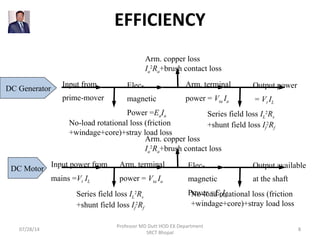
1) There are several types of losses that reduce the efficiency of DC machines, including electrical or copper losses, core losses, brush losses, mechanical losses, and stray load losses.
2) Electrical losses include losses from the armature winding resistance, shunt field winding resistance, series field winding resistance, and interpole winding resistance.
3) Core losses are hysteresis and eddy current losses and account for around 20% of full load losses.
4) Brush losses are due to the voltage drop and current at the brush contact with the commutator.