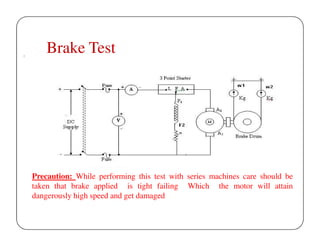
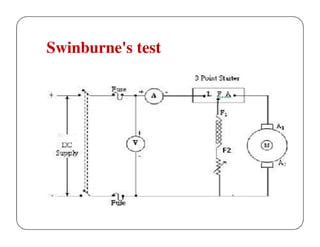
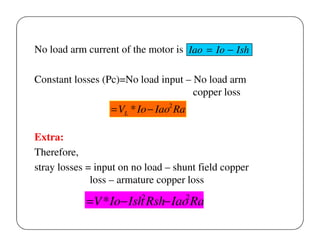
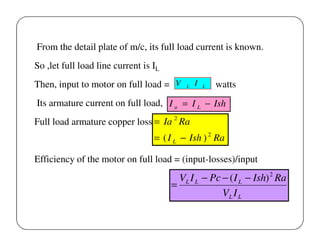
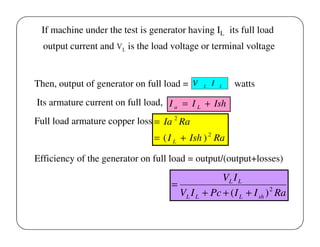
This document discusses different methods for testing DC machines. It describes the objectives of testing as determining if a machine's performance matches its design specifications and investigating any variations. Three main testing methods are outlined: direct, indirect, and regenerative. The direct method involves directly loading the machine and measuring efficiency. The indirect method determines performance characteristics from no-load test data using methods like Swinburne's test. Swinburne's test involves running the machine at no-load and recording parameters to calculate constant and stray losses. Examples of calculations for torque, output, and efficiency using data from brake tests are also provided.