- Local anesthetics are drugs that cause reversible loss of sensation, especially pain, in a localized area of the body when applied topically or injected locally. They block the generation and conduction of nerve impulses at the site of contact without damaging neurons.
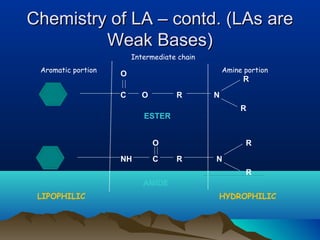
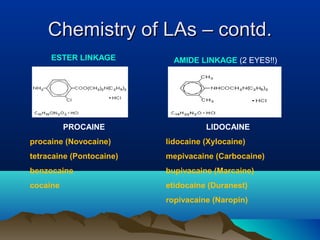
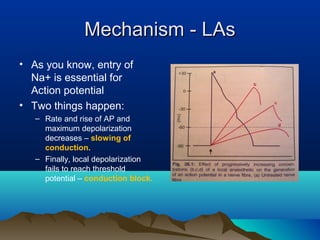
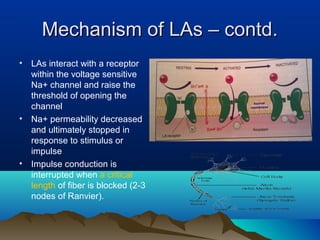
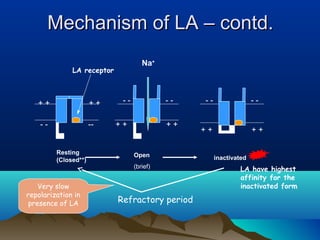
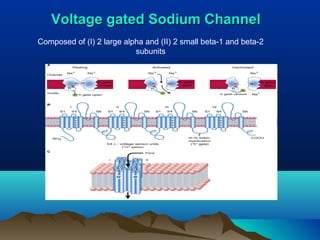
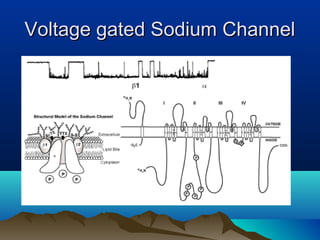
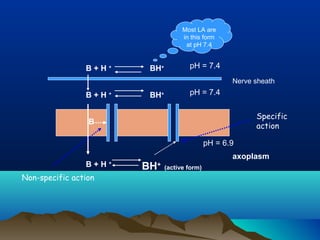
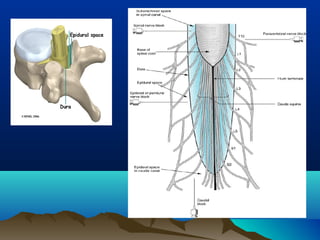
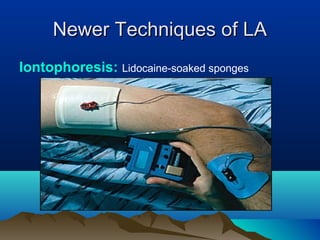
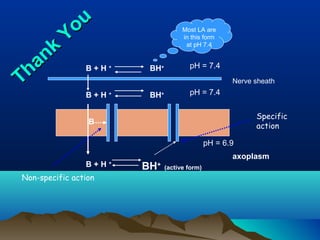
- Common uses include dentistry, excision procedures, dermatology, and spinal or regional anesthesia. Local anesthetics work by inhibiting sodium influx through voltage-gated sodium channels in neurons, interrupting action potential generation and signal conduction.
- Examples of side effects include central nervous system stimulation or depression in high doses, cardiovascular effects like arrhythmias and hypotension, and hypersensitivity reactions.