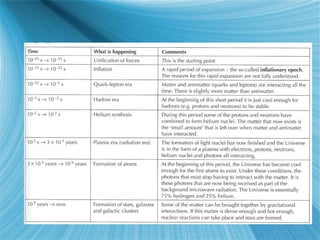
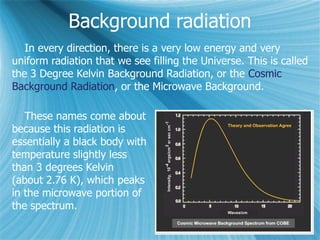
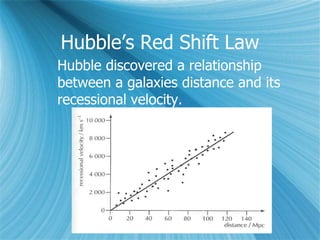
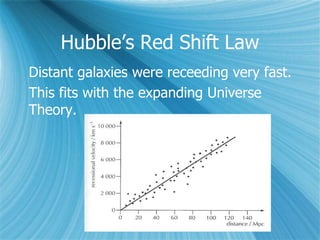
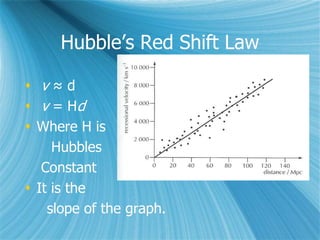
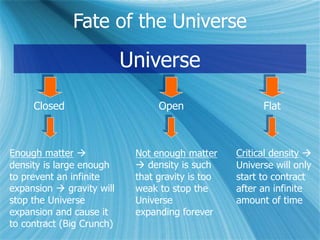
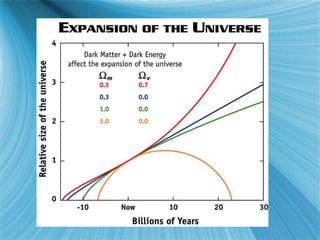
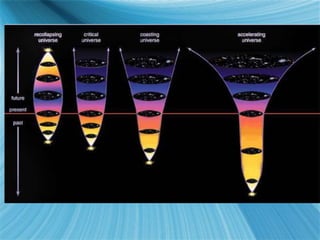
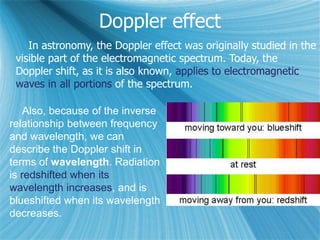
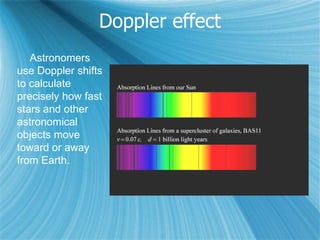
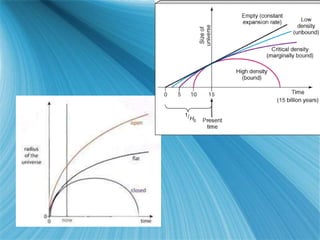
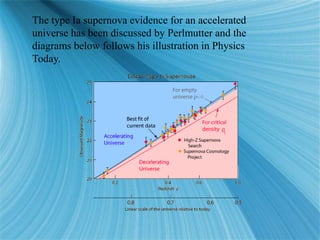
The Big Bang model describes the origin and evolution of our universe. It postulates that approximately 13.8 billion years ago, the entire observable universe was only a few millimeters in size and extremely hot and dense. The universe has been expanding and cooling ever since. Evidence for the Big Bang includes the expansion of the universe, the cosmic microwave background radiation, and the relative abundance of light elements like hydrogen and helium.