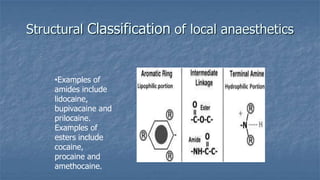
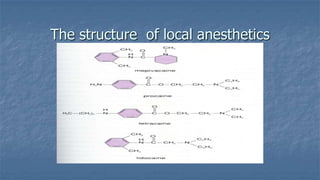
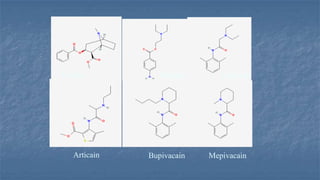
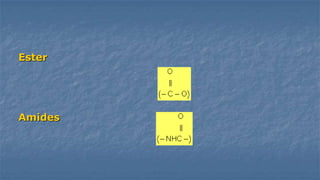
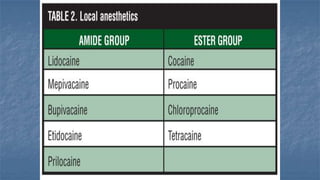
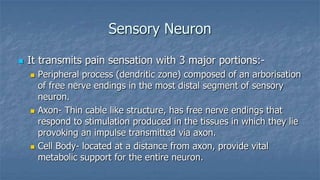
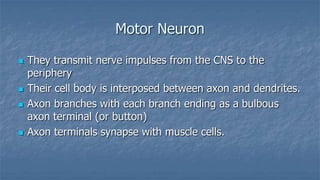
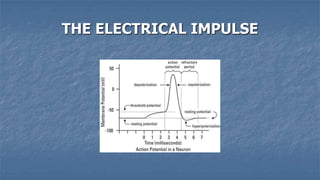
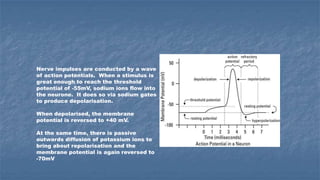
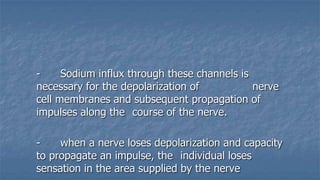
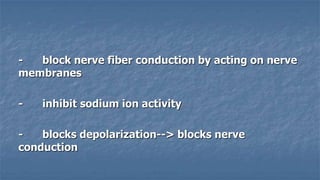
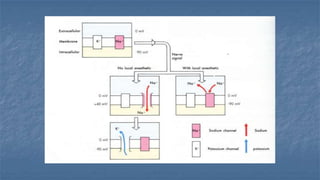
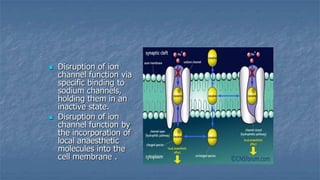
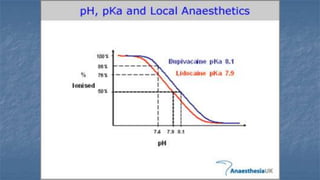
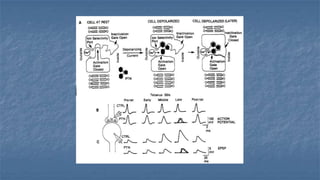
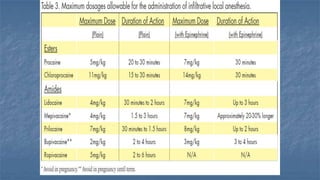
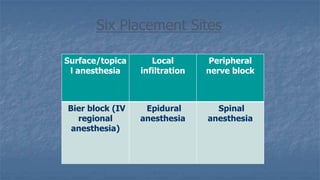
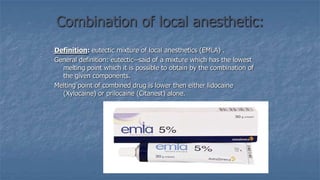
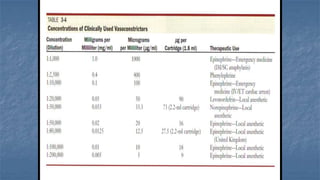
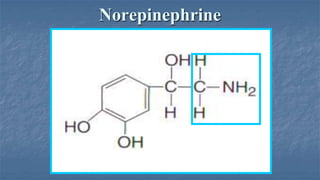
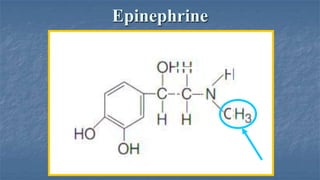
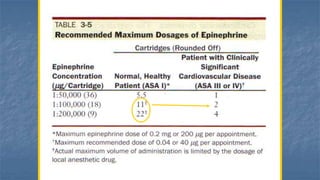
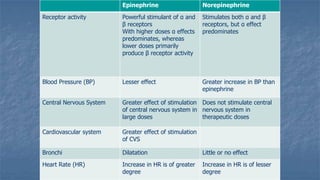
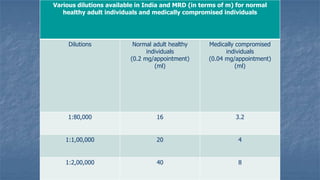
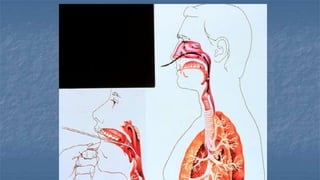
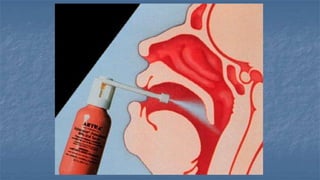
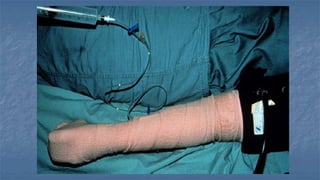
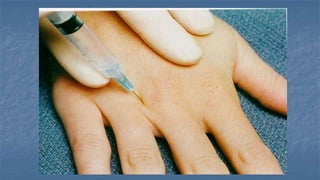
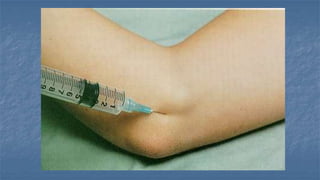
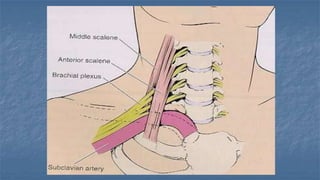
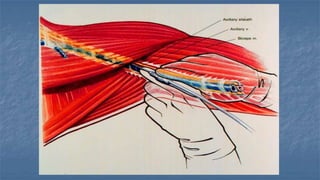
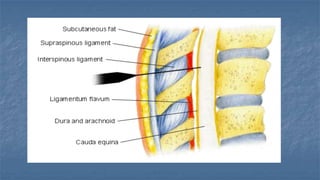
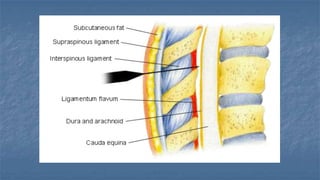
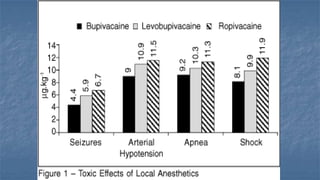
Local anaesthesia involves blocking nerve transmission through injection of local anaesthetic drugs near nerve endings or trunks. The document discusses various local anaesthetics including esters like cocaine and procaine, and amides like lidocaine, bupivacaine and prilocaine. It describes how local anaesthetics work by inhibiting sodium channels and preventing nerve impulse conduction. The ideal properties, structures, mechanisms of action, and uses of different local anaesthetics are summarized.