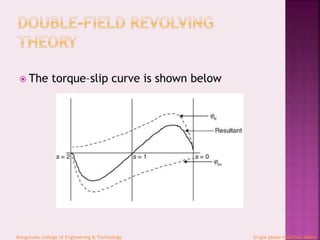
The document provides an overview of single-phase induction motors, detailing their construction, operation, and starting methods. It describes the motor's similarity to three-phase induction motors and outlines the stator's design and functioning principles, including its need for external starting assistance. Various starting methods and split-phase techniques for single-phase motors are also mentioned, along with references for further reading.