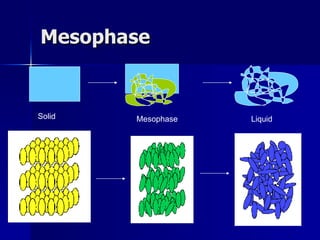
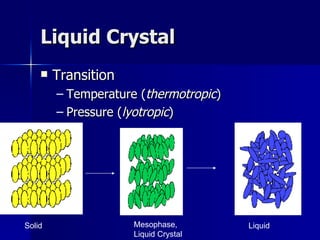
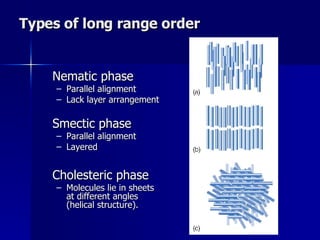
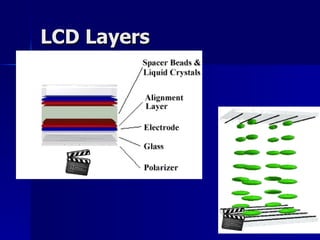
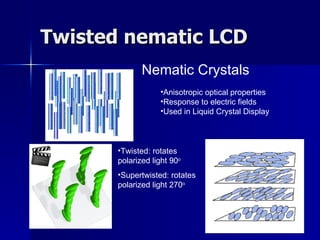
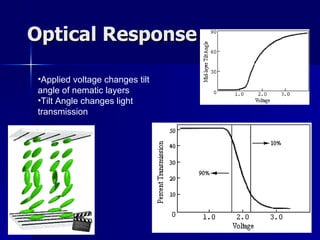
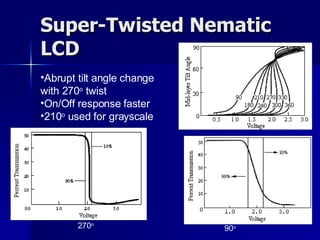
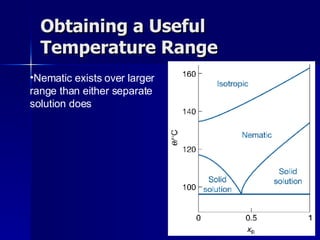
This document discusses liquid crystals and their use in liquid crystal displays (LCDs). It describes the different phases of liquid crystals including nematic, smectic, and cholesteric. Nematic liquid crystals are used in LCDs as they have anisotropic optical properties and can change the orientation of polarized light in response to electric fields. LCDs work by applying a voltage to change the tilt angle of the nematic crystals and control the transmission of light, allowing pixels to be switched on or off. Super-twisted nematic LCDs provide faster response times for grayscale images.