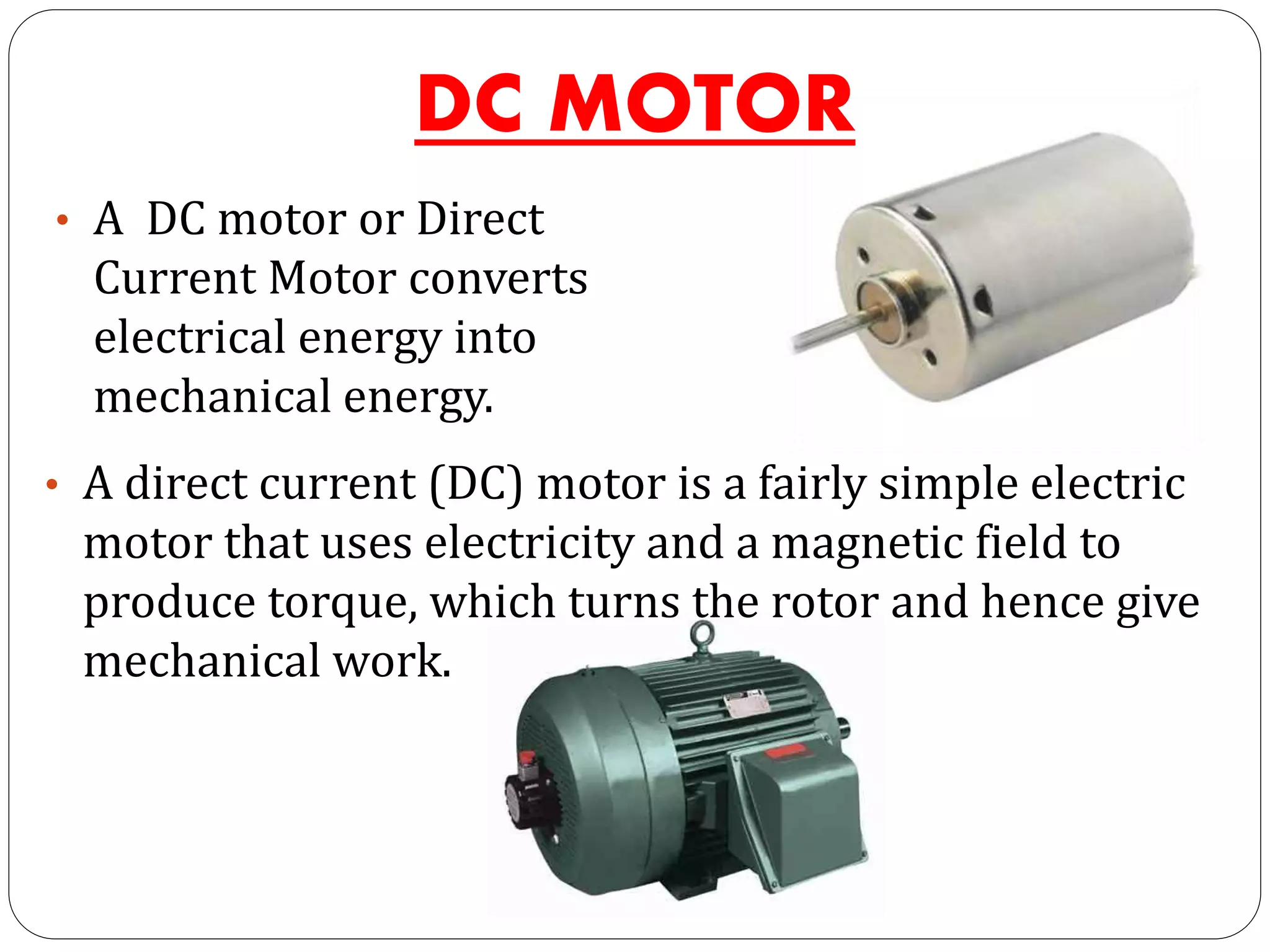
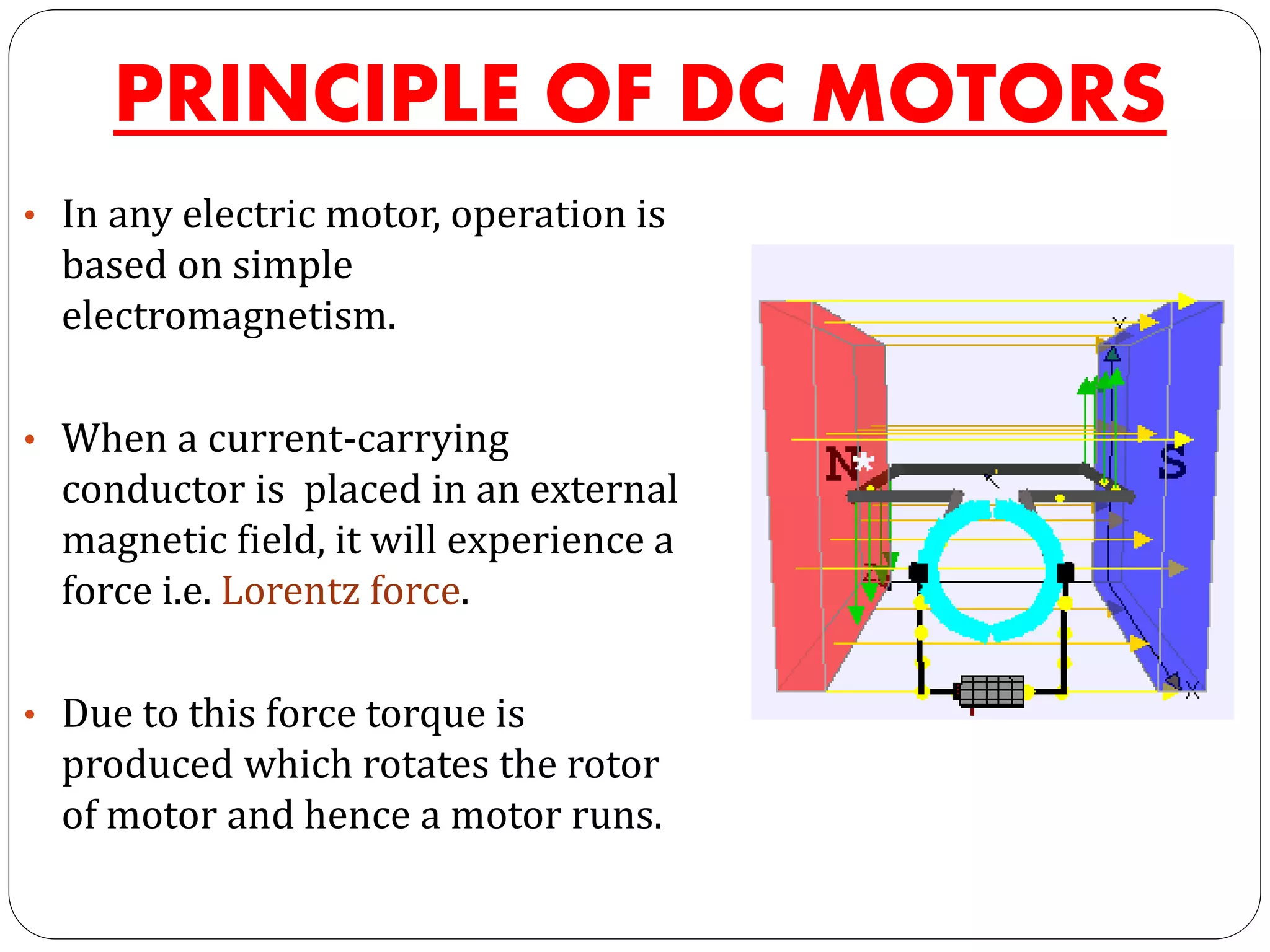
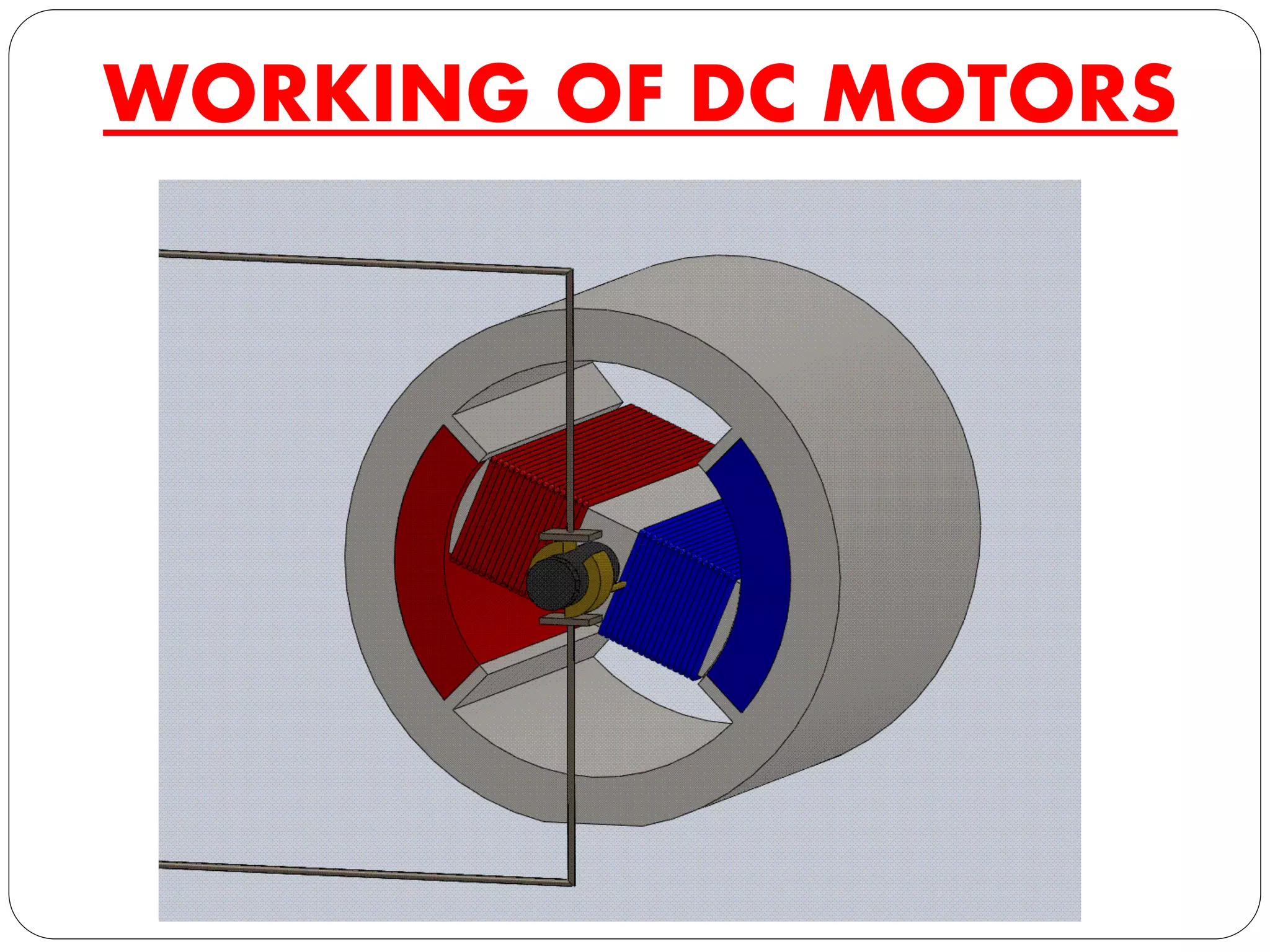
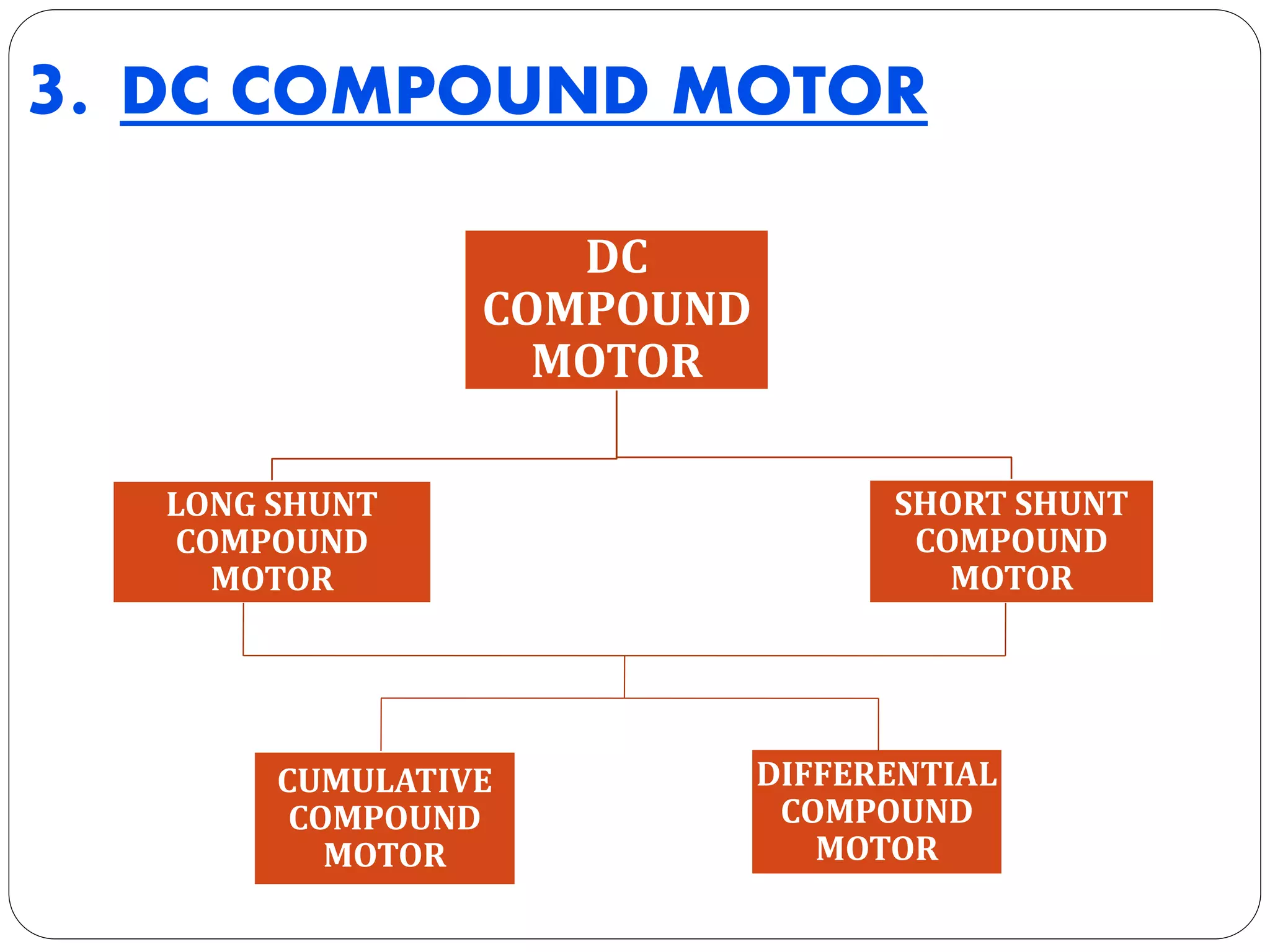
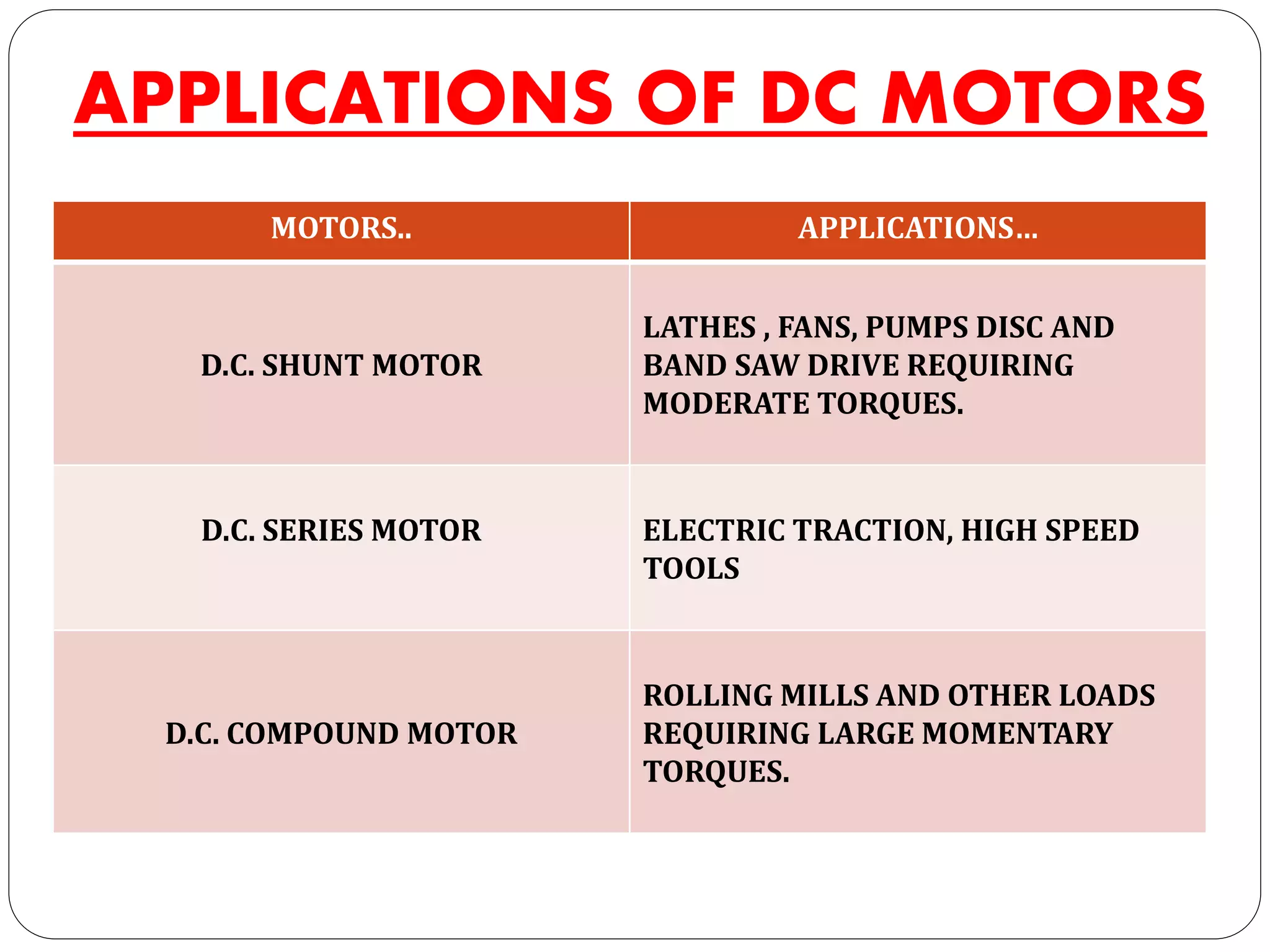
The document discusses DC motors. It begins with an introduction to DC motors, noting they convert electrical to mechanical energy. It then covers the principles, construction, types, and applications of DC motors. The principles section explains how DC motors work using electromagnetism and the Lorentz force. Construction includes field and armature windings. There are three main types - shunt, series, and compound motors - which vary in how their field windings are connected. Applications include uses for different motor types like fans, tools, and mills.