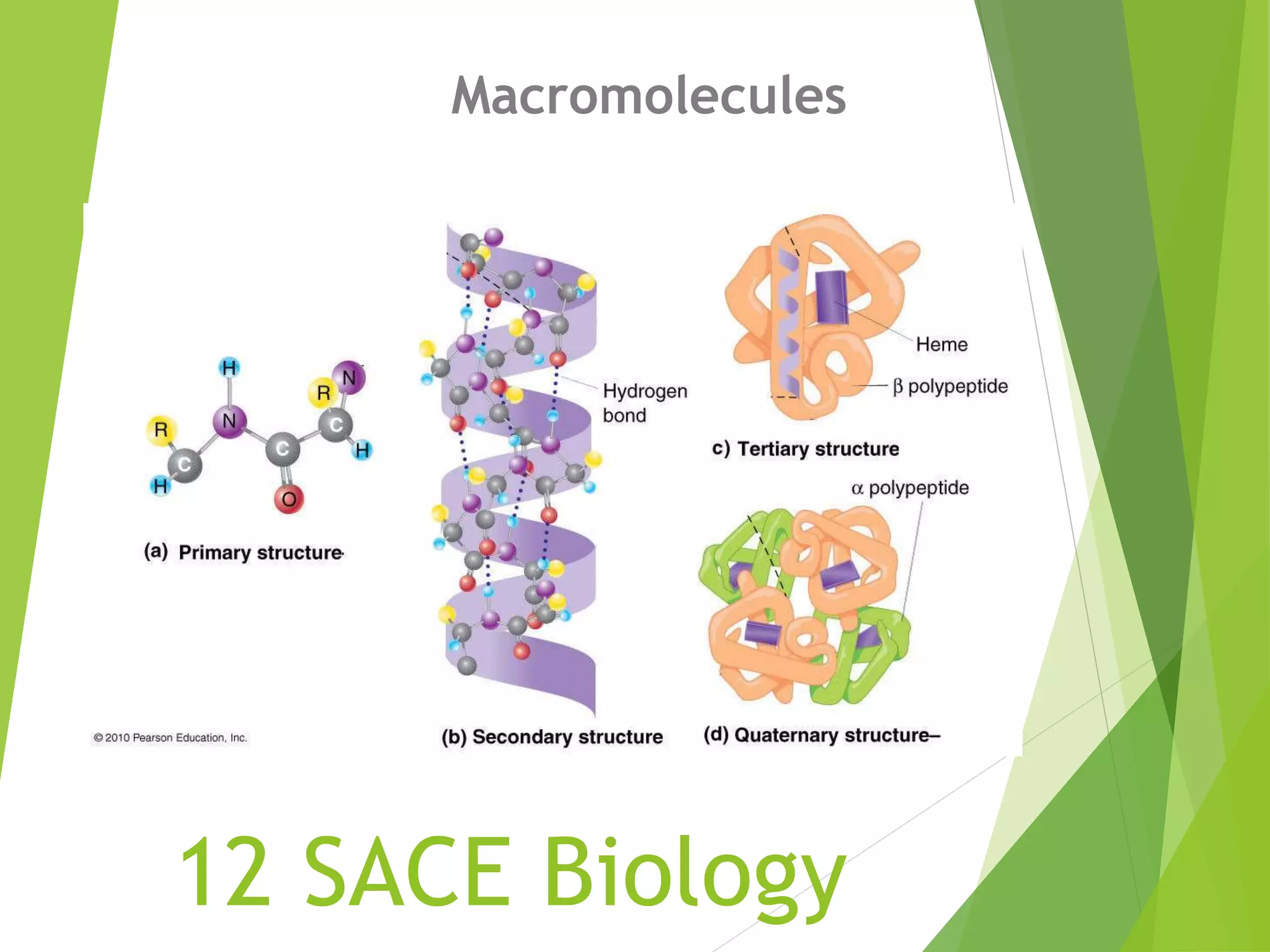
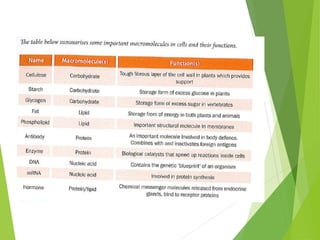
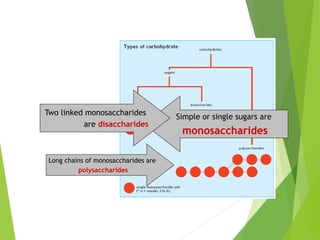
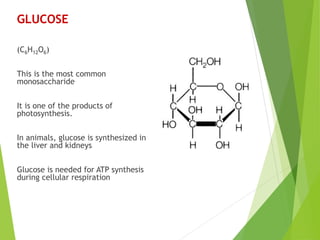
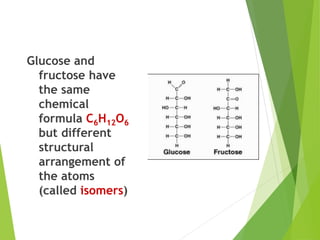
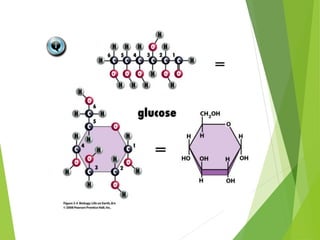
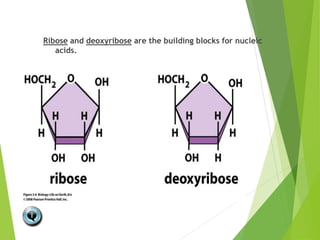
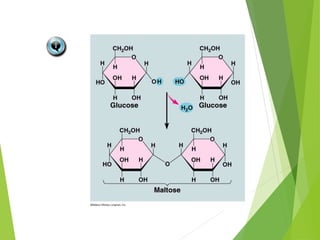
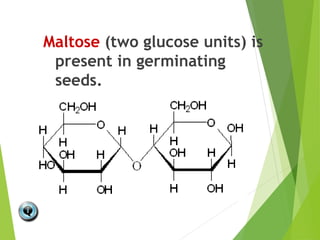
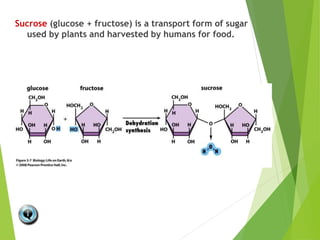
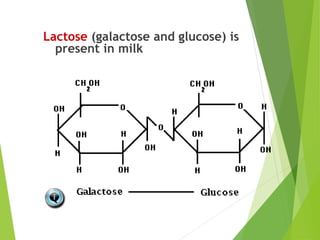
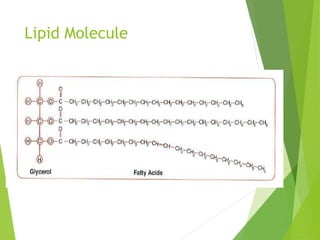
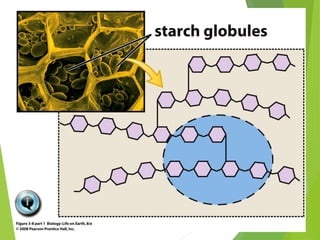
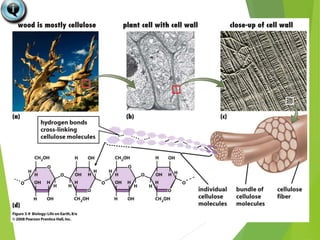
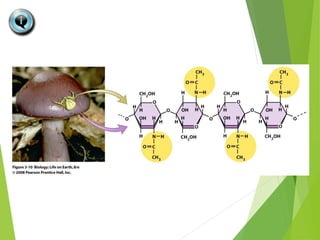
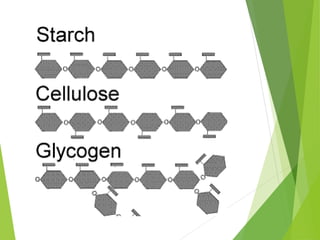
The document discusses macromolecules, which are large complex organic molecules that are essential for life. There are four main classes of macromolecules: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Carbohydrates include monosaccharides like glucose and fructose, disaccharides formed from two monosaccharides bonded together like sucrose, and polysaccharides made of long chains of monosaccharides like starch, glycogen, and cellulose. Lipids include fats, oils, waxes, and phospholipids, with phospholipids containing a phosphate group allowing them to form cell membranes. The document provides examples and information about specific macromolecules like glucose, starch, and phospholipids, and explains they are