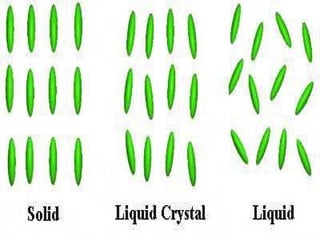
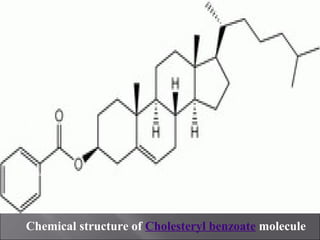
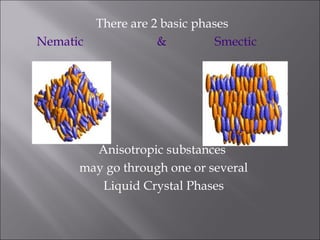
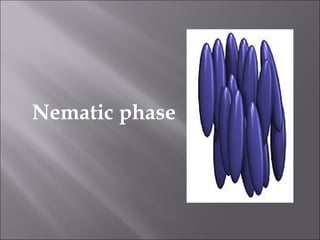
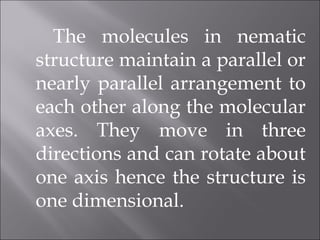
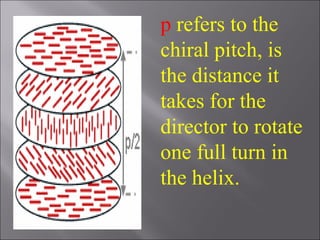
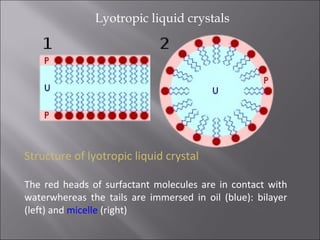
Liquid crystals are a state of matter with properties between liquids and solids, first examined by Friedrich Reinitzer in 1888. They are classified into thermotropic and lyotropic types, with phases including nematic and smectic, and can be influenced by temperature, pressure, and electric fields. The nematic phase is predominantly used in LCD technology and other applications such as thermometers and protective gear.