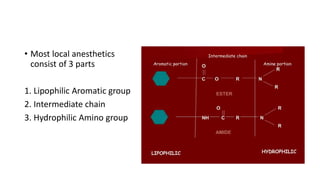
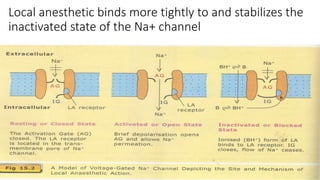
1. Local anesthetics cause reversible loss of sensation, especially pain, when applied topically or injected locally. They work by blocking sodium channels and preventing nerve impulse conduction.
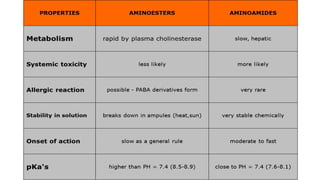
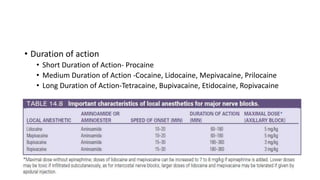
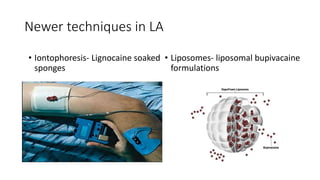
2. The first local anesthetic used was cocaine in the 1880s. Modern agents include amide-linked drugs like lidocaine and bupivacaine, and ester-linked drugs like procaine.
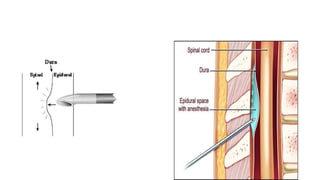
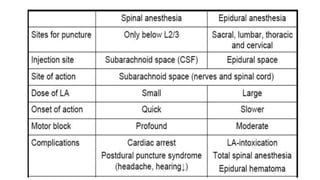
3. Local anesthetics are used for minor surgery and procedures through techniques like infiltration, nerve blocks, and regional blocks like epidurals and caudals. Proper administration and drug properties allow safe anesthesia for specific procedures.