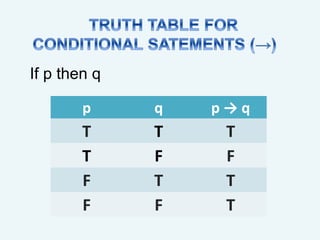
This document discusses propositional logic and truth tables. It defines primitive and compound propositions. Logical connectives like negation, disjunction, and conjunction are explained. Propositional variables are used to represent statements that can be true or false. Truth tables list all possible combinations of true and false values for propositional variables and determine the truth value of compound statements formed from logical connectives. The number of rows in a truth table is determined by 2 to the power of the number of propositional variables. Several examples of truth tables are given for logical connectives like negation, disjunction, conjunction, implication, and biconditional.