- The document discusses equations for calculating the induced EMF in alternator windings.
- It derives the basic EMF equation for a concentrated full-pitched winding as Eph=4.44fTph, where f is frequency, Tph is turns per phase.
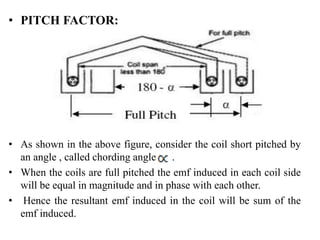
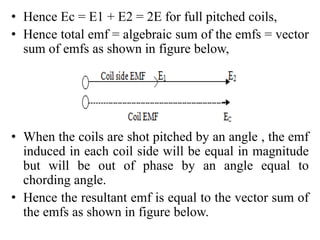
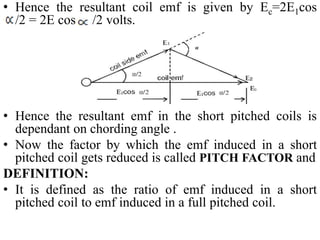
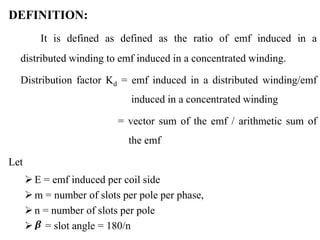
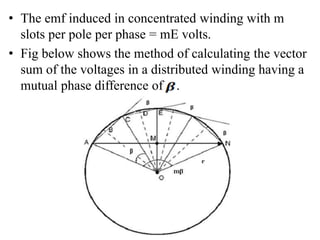
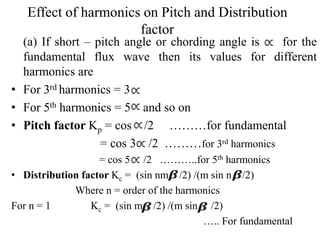
- It introduces pitch factor Kp and distribution factor Kd to account for short-pitched and distributed windings.
- The general EMF equation is given as Eph=4.44fTphKpKd, accounting for various winding configurations.
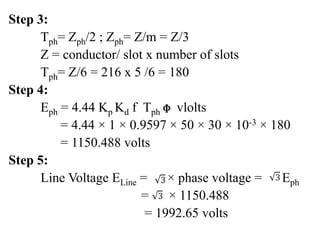
- Examples are given to demonstrate calculating EMF values using the equations.