Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX


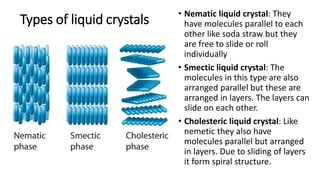



Liquid crystals have properties between liquids and crystalline solids. They are made up of long, rod-shaped organic molecules that are arranged parallel to each other but can flow like liquids. There are three main types of liquid crystals - nematic have molecules arranged parallel but able to slide, smectic have molecules in parallel layers that can slide, and cholesteric form spiral structures as the layers slide. Liquid crystals have numerous applications, including digital displays where changing the crystal arrangement causes opacity and transparency, monitoring body temperature where color changes correspond to temperature, and LCD displays which use their light modulating properties.




