- DC machines can operate as either generators or motors. A generator produces voltage when its coil rotates through a magnetic field, while a motor produces torque on its coil when current passes through it in a magnetic field.
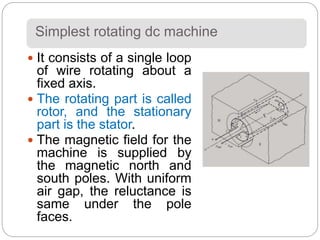
- The simplest DC machine is a single loop of wire rotating through magnetic poles. Induced voltage and torque depend on flux, speed/current, and construction constants.
- Real DC machines use commutators and brushes to produce DC output from the AC voltage induced in the rotor coils. Problems during commutation like sparking are reduced by techniques like interpoles.
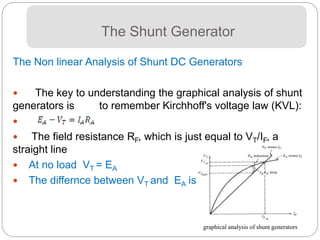
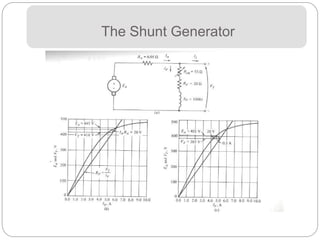
- The internal voltage and torque equations account for flux, speed/current, and construction constants. Power losses include copper, brush,