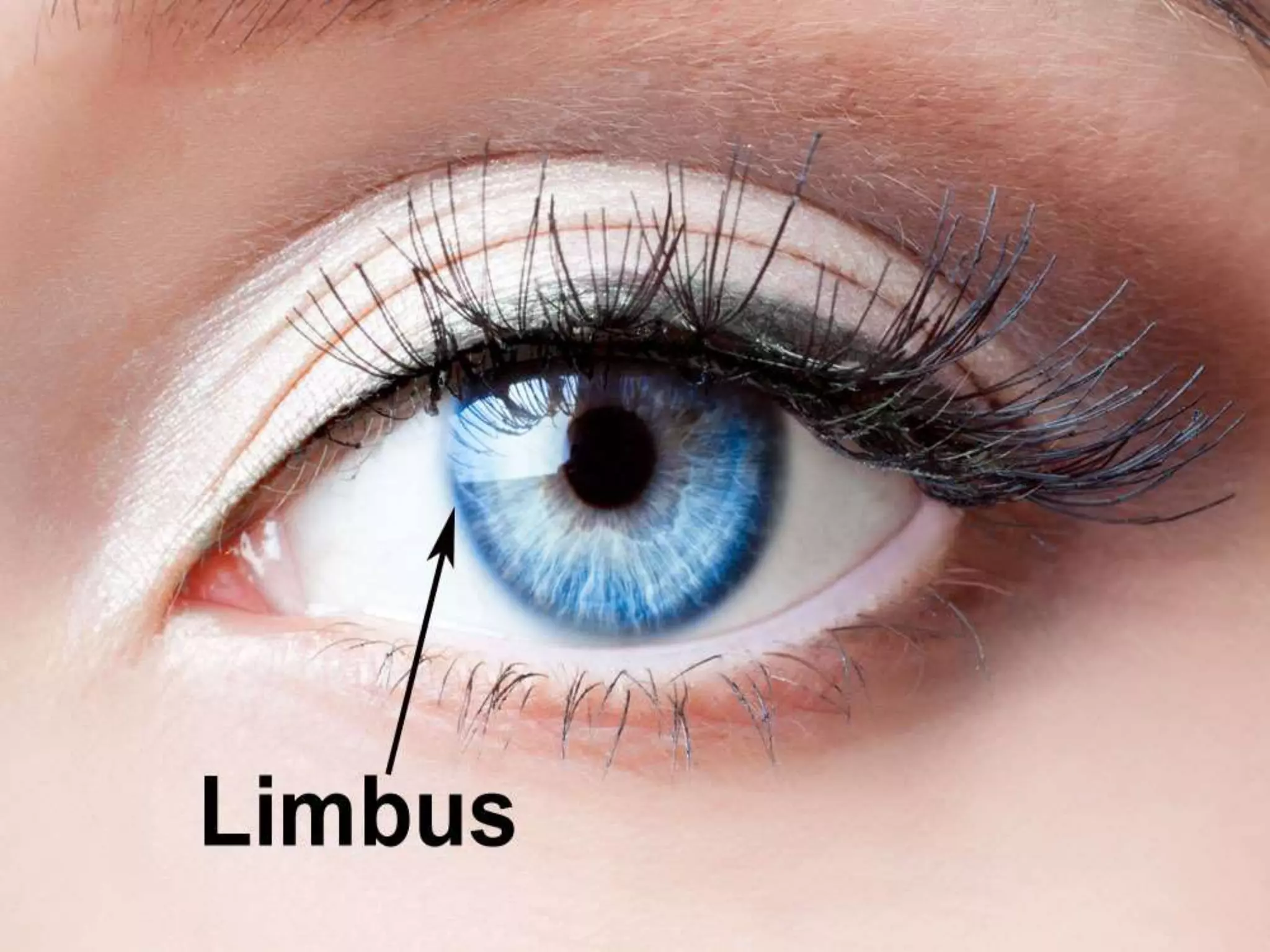
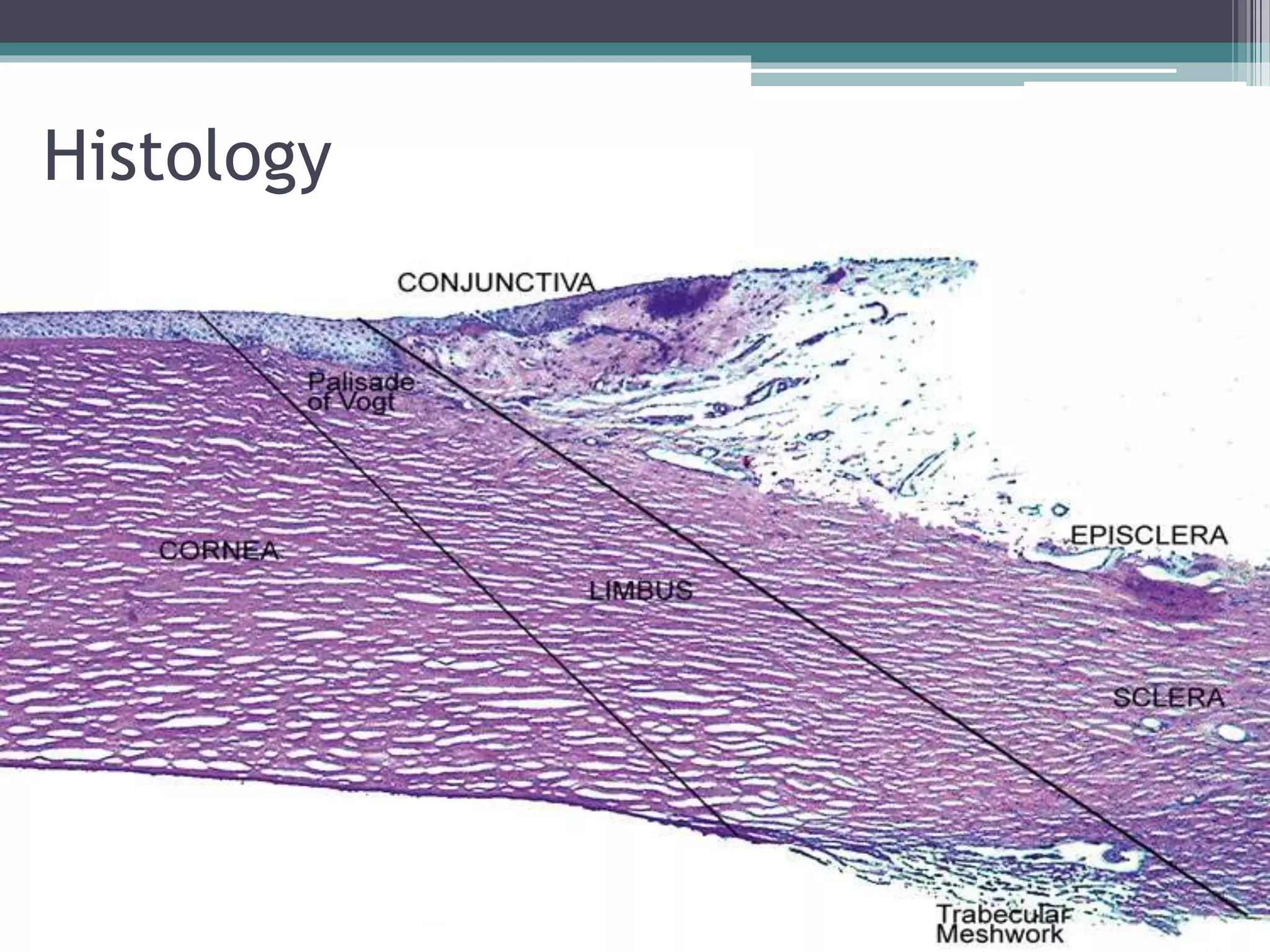
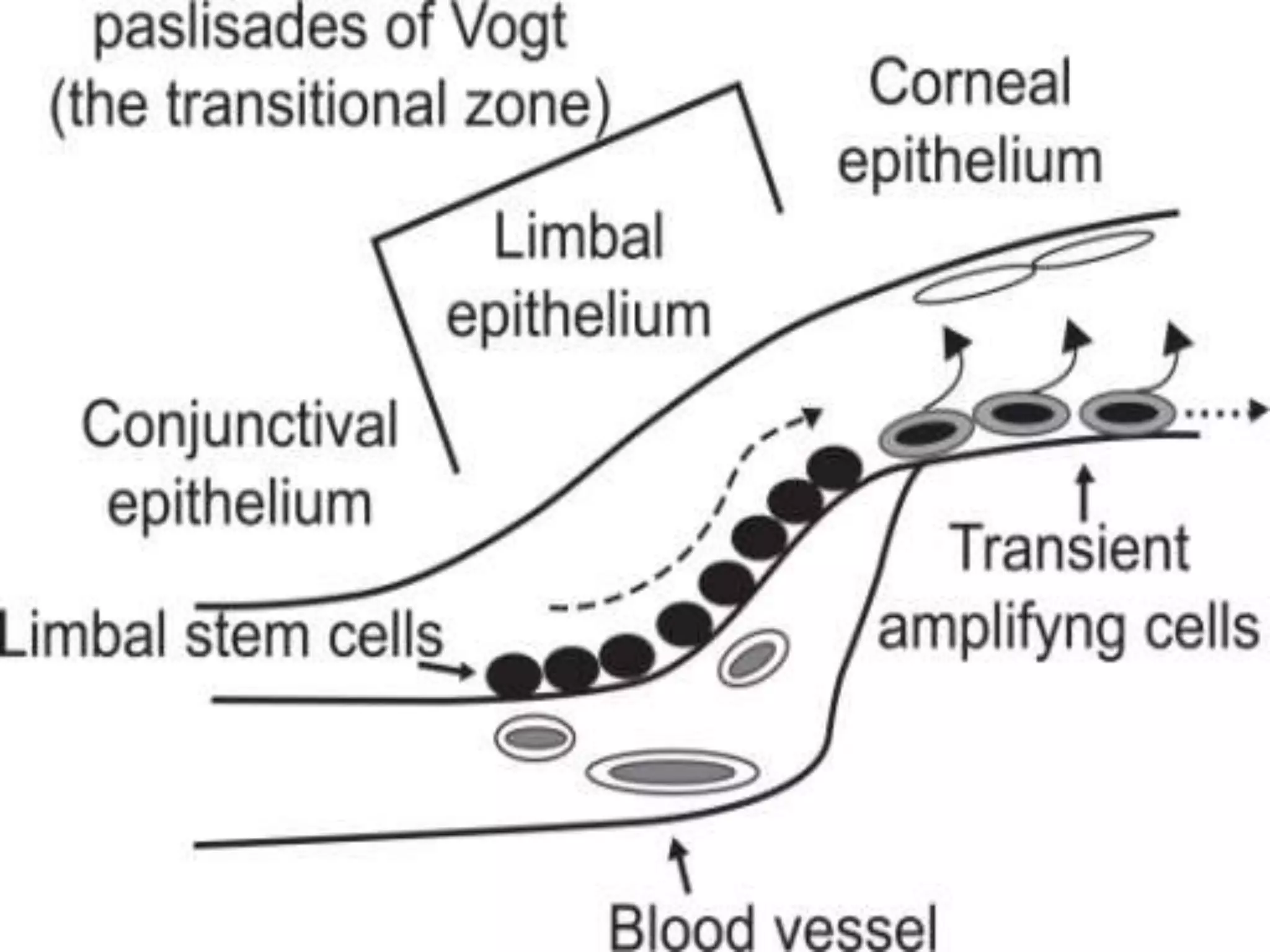
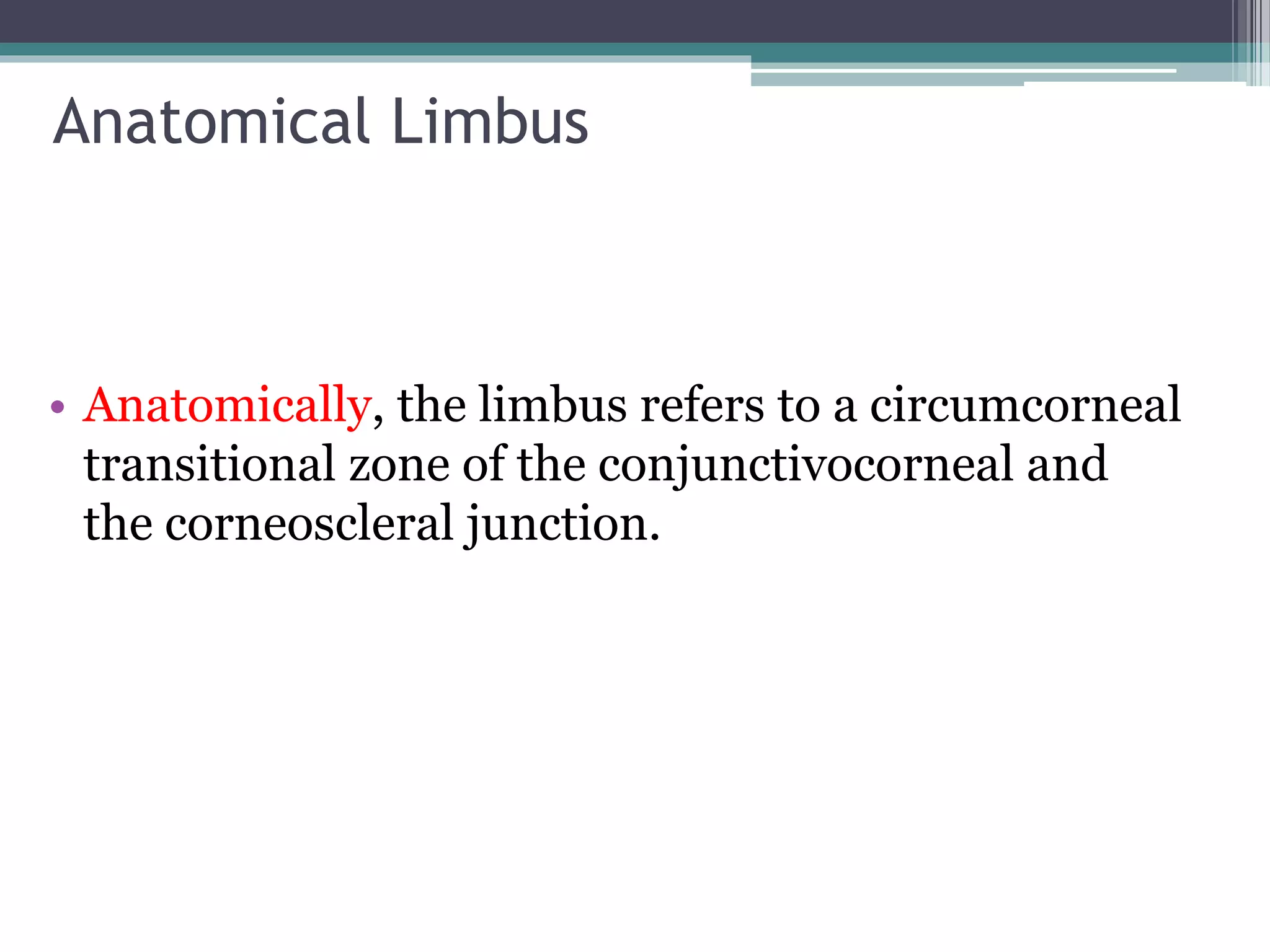
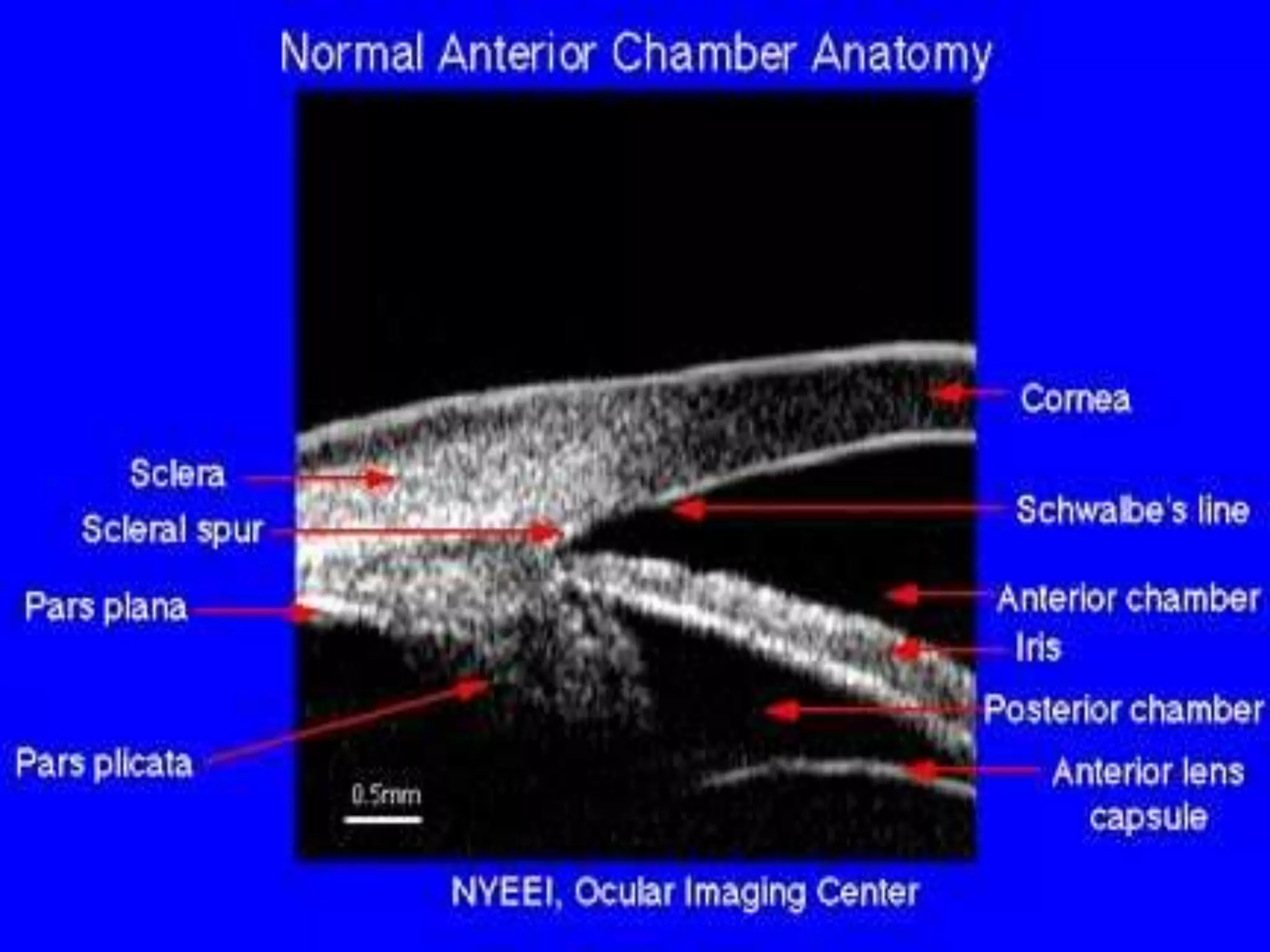
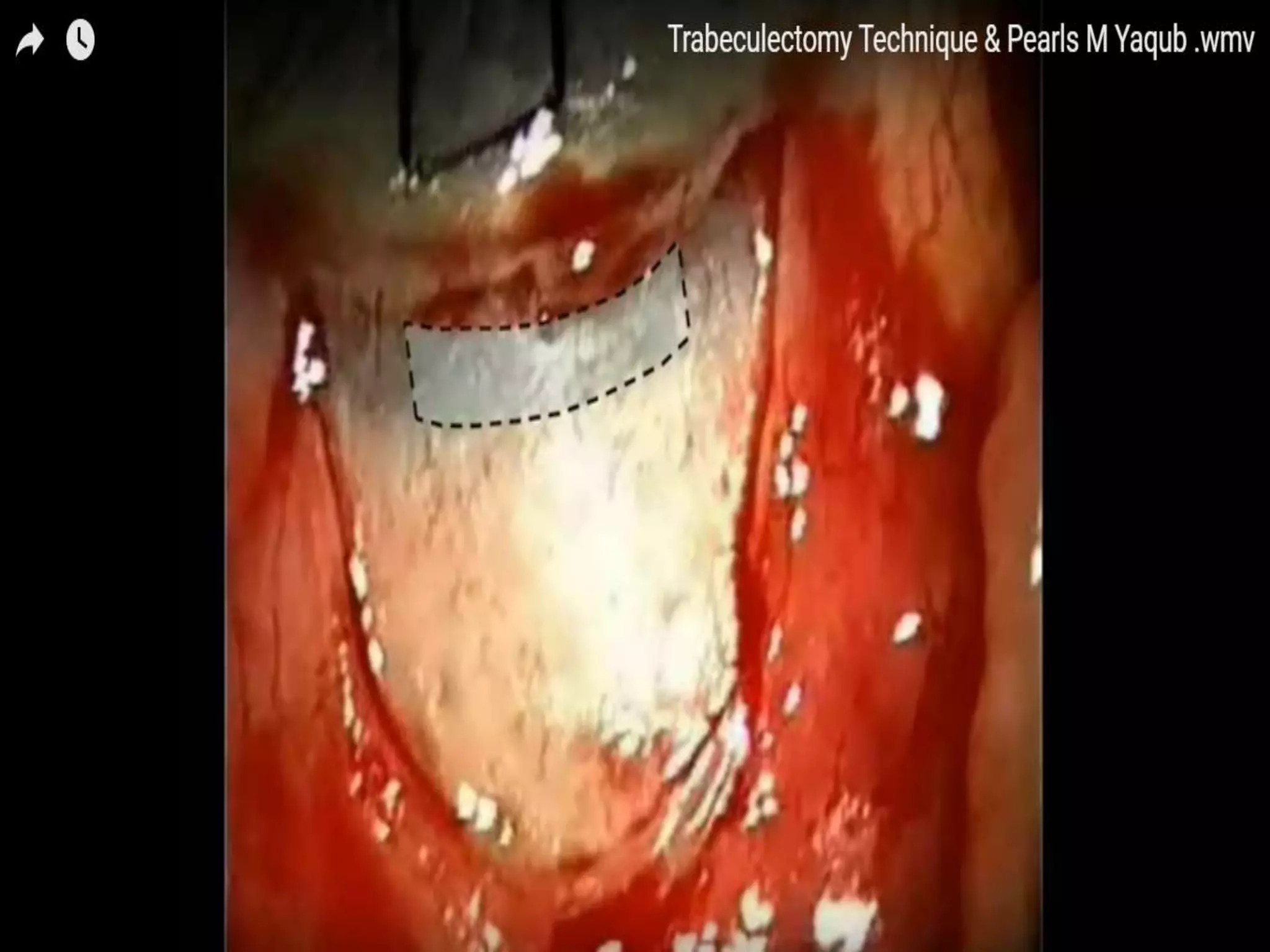
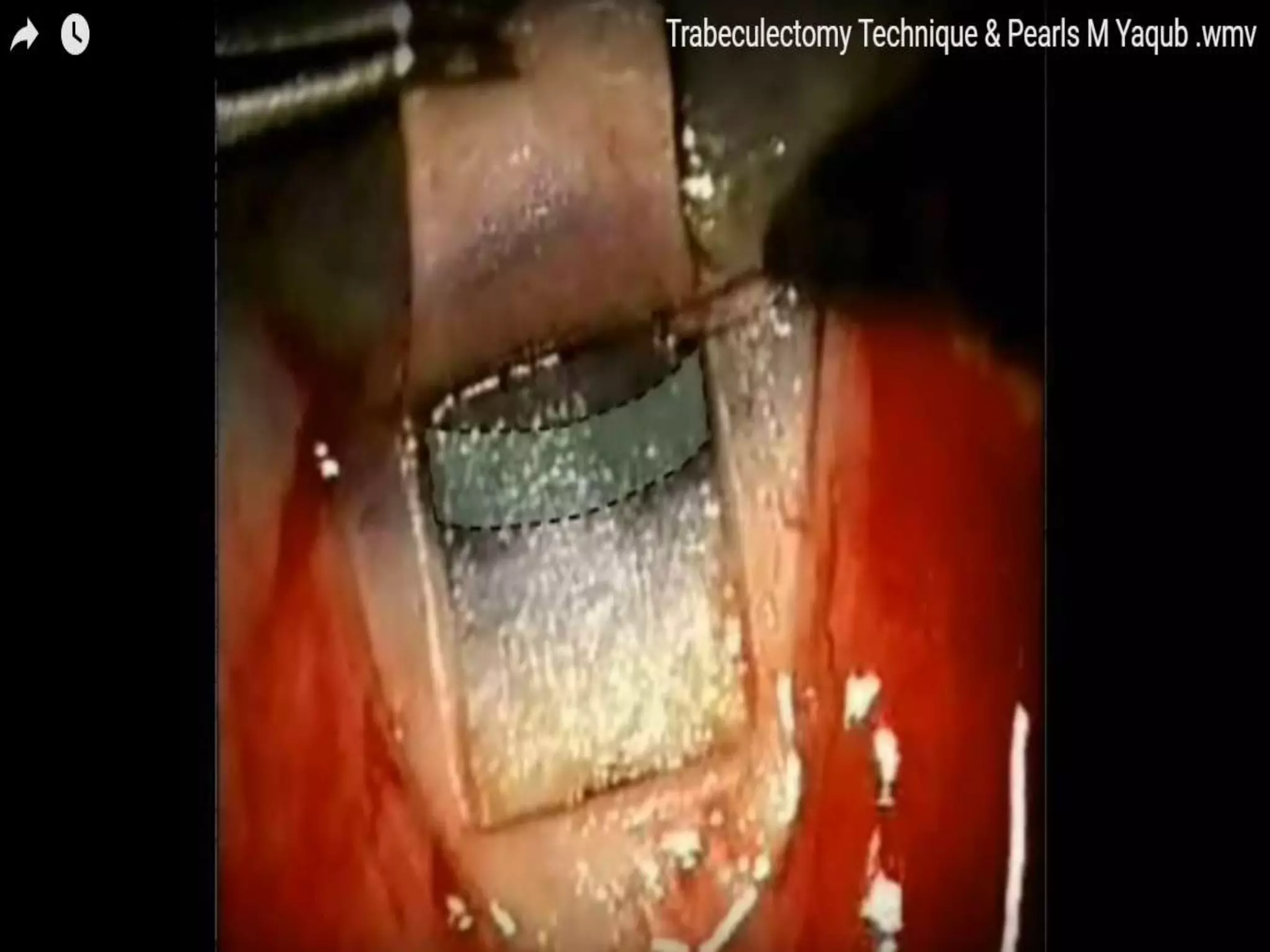
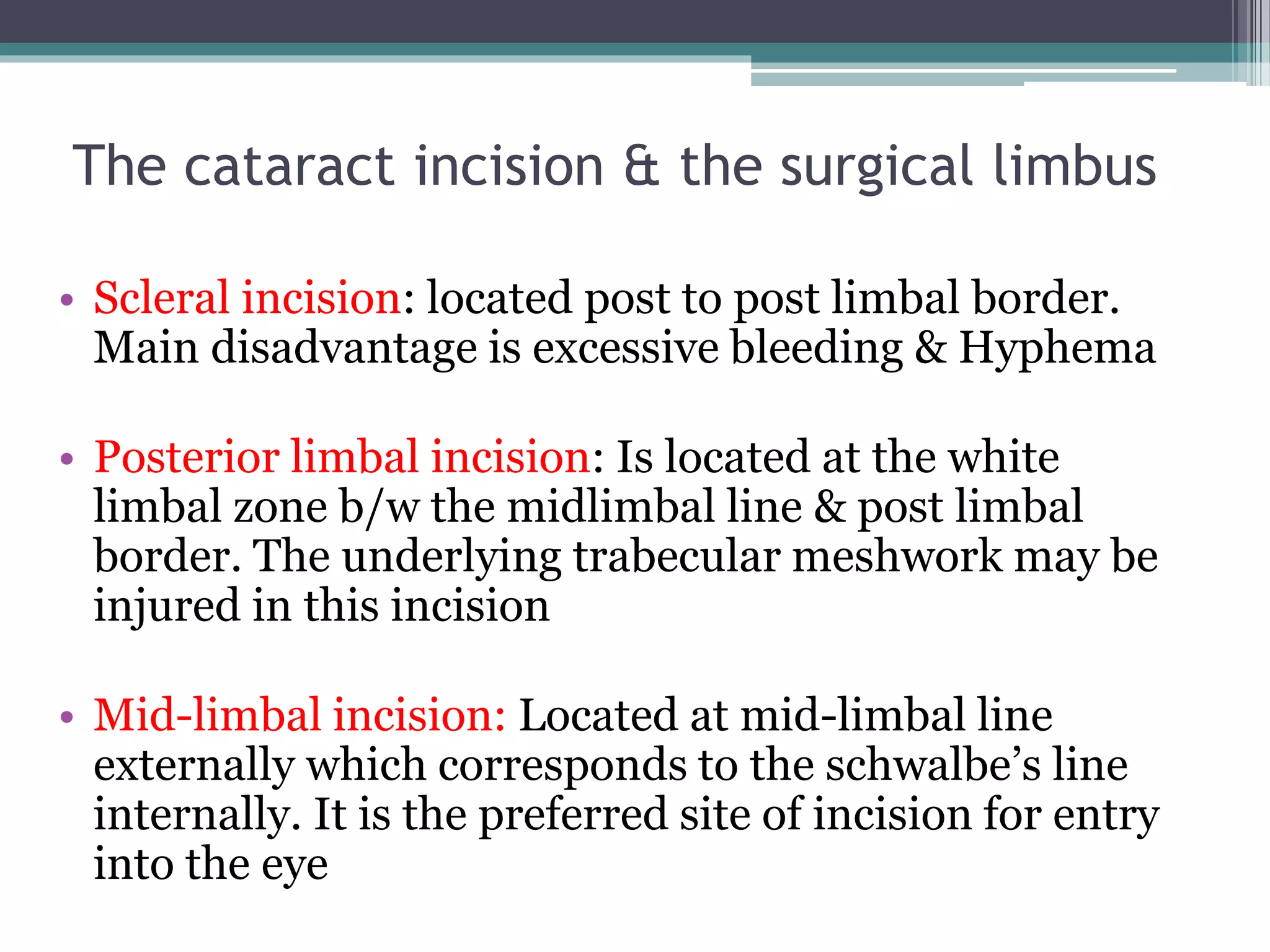
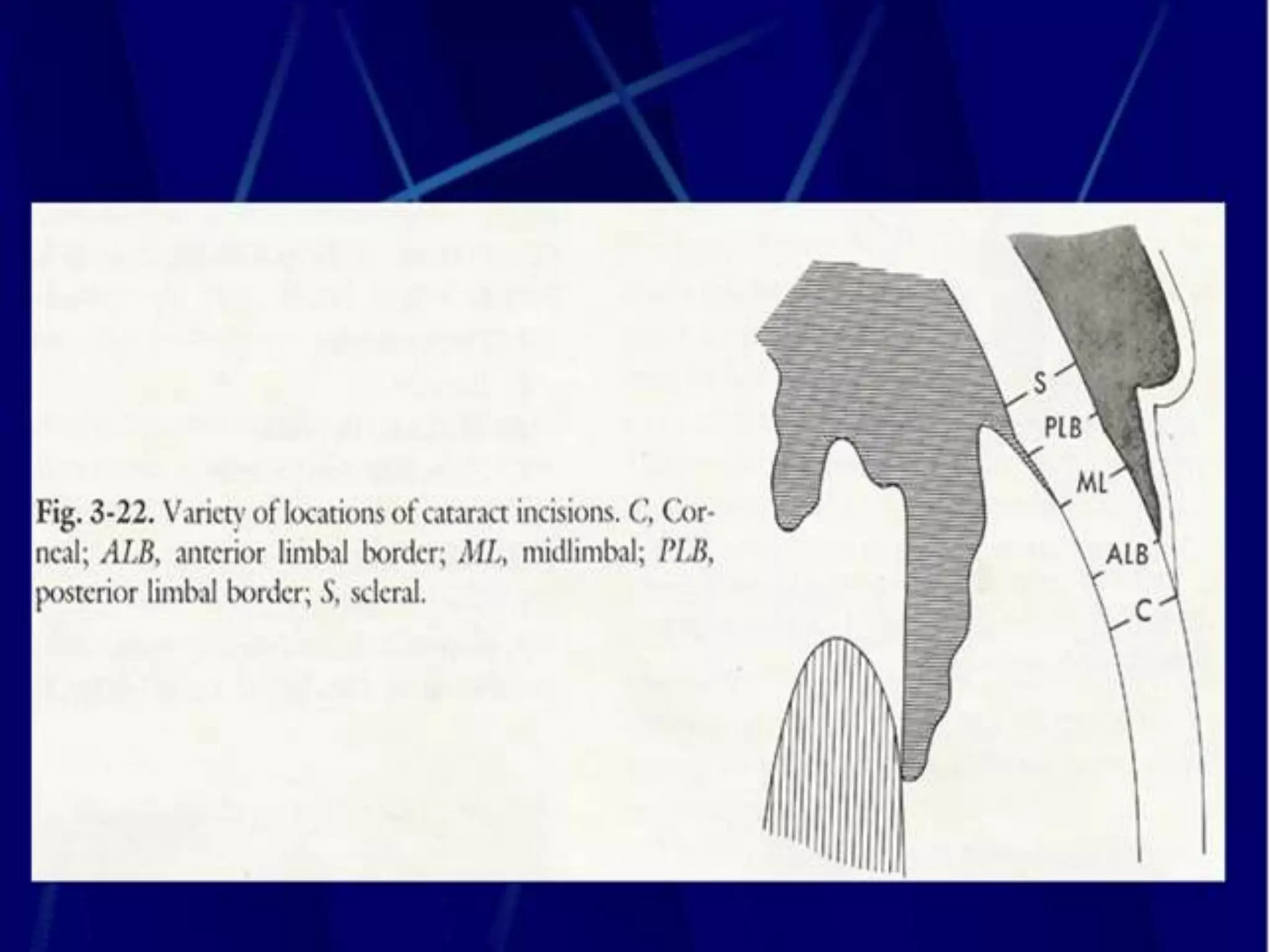
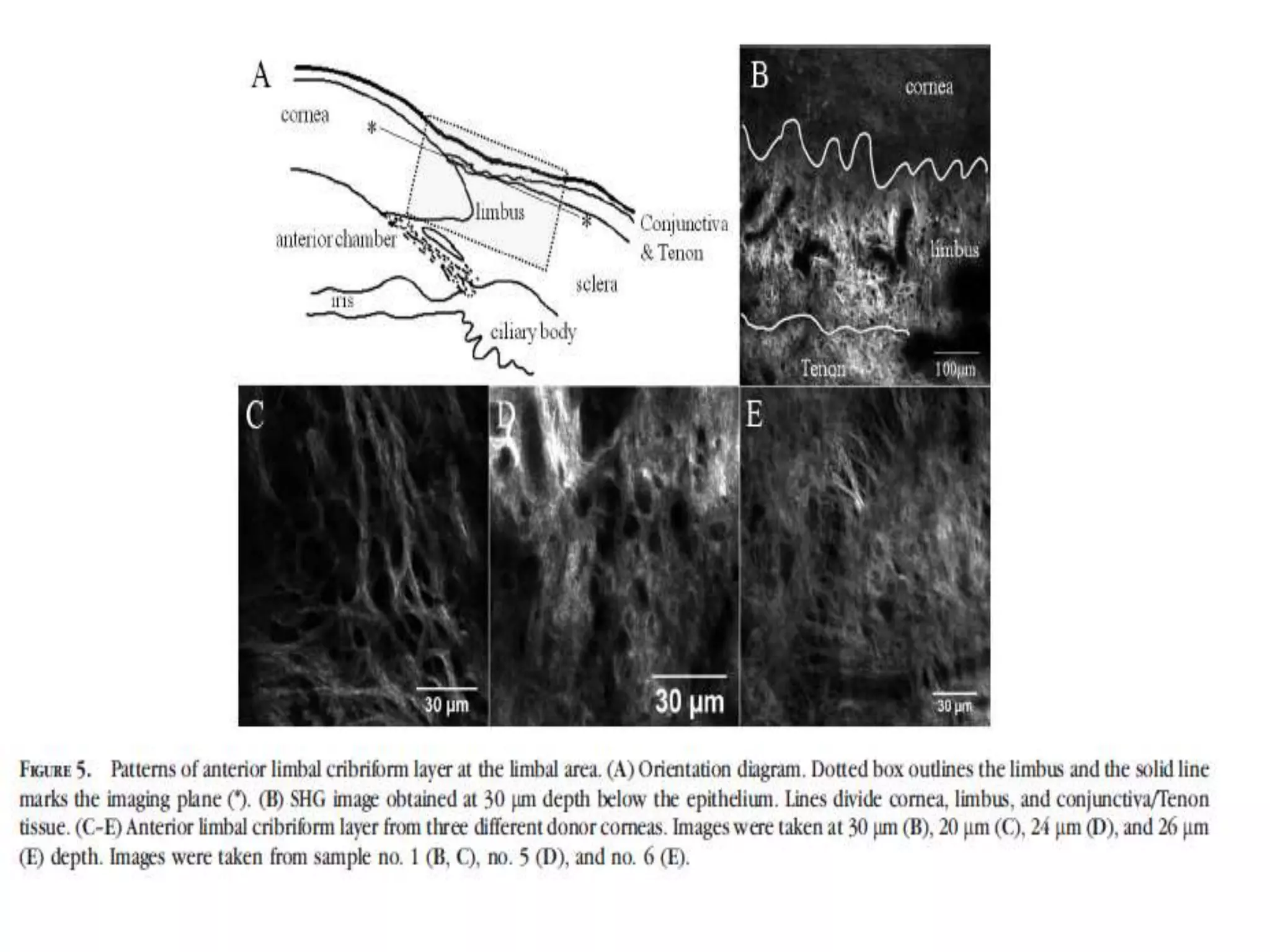
The document discusses the anatomy and surgical applications of the limbus. It defines the limbus as the transitional zone between the cornea and sclera, containing the pathways for aqueous humor outflow. Histologically, it describes how the layers of the cornea and conjunctiva become continuous at the limbus. Surgically, it notes the anterior limbal border, blue limbal zone, mid-limbal line, posterior limbal border, and white limbal zone. The best site for cataract incisions is the mid-limbal line, while anterior or posterior incisions risk damage to underlying structures. The limbus contains stem cells that renew the corneal epithelium.