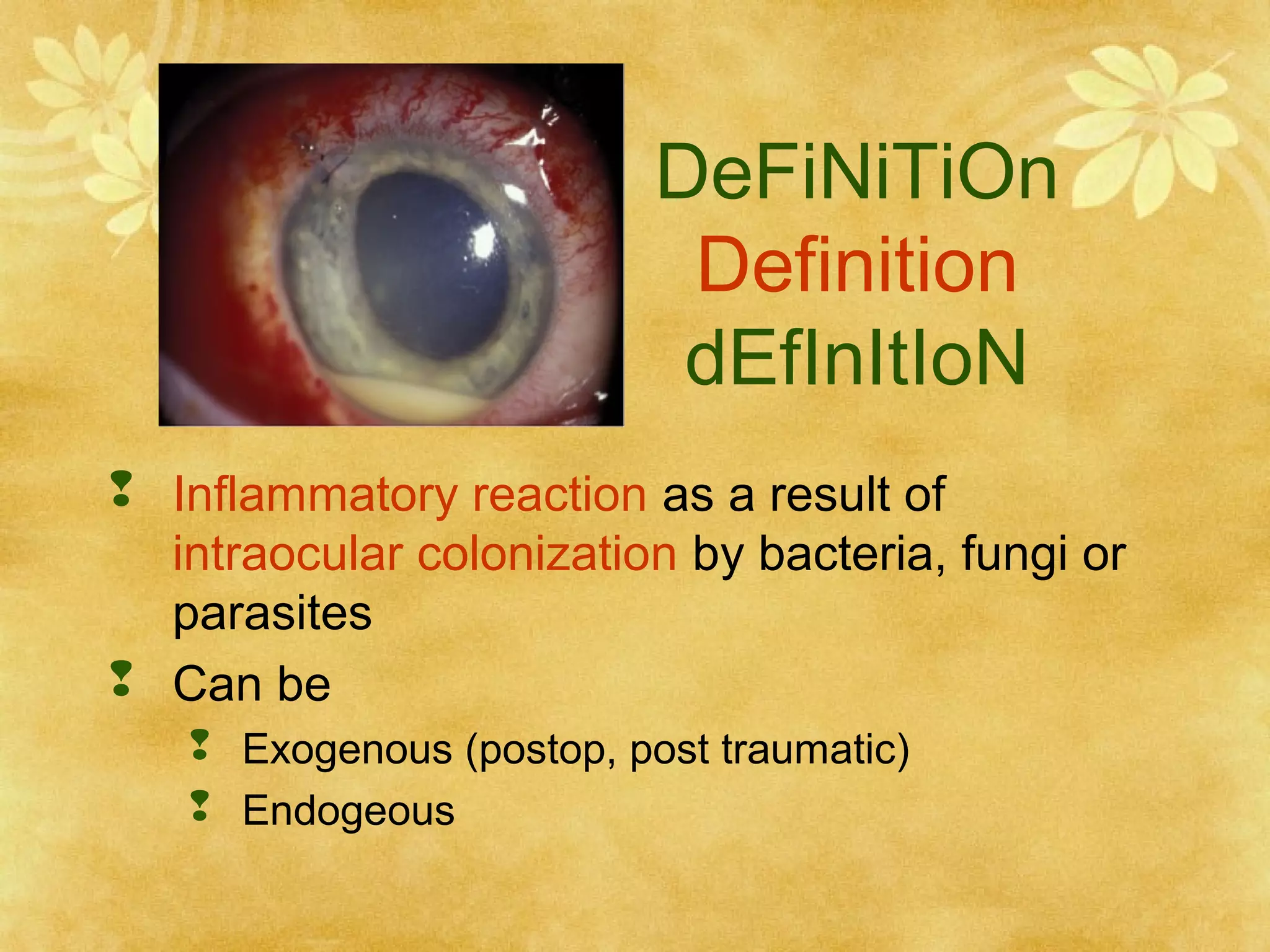
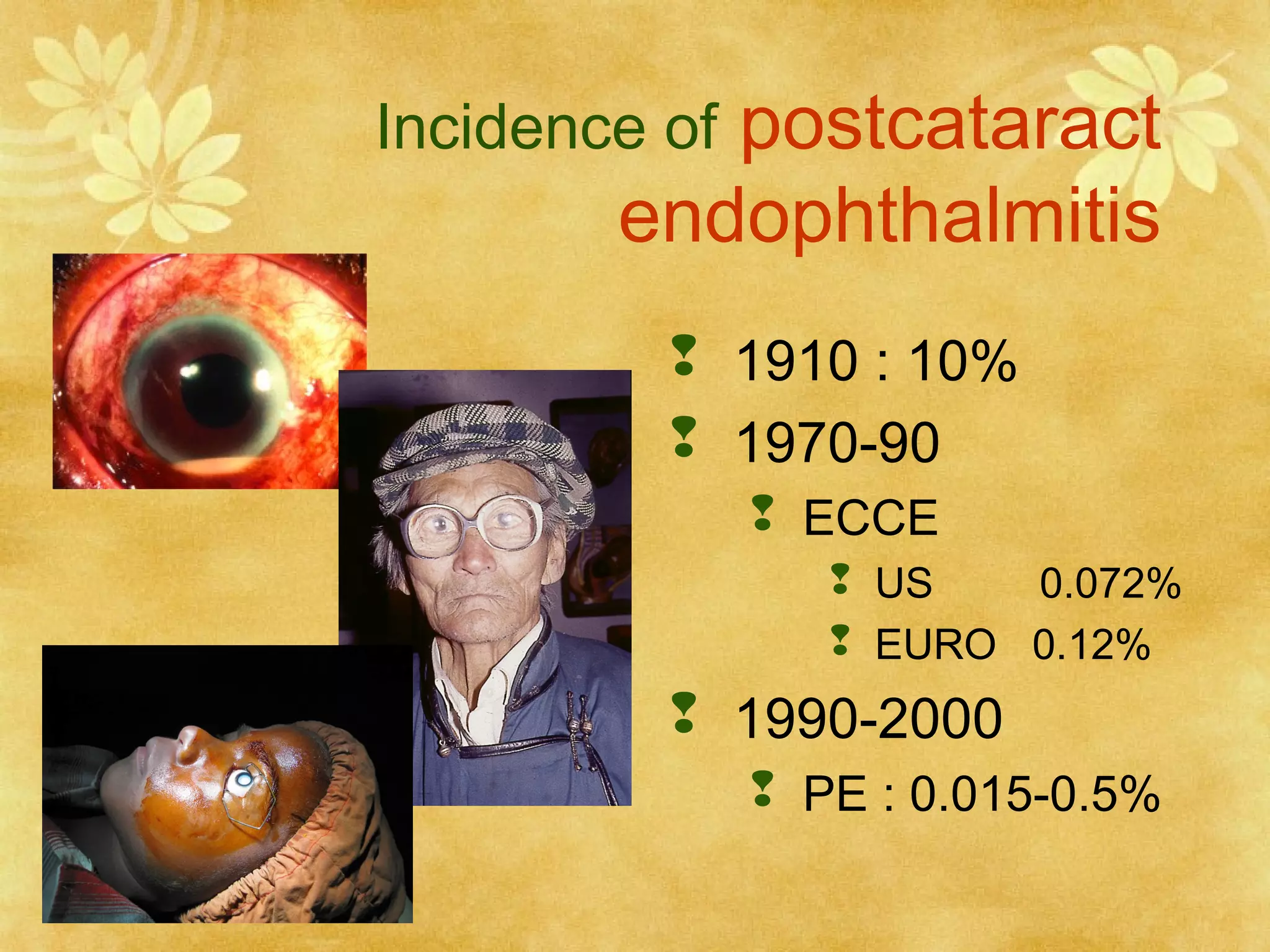
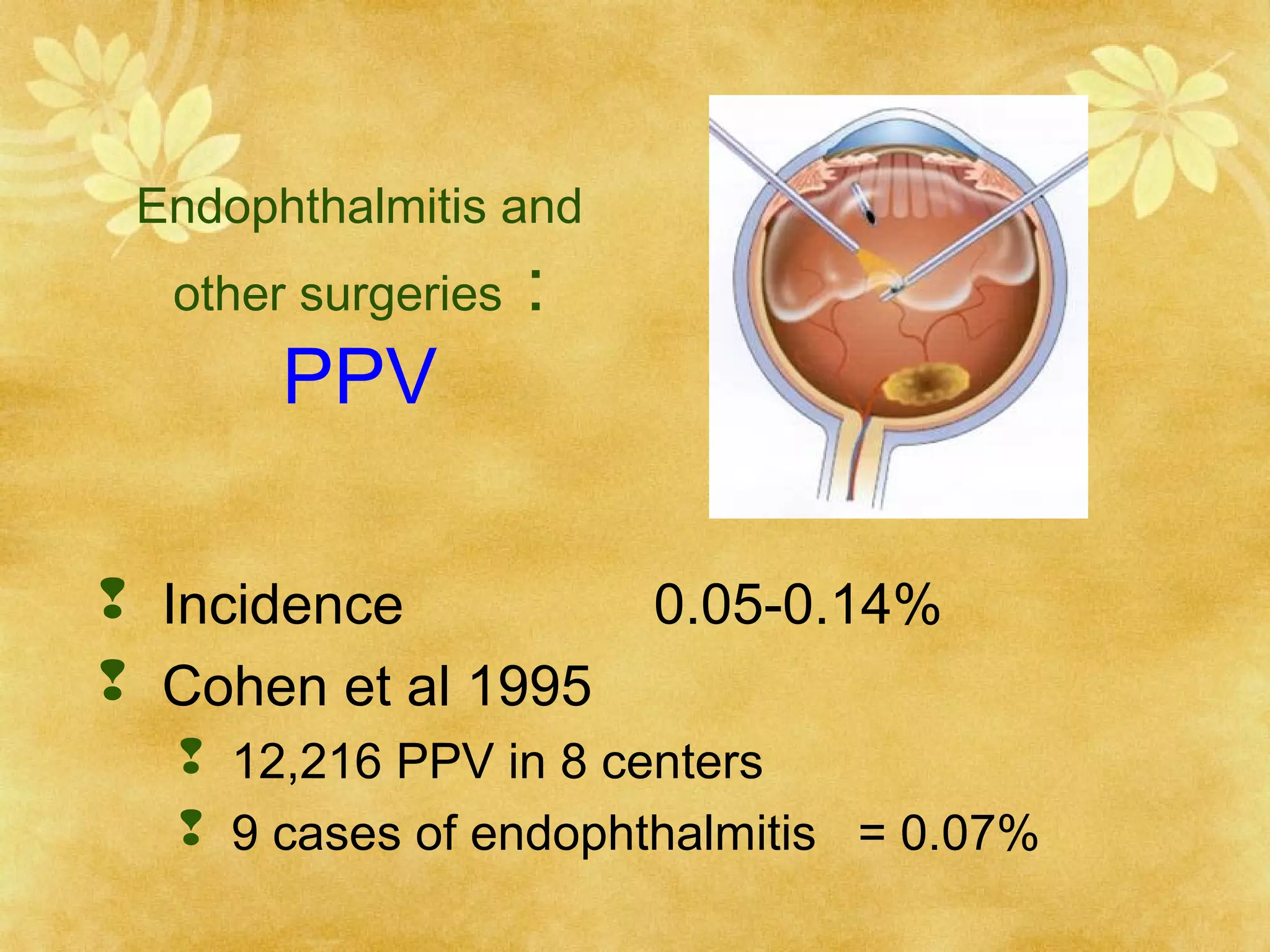
1. Endophthalmitis is an inflammatory reaction within the eye resulting from bacterial, fungal, or parasitic colonization. It can be exogenous (post-operative, post-traumatic) or endogenous.
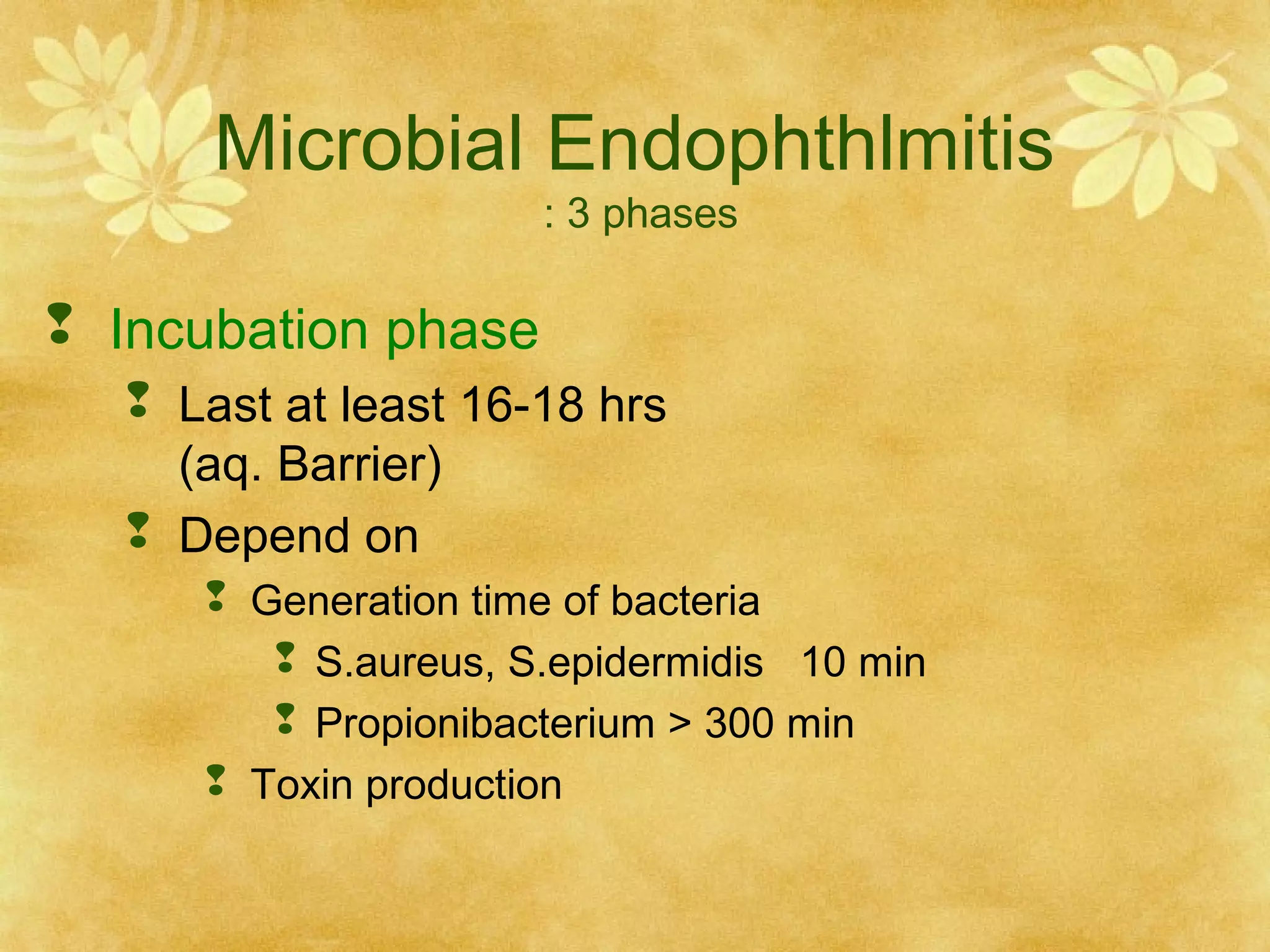
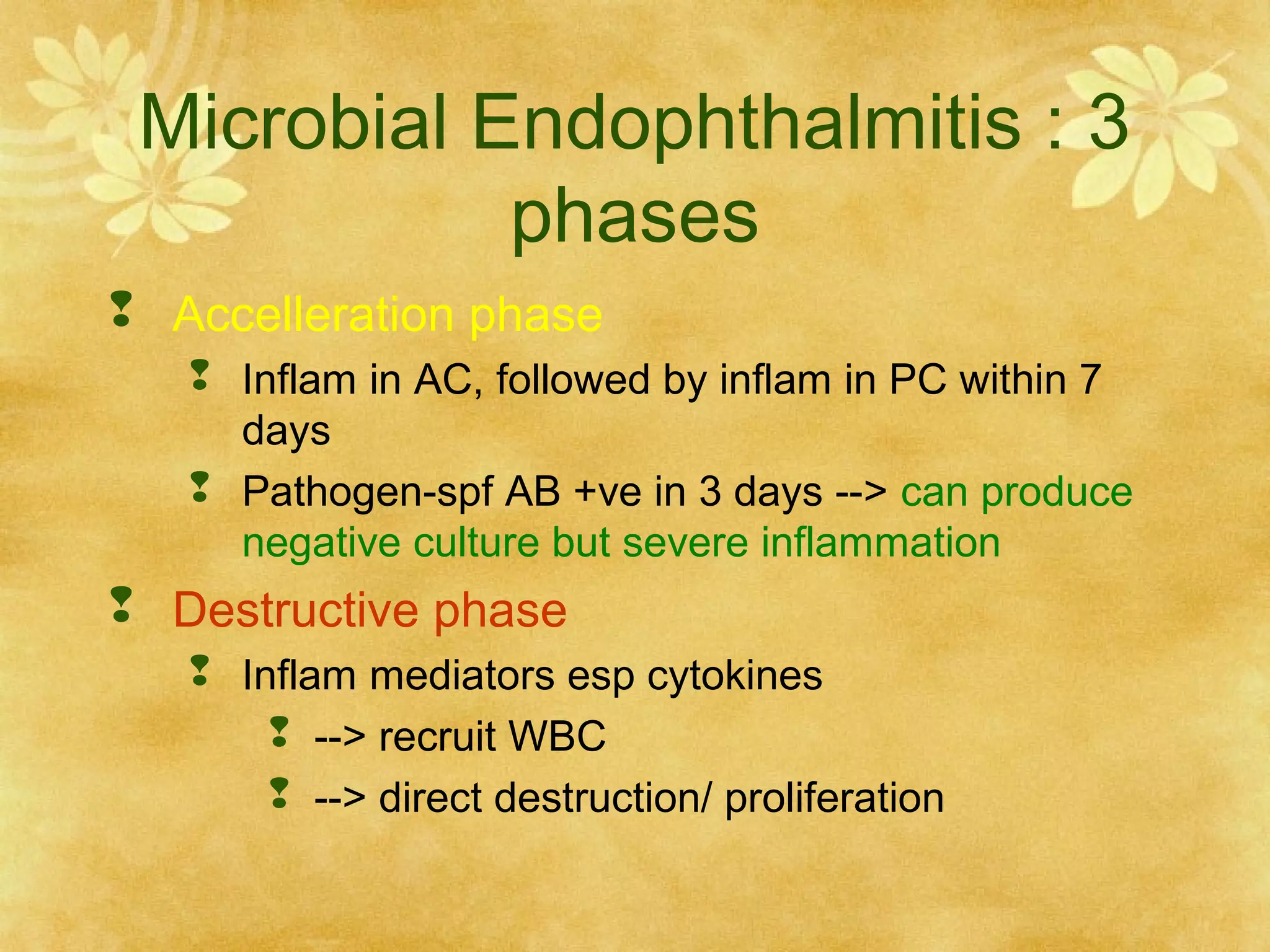
2. Microbial endophthalmitis occurs in three phases - incubation, acceleration, and destructive. The incubation phase lasts at least 16-18 hours as bacteria multiply. The acceleration phase sees inflammation spread from the anterior chamber to the posterior chamber within 7 days. The destructive phase involves inflammatory mediators recruiting white blood cells to directly destroy ocular tissues.
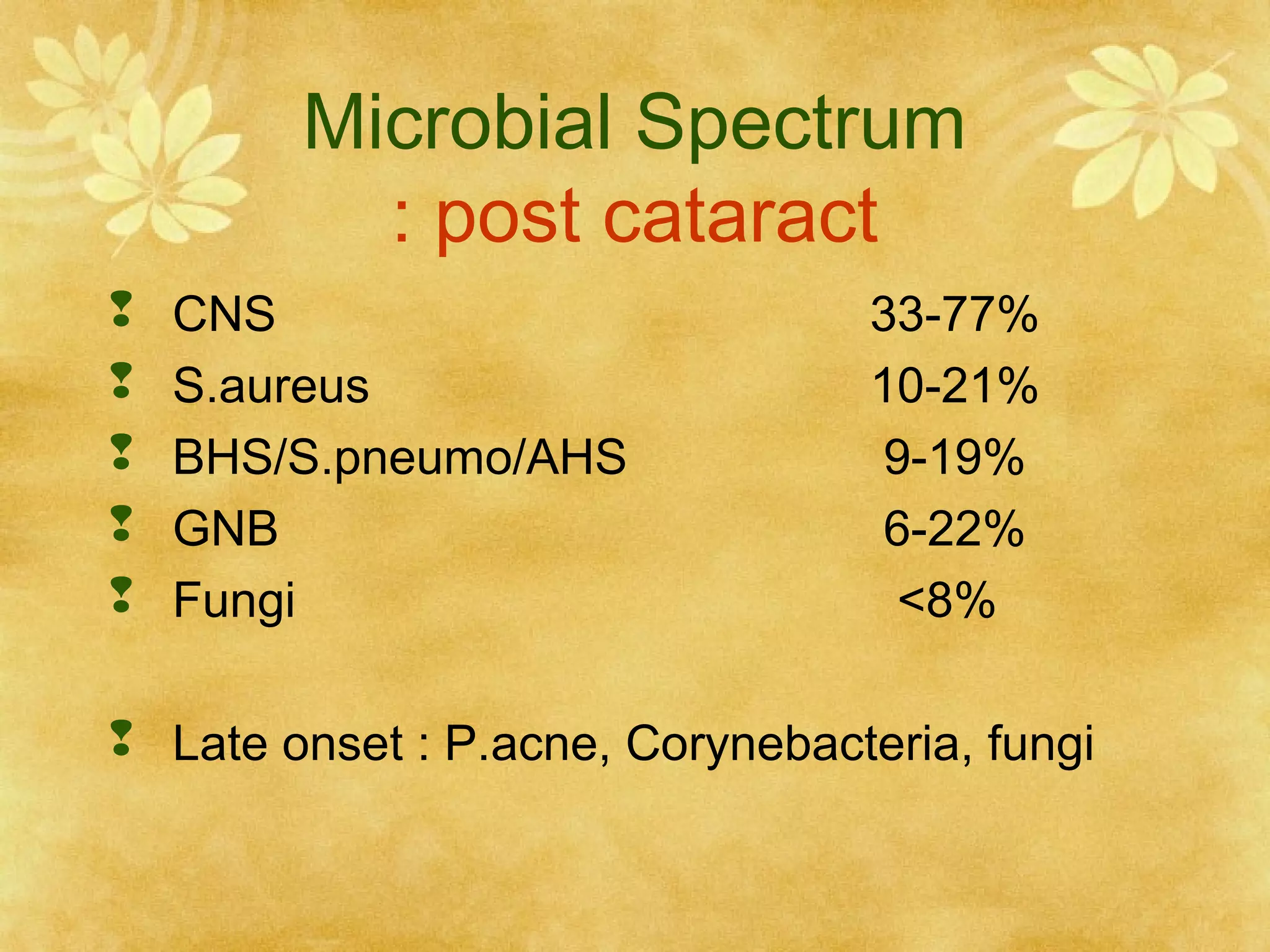
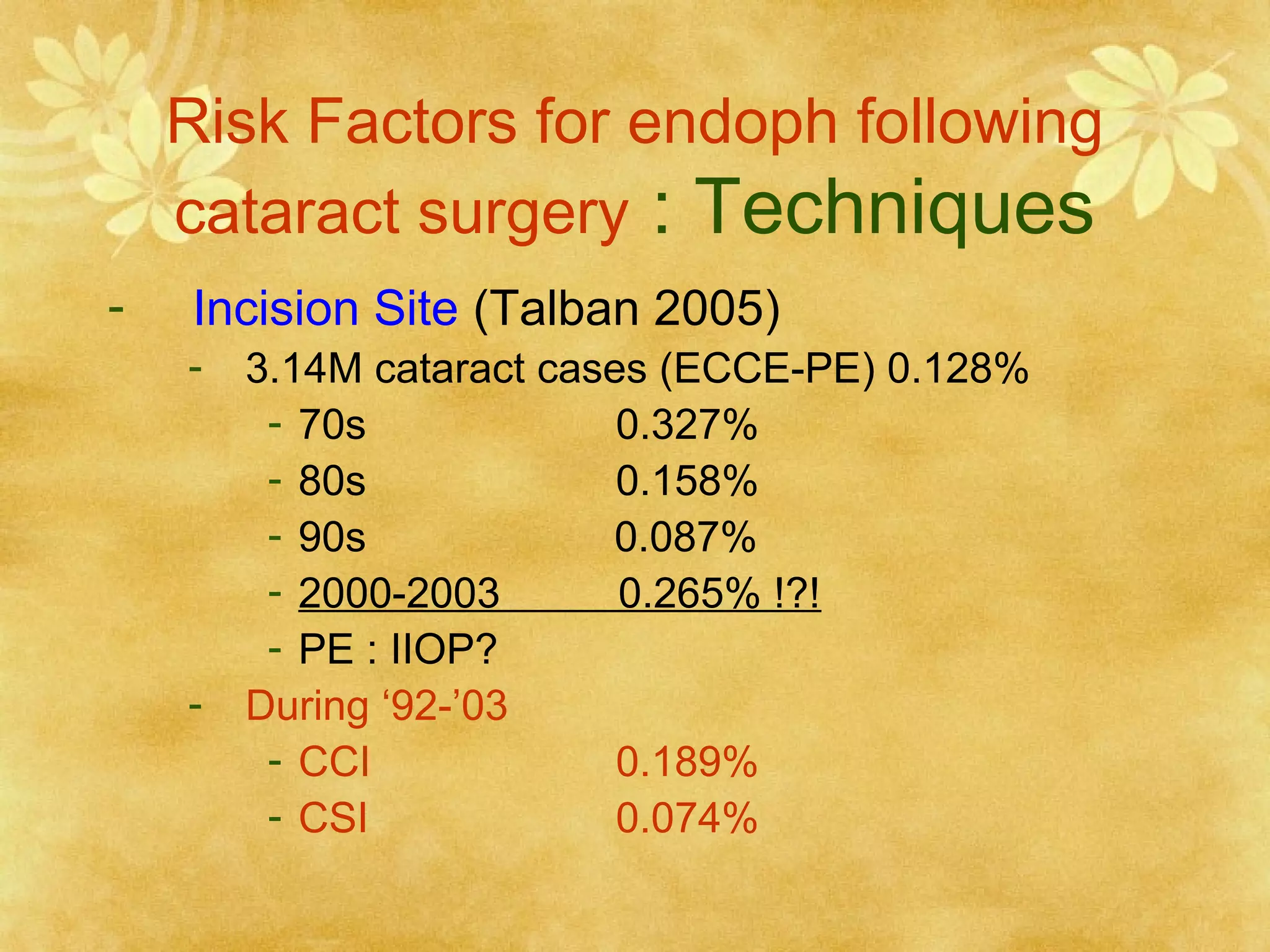
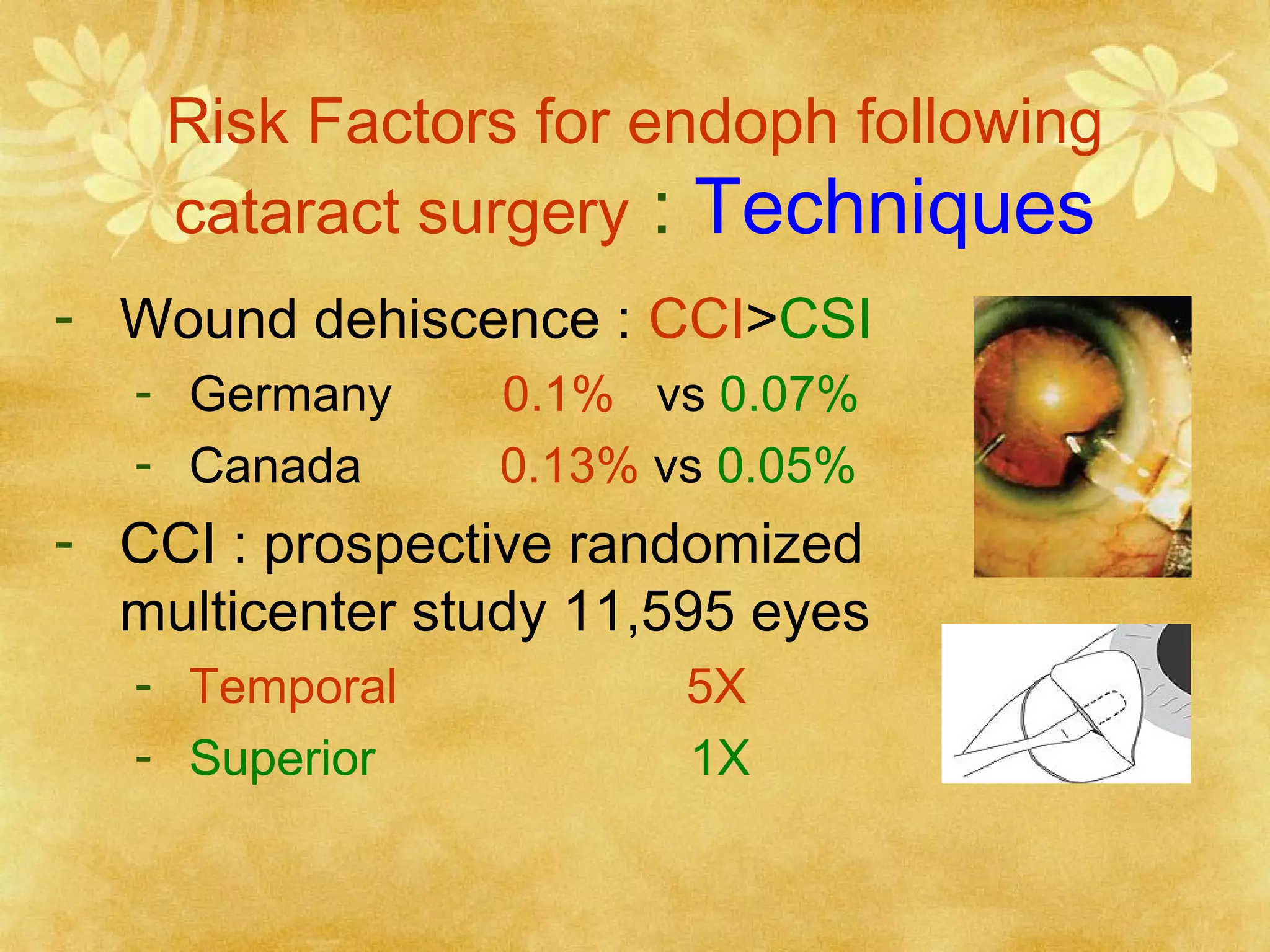
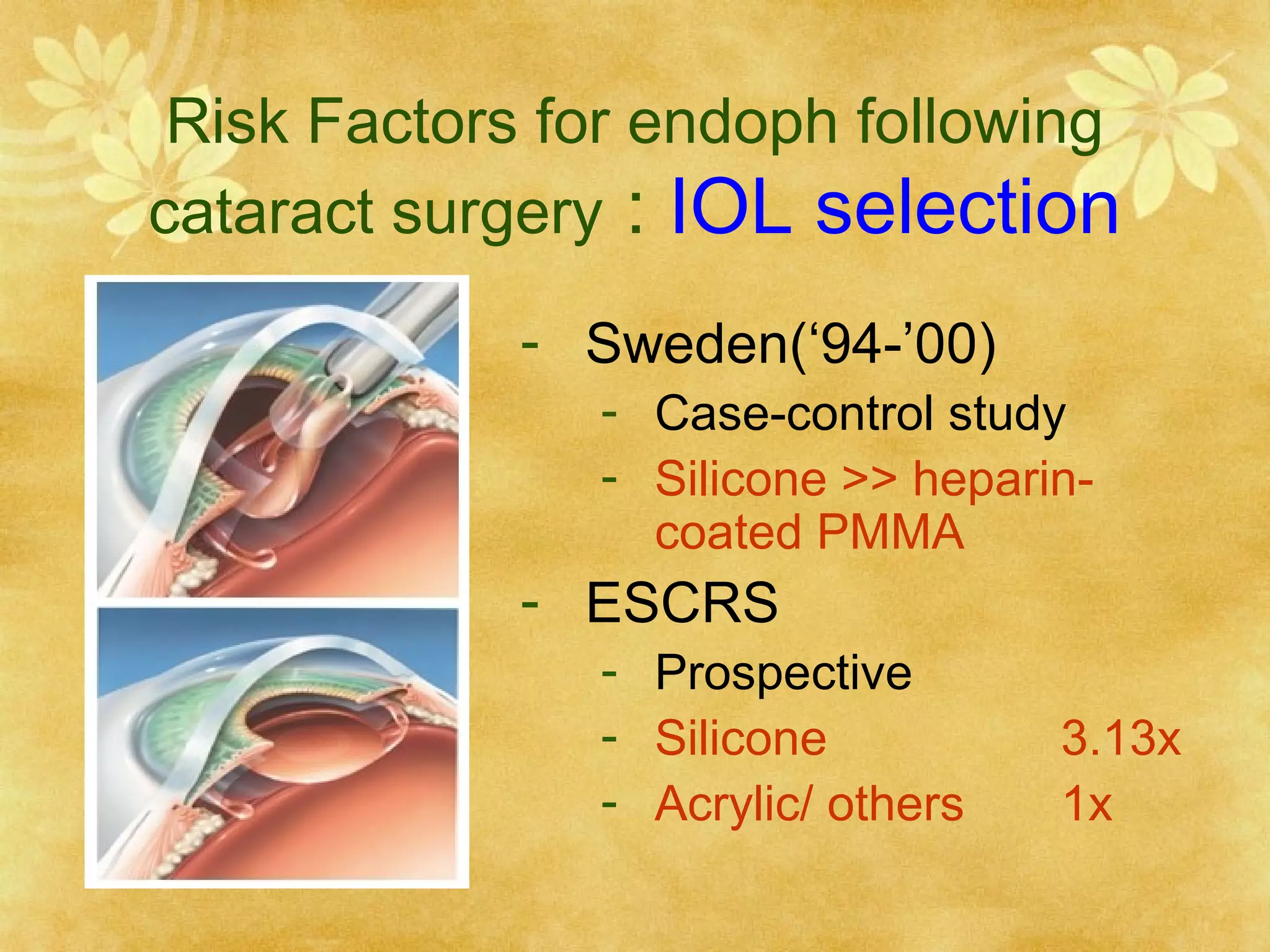
3. Risk factors for post-cataract endophthalmitis include wound leakage, capsular defects, vitreous