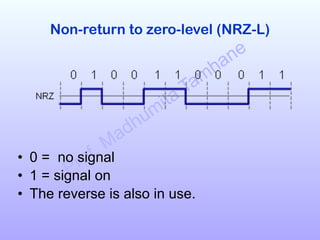
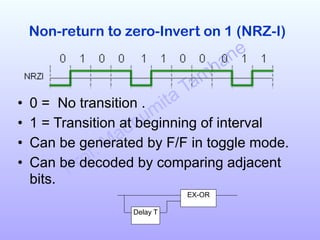
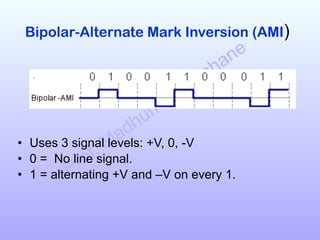
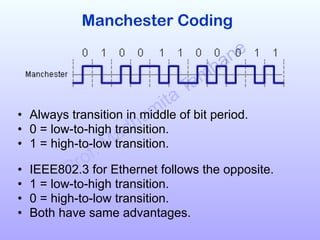
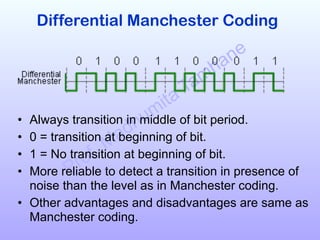
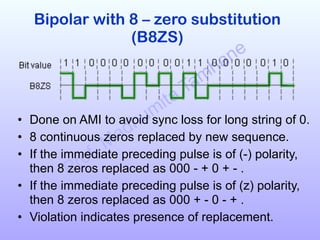
The document discusses various line coding schemes used to convert digital data into digital signals, highlighting types such as unipolar, polar, bipolar, and Manchester encoding. It explains the advantages and disadvantages of different encodings, including non-return to zero (NRZ), alternate mark inversion (AMI), and differential Manchester coding. Additionally, it addresses techniques like bipolar with zero substitution (B8ZS) and high-density bipolar (HDB3) to maintain synchronization in the presence of long sequences of zeros.