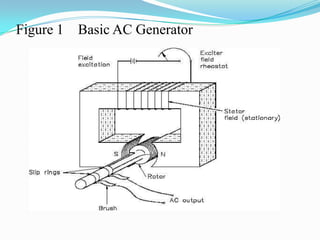
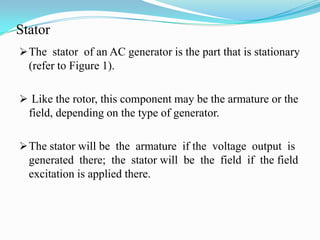
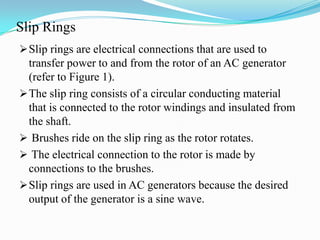
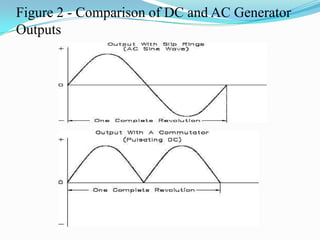
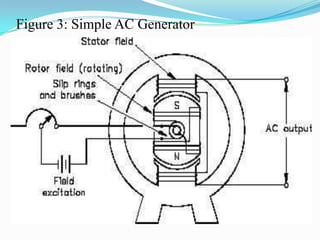
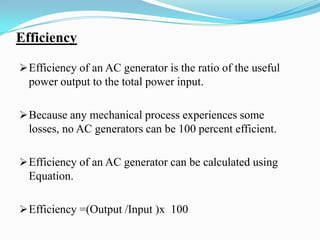
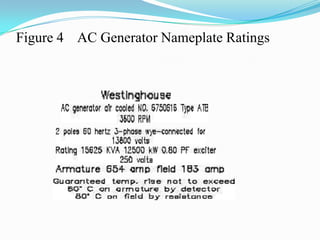
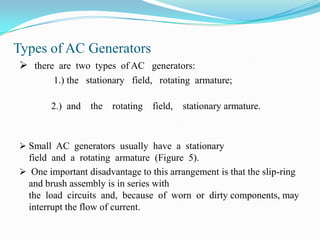
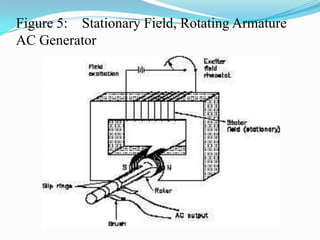
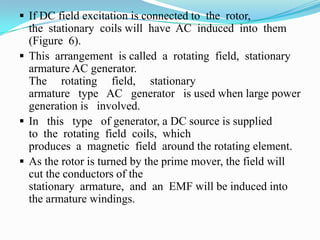
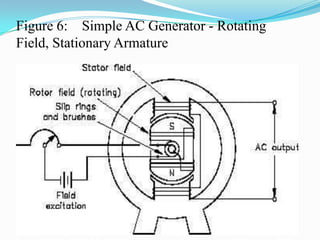
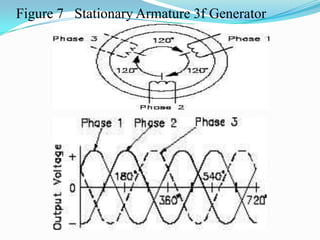
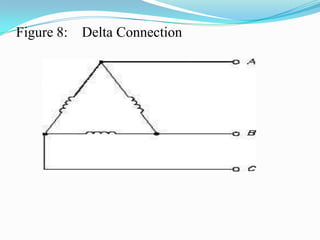
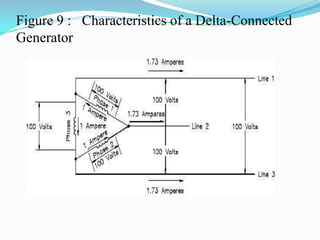
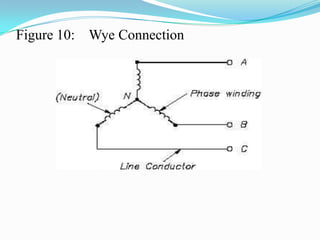
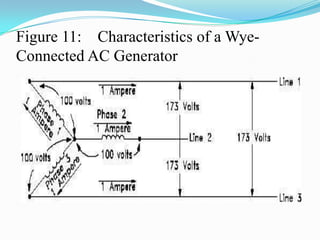
An AC generator consists of components such as the field, armature, prime mover, rotor, stator, and slip rings, which work together to produce alternating current voltage through the rotation of its parts. The efficiency of the generator is impacted by internal resistance, hysteresis losses, and mechanical losses, and can be calculated based on output and input power. There are different types of AC generators including stationary field with rotating armature and rotating field with stationary armature, as well as three-phase configurations that improve power delivery and efficiency.