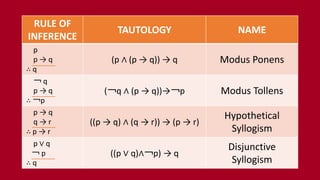
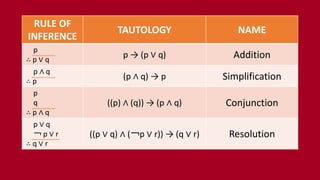
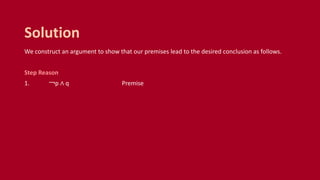
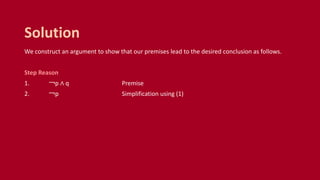
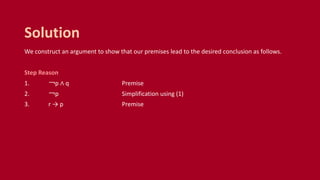
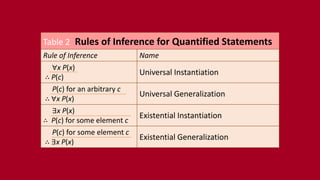
This document summarizes rules of inference in propositional logic. It defines an argument as a sequence of propositions where all but the final proposition are premises and the final is the conclusion. An argument is valid if the truth of the premises implies the truth of the conclusion. Various rules of inference are provided, including modus ponens, modus tollens, and hypothetical syllogism. Examples are given of identifying and applying different rules of inference to determine the validity of arguments.