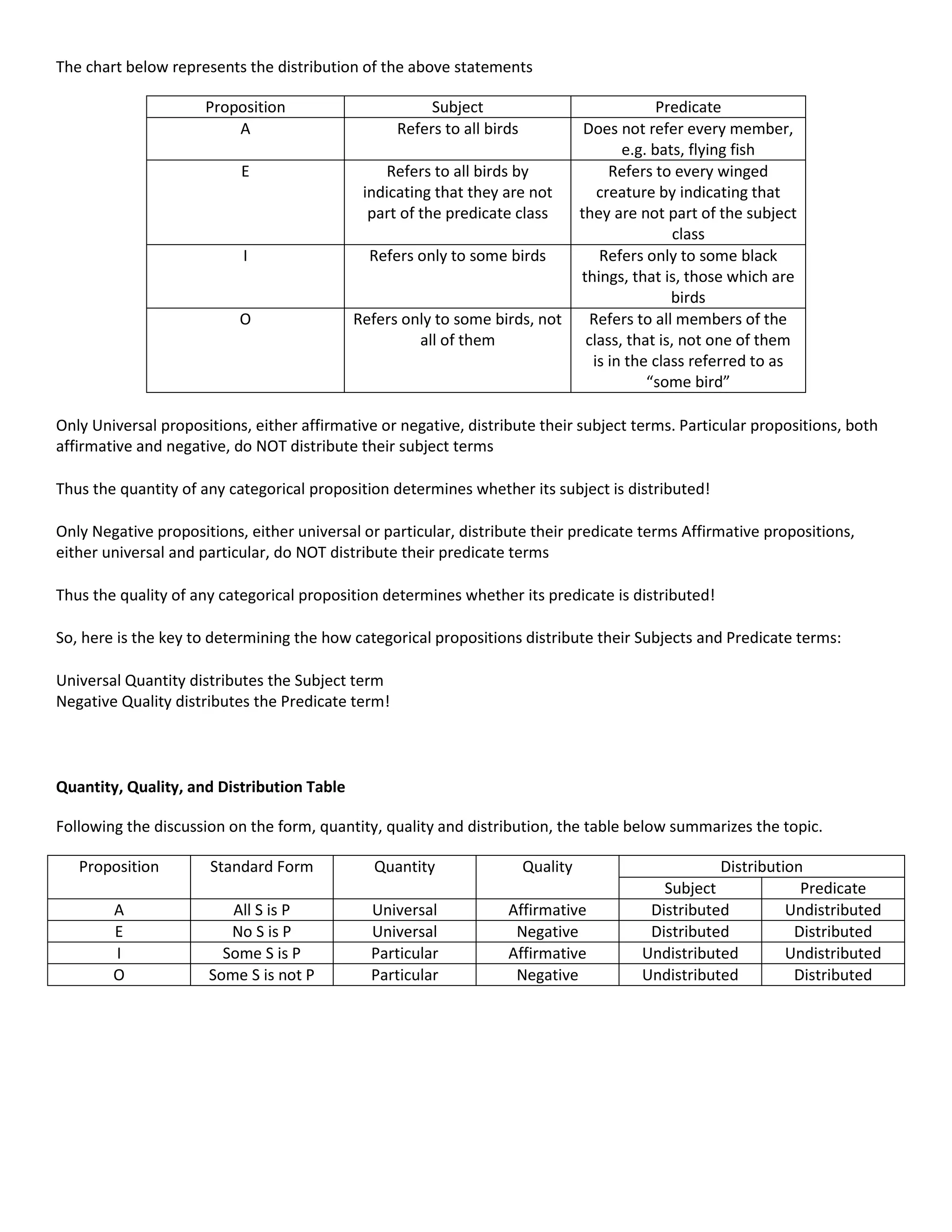
Propositions can take three forms: categorical, hypothetical, or modal. This document focuses on categorical propositions, which make a direct statement about the relationship between a subject and predicate term. There are four types of categorical propositions based on their quality (affirmative or negative) and quantity (universal or particular): A propositions are universal and affirmative, E propositions are universal and negative, I propositions are particular and affirmative, and O propositions are particular and negative. The distribution of a term depends on the proposition's quality and quantity - universal propositions distribute the subject term, while negative propositions distribute the predicate term.